
A formal fallacy is simply an argument whose form is invalid. Thus, any argument that has that form will automatically be invalid, regardless of the meaning of the sentences. Two formal fallacies that are similar to, but should never be confused with, modus ponens and modus tollens are denying the antecedent and affirming the consequent.
Full Answer
What are the 5 types of fallacies?
- since every president has been a man the next must be a man
- you have to be over 6′ to be in the nba
- if you are successful then you are necessarily intelligent
- To be a MVP in baseball you must be at least 5′7
- By the time you reach 30 you “naturally” mature
What are some real life examples of fallacies?
What are the 4 types of fallacies?
- Ad Hominem.
- Strawman Argument.
- Appeal to Ignorance.
- False Dilemma.
- Slippery Slope Fallacy.
- Circular Argument.
- Hasty Generalization.
- Red Herring Fallacy.
What is a formal fallacy?
What Is a Formal Fallacy? A formal fallacy is a specific type of error in a deductive argument, and it is identifiable by examination of the argument's overall structure. These fallacious arguments are different from an informal fallacy that often needs closer analysis of the subject details.
What does formal fallacies mean?
In philosophy, a formal fallacy is a pattern of reasoning that is always wrong. This is due to a flaw in the logical structure of the argument which renders the argument invalid. A formal fallacy is contrasted with an informal fallacy, which may have a valid logical form, but be false due to the characteristics of its premises, or its justification structure.
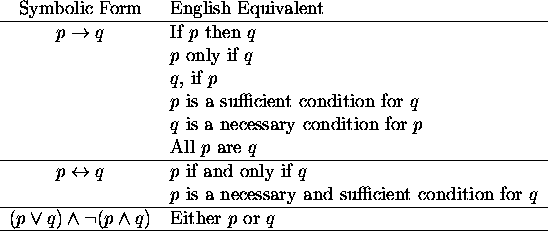
What are the 2 types of fallacies?
There are two main types of fallacies:A formal fallacy is an argument with a premise and conclusion that doesn't hold up to scrutiny.An informal fallacy is an error in the form, content, or context of the argument.
What are informal and formal fallacies?
A formal fallacy is a flaw in the structure of a deductive argument which renders the argument invalid, while an informal fallacy originates in an error in reasoning other than an improper logical form. Arguments containing informal fallacies may be formally valid, but still fallacious.
What is a formal fallacy quizlet?
A formal fallacy is an error in logic that can be seen in the argument's form without requiring an understanding of the argument's content.
What is the meaning of formal fallacies?
Definition of formal fallacy : a violation of any rule of formal inference. — called also paralogism. —contrasted with material fallacy and verbal fallacy — compare affirmation of the consequent, denial of the antecedent, ignoratio elenchi, illicit process, petitio principii.
What are the 3 formal fallacies?
The standard Aristotelian logical fallacies are:Fallacy of four terms (Quaternio terminorum);Fallacy of the undistributed middle;Fallacy of illicit process of the major or the minor term;Affirmative conclusion from a negative premise.
What is not a formal fallacy?
Formal fallacies are created when the relationship between premises and conclusion does not hold up or when premises are unsound; informal fallacies are more dependent on misuse of language and of evidence.
What fallacy reflects?
For them, a fallacy is reasoning that comes to a conclusion without the evidence to support it. This may have to do with pure logic, with the assumptions that the argument is based on, or with the way words are used, especially if they don't keep exactly the same meaning throughout the argument.
What idea regarding finance was said to cause mortification to our nation and triumph to the enemies of the United States?
The idea that the federal government is subject to or under the power of each individual state causes mortification to our nation and "triumph to" enemies of the United States. Hamilton says that there is error and a "delusive system of quotas and requisition" in the current law.
Formal and informal fallacies
The most general classification that can be made of the fallacies is the one that distinguishes between formal and informal fallacies. While in the latter the error of reasoning has to do with the content of the propositions, in the formal fallacies the error of reasoning is in the way in which the propositions are related to each other.
1. False disjunctive syllogism
In this fallacy, one starts from a disjunction of the style "A and / or B". When one of the possibilities is affirmed, the other is assumed to be false. Of course, this conclusion does not follow from the premises.
2. Affirmation of the consequent
In this formal fallacy it is assumed that if a premise is true, then the consequence of this premise also indicates whether its predecessor is true or not.
3. Denial of antecedent
In this kind of formal fallacy the reasoning is articulated as if denying a premise its conclusion had to be necessarily false.
4. False denial of the conjunction
This fallacy occurs when as a phenomenon does not occur as a result of a set of elements, one of those elements is denied.
5. Undistributed middle term
In this fallacy there is an element that connects two others and that does not appear in the conclusion, although one of them does not include it in its entirety.
6. Categorical syllogism with negative premises
This fallacy occurs in any categorical syllogism in which both premises are a negation, since from them nothing can be concluded.
Why are formal fallacies considered formal fallacies?
These are formal fallacies because the mistake in reasoning stems from the structure (the form) of the argument. It is well worth the effort to study formal fallacies and their corresponding terminology because these two fallacies are extremely common—perhaps the two most common fallacies committed by evolutionists.
What is the second premise of affirming the antecedent?
