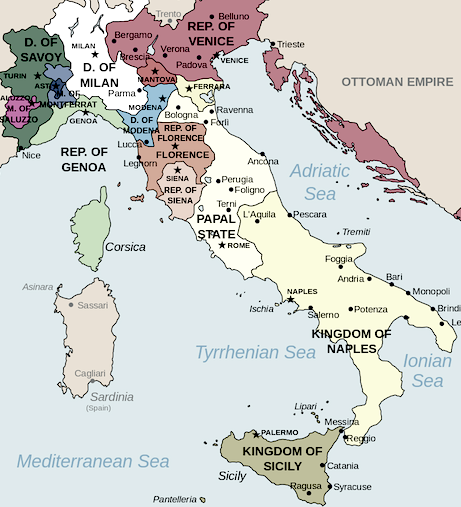
The Italian city-states were numerous political and independent territorial entities that existed in the Italian Peninsula
Italian Peninsula
The Italian Peninsula or Apennine Peninsula is a peninsula extending 1,000 km from the Po Valley in the north to the central Mediterranean Sea in the south. The peninsula's shape gives it the nickname lo Stivale. Three smaller peninsulas contribute to this characteristic shape, namely Calabria, Salent…
How did Italian city states become so powerful?
Trade made the city-states wealthy. Many were successful and powerful because they specialized and were located in the middle of trade routes. Venice was the most powerful Italian city-state and it specialized in shipping allowing it to control the trade routes in the Mediterranean Sea.
How did Italian city states gain there wealth?
The consumers demand goods affected the Italian city-states because they expanded greatly and grew also in power. Northern and Central Italy became more prosperous than the South because of the trade routes. Spices, dyes, silks were imported to Italy and then resold throughout Europe. What were key characteristics of Italy during the Renaissance?
What are the five city states of Italy?
Inflation, Russia-Ukraine conflict, COVID in focus in president's first State of the Union address Here is the full ... Along with twenty-seven members of the European Union including France, Germany, Italy, as well as countries like the United Kingdom ...
How were Italian city states different from Greek city states?
Greek city states were protected by stout stone walls. The members of a particular city-state lived in its center and also in the villages adjacent to it. Different city-states could choose the same god as their protector. The residents of a city-state formed a religious association and were obliged to honor their protective god.
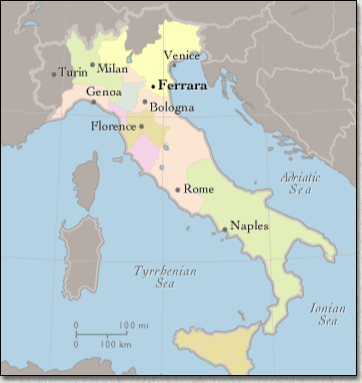
What are the 5 city-states of Italy?
After a series of trade and political rivalries, five major cities emerged: Milan, Venice, Florence, Naples, and the Papal States. Despite some hostilities between the five, they eventually came to an alliance through the Treaty of Lodi.
What are 3 Italian city-states?
At the time of the Renaissance Italy was governed by a number of powerful city-states. These were some of the largest and richest cities in all of Europe. Some of the more important city-states included Florence, Milan, Venice, Naples, and Rome.
Why did Italy have city-states?
As wealth flowed into Europe through Italy, these cities formed their own local governments to oversee their growth from trade, although most were technically still ruled by larger powers like the Holy Roman Empire. We call these cities communes.
What are the city-states?
Key Takeaways: City StateA city-state is an independent, self-governing country contained totally within the borders of a single city.The ancient empires of Rome, Carthage, Athens, and Sparta are considered early examples of city-states.Once numerous, today there are few true city-states.More items...•
Is Venice a city-state?
Venice is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is situated across a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by bridges, of which there are 400.
How many states make up Italy?
Italy is divided into 20 administrative regions, which correspond generally with historical traditional regions, though not always with exactly the same boundaries. A better-known and more general way of dividing Italy is into four parts: the north, the centre, the south, and the islands.
When did Italy split into city-states?
14th centuryIn the 14th century, Northern Italy and upper-central Italy were divided into a number of warring city-states, the most powerful being Milan, Florence, Pisa, Siena, Genoa, Ferrara, Mantua, Verona and Venice.
How was Naples different from the other Italian city-states?
How was Naples different from the other Italian city-states? It did not have a large professional middle class. How did Italian city-states like Venice and Florence become major banking and trade centers? Their location made them a natural route for travel between Europe, Africa, and Asia.
How did Italian city states become wealthy?
A. Italian states gained their wealth through trade. Italy was a good location for trade because it was surrounded by seas and was in the center of the Mediterranean world. o Several cities in Italy became major trade and manufacturing centers and some specialized in certain crafts.
What was the most powerful city state in Italy?
Venice. Venice wins first place in politics and society because it was a republic, with the head of government being the Doge, and Venice and Genoa were either ruled by one family, one dictator, or too many different peopl.
What made the formation of the Italian city-states possible?
What made the formation of the Italian city-states possible had mostly to do with Italy's difference from the rest of Europe during the end of the Middle Ages. Italy still retained much of its ancient Roman heritage. It was more urban, with several heavily-populated cities. Due to their size and influence, many of these cities made attempts to declare their independence, either from the Church or from the Holy Roman Emperor.