Since the second premise affirms that p (the antecedent) is true, this type of argument is called “affirming the antecedent” and is perfectly valid. (Recall, “valid” means that if the premises are true, so is the conclusion). The Latin name for this type of argument is modus ponens, which means the “method of affirming.”.
What is the most general classification of fallacies?
The most general classification that can be made of fallacies is what distinguishes between formal fallacies and informal ones . While in the latter the reasoning error has to do with the content of the propositions, in the formal fallacies the reasoning error is in the way in which the propositions relate to each other. Therefore, formal fallacies are always objectively, while in the case of informal ones, a debate is generated about whether or not there is an argumentation error, given that their nature always depends on the context in which they are used.
How many terms are there in the fallacy?
In this fallacy There are four terms, instead of three, which would be necessary to be valid . This happens because one of the terms has two meanings. Example : "Man is the only animal capable of taming the fire, the woman is not a man, so the woman can not tame the fire.".
Why is fallacy important?
In the world of philosophy and psychology, the concept of fallacy is very important, because it gives an idea of the quality of the reasoning that we can use to argue a point of view. What is a fallacy? It is, simply, a reasoning error, a type of argumentation in which the premises that are used do not lead to the conclusion.
What is fallare in argumentation?
It is, simply, a reasoning error, a type of argumentation in which the premises that are used do not lead to the conclusion. In fact, the term is derived from the word "fallare", which means to lie or cheat. That is, it serves to emphasize the deceptive nature of these arguments.
What is the fallacy of average term not distributed?
5. Average term not distributed. In this fallacy there is an element that connects two others and that does not appear in the conclusion , although one of them does not include it in its entirety. Example : "All mammals have eyes, some mollusks have eyes, therefore, some mollusks are mammals.". 6.
Why is it not easy to recognize a fallacy?
But recognizing a fallacy is not easy, because it can take different forms. In fact, there are many types of fallacies, some of which do not resemble each other .
Is a formal fallacy objective?
Therefore, formal fallacies are always objectively, while in the case of informal ones, a debate is generated about whether or not there is an argumentation error, given that their nature always depends on the context in which they are used.
What is formal fallacy?
A formal fallacy is one which involves an error in the form, arrangement or technical structure of an argument. The question in view is not whether a conclusion is true or false, but whether the form of the argument is correct or incorrect, valid or invalid.
What is a fallacy in argument?
A fallacy is a defect in an argument which misleads the mind. The defect may be intentional or unintentional. If the defect is intentional, we sometimes call it a sophism. One's understanding of fallacies may be used for good, in order to avoid or expose error; or it may be used for evil, in order to subtly deceive.
What are some examples of ambiguity?
B. Amphibology or Semantic and Syntactic Ambiguity 1 Example: Lots for sale. (Semantic Ambiguity: Allotments of land or numerous things?) 2 Example: Laurie calls her mother when she's alone. (Syntactic Ambiguity: Who is alone, Laurie or her mother?)
Formal Fallacies Versus Informal Fallacies
Some people distinguish formal fallacies from informal ones. To understand the difference you first have to know that there are two kinds of arguments that actually support their conclusions: valid and inductive. In a valid argument, true premises guarantee a true conclusion.
Free Thinkers and Fallacies
Regardless of what kind of fallacies we’re talking about, free thinkers are committed to avoiding them. They’re committed to developing critical thinking skills–including the ability to identify and avoid errors in reasoning.
What is a formal fallacy?
In philosophy, a formal fallacy, deductive fallacy, logical fallacy or non sequitur ( Latin for "it does not follow") is a pattern of reasoning rendered invalid by a flaw in its logical structure that can neatly be expressed in a standard logic system, for example propositional logic.
What is a mathematical fallacy?
Mathematical fallacies are typically crafted and exhibited for educational purposes, usually taking the form of spurious proofs of obvious contradictions . A formal fallacy is contrasted with an informal fallacy, which may have a valid logical form and yet be unsound because one or more premises are false.
What is a fallacy in logic?
Premises in formal logic are commonly represented by letters (most commonly p and q). A fallacy occurs when the structure of the argument is incorrect, despite the truth of the premises.
What is affirmative conclusion?
Affirmative conclusion from a negative premise. Other logical fallacies include: The self-reliant fallacy. In philosophy, the term logical fallacy properly refers to a formal fallacy—a flaw in the structure of a deductive argument, which renders the argument invalid .
Can an argument contain a formal fallacy?
By extension, an argument can contain a formal fallacy even if the argument is not a deductive one; for instance an inductive argument that incorrectly applies principles of probability or causality can be said to commit a formal fallacy.
Is a logical argument a non-sequitur?
While a logical argument is a non sequitur if, and only if, it is invalid, the term "non sequitur" typically refers to those types of invalid arguments which do not constitute formal fallacies covered by particular terms (e.g., affirming the consequent ). In other words, in practice, " non sequitur " refers to an unnamed formal fallacy.
Is the conclusion a necessary consequence of the premise?
Therefore, A is true. Even if the premise and conclusion are all true, the conclusion is not a necessary consequence of the premise. This sort of non sequitur is also called affirming the consequent . An example of affirming the consequent would be: If Jackson is a human (A), then Jackson is a mammal.