How did the cities of Europe gain independence?
As trade increased in Europe, these cities also asserted their independence by becoming major hubs of trade and commerce. Pisa, Genoa, and Venice became important in trade along the Mediterranean, Venice becoming the most successful. Florence became important in the world of banking and wool trade. Trade rivalries emerged as these cities increased in political and economic power. Eventually, smaller city-states were absorbed into the much larger ones. Some smaller cities retained their independence, but five particular cities became the major powers among the city-states: Milan, Florence, Venice, Naples, and the Papal States.
What alliance did the city states form to drive the French out of the city?
The remaining cities do form another alliance, often called the League of Venice, to drive the French out. They are able to fight the French as they are returning north, driving them away before they are able to conquer any other territories. Later on, the Aragonese take Naples away from the French. From there on, the city-states managed to form short-term alliances, none of which was as powerful as the Treaty of Lodi. In the meantime, Spain and France continued to fight over the conquest of Italy, further complicating any alliances.
Why did Italy have city states?
Each city consited of a powerful city and the surrounding towns and countryside. Italian city-states conducted their own trade, collected their own taxes, and made their own laws.
How did trade make Italy rich?
Trade made the Italian city-states wealthy. Italy's location on the central Mediterranean placed its cities in the middle of the trade routes. People from all over Europe came to northern Italy to buy, sell, and do their banking. Many city-states developed specializations.
Where did the Renaissance spread?
Renaissance ideas spread to the rest of Europe from the city-states of Italy.
What was the trade center of Genoa?
Genoa was a trading center for ivory and gold. Venice had hundreds of ships that controlled the trade routes in the Mediterranean sea, and silk, spices, and perfume flowed into Wenice. The wealth of many city-states encouraged art and learning.
What was the role of the Italian city state in the Renaissance?
This wealth allowed prominent families to support artists, scientists, and philosophers spurring on new ideas and artistic movements. Florence. Florence is where the Renaissance first began.
What were the cities of the Renaissance?
At the time of the Renaissance Italy was governed by a number of powerful city-states. These were some of the largest and richest cities in all of Europe. Some of the more important city-states included Florence, Milan, Venice, Naples, and Rome. Map of Italian city-states.
What was the city of Naples known for?
He supported Renaissance artists, writers, and philosophers. Naples also became known for its music and is where the mandolin was invented. Naples was captured by Spain in 1504.
What was a guild in the city state?
Guilds were powerful institutions in the city-states. In some city-states you had to be a member of a guild to run for public office.
Where did the Renaissance begin?
Florence. Florence is where the Renaissance first began. It was ruled by the powerful Medici Family who used their money to support artists such as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo. One of the early architectural achievements of the Renaissance was the massive dome on the Florence Cathedral.
Which empire controlled the seas around the east coast of Italy and was famous for its artistic glassware?
However, when the Ottoman Empire conquered Constantinople, Venice 's trade empire began to shrink. Venice controlled the seas around the east coast of Italy and was famous for its artistic glassware. Rome. The pope ruled both the Catholic Church and the city-state of Rome.
Which countries signed the Peace of Lodi?
Milan, Naples, and Florence signed a peace treaty called the Peace of Lodi in 1454. This helped to establish boundaries and peace for around 30 years.
What were the city states in Italy?
In the north, the major city-states to emerge were Florence, Venice, and Milan. Rome achieved a similar status in the 14th century while the papacy was in Avignon but in the 15th century was brought again under papal control.
Who were the thinkers of the Italian city states?
In response to the complex diplomatic conditions of the time, political thought in the Italian city-states flourished. Thinkers such as the notary Bruno Latini (c. 1220–94), Marsilius of Padua (c. 1275–1343), and the jurist Bartolus of Sassoferrato (1314–57) all elaborated political theories that justified and paid tribute to republican government.
What did cities do after the pope?
After throwing off the traditional lordship of pope or emperor, many cities turned to ideas of popular sovereignty at the expense of traditional elite prerogatives. They developed complex political processes to bar elite families from governing.
What party did the Imperial Cities adhere to?
Imperial cities generally adhered to the Ghibelline party , and papal cities, to the Guelf. The emperors’ and popes’ repeated demands for military and financial support for endless wars exhausted city dwellers and spurred movements for independence.
What is a city state?
Generally defined, city-states were cities that had won their independence from the Holy Roman Empire or the papacy. Instead of recognizing the pope or emperor as the highest authority, they held popular sovereignty as a guiding principle.
What is the history of Italy?
This was especially true in the late Middle Ages and early Renaissance when Italian cities gained such economic and political prominence that , independently of one another, many were considered actors on the European political stage.
What was the most urbanized area in Europe in the Middle Ages?
Throughout the Middle Ages the Italian peninsula (especially its northern half) was one of the most urbanized areas of Europe, with up to 30 percent of people living in cities. Some such as Rome, Naples, Florence, Milan, and Venice were larger, while others such as Perugia, Siena, Pisa, Ferrara, Urbino, or Verona were small.