
What are facts about manganese?
Who knew?
- Manganese is a transition metal, according to Chemicool. ...
- According to the Los Alamos National Laboratory, the word manganese comes from the Latin word for magnets, "magnes." Manganese, however, by itself is not magnetic. ...
- Pure manganese is reactive, burns in oxygen, rusts in water and dissolves in dilute acids, according to Lenntech.
Is manganese radioactive or not?
Manganese deficiency can lead to various health problems, including skin diseases, skeleton disorders, glucose intolerance and birth defects. Isotopes of Manganese. There is one naturally occurring isotope of manganese, manganese-55. There are eighteen radioactive isotopes of manganese, with atomic masses ranging from 46 to 65.
What is the normal phase of manganese?
The most stable oxidation state for manganese is +2, which has a pale pink color, and many manganese (II) compounds are known, such as manganese (II) sulfate (MnSO 4) and manganese (II) chloride (MnCl 2 ). This oxidation state is also seen in the mineral rhodochrosite ( manganese (II) carbonate ).
What is the hardness MOH of manganese?
Manganese is a silvery-white, brittle metal, possessing a density of 7.2–7.46 g/cm 3, a hardness of 5–6 (Mohs scale), and a melting temperature of 1244°C.Manganese is a transition metal, belonging to the group of siderophiles (a geochemical class after V.M. Goldschmidt) and occupying the 25th place (atomic number) of the VII group of the 4th period in D.I. Mendeleev’s periodic table; it ...

Technology, Instrumentation
Manganese nodules are authigenic deposits composed principally of manganese oxides enriched in Fe and Co, Ni, and Cu. They occur in all the world's oceans but are generally found in areas where sediment accumulation rate is slow. Indeed, Mn nodules grow slowly—millimeters to 10s of millimeters per million years.
Manganese nodule fields from the Northeast Pacific as benthic habitats
Thomas Kuhn, ... Pedro Martinez Arbizu, in Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat (Second Edition), 2020
Ocean Interfaces & Human Impacts
Manganese nodules (also referred to as polymetallic nodules) are spherical precipitates of manganese, iron oxides and other metals (e.g., copper, cobalt, and zinc) that form around a core material, such as a shell fragment or shark's tooth.
Deep-Sea Sediments
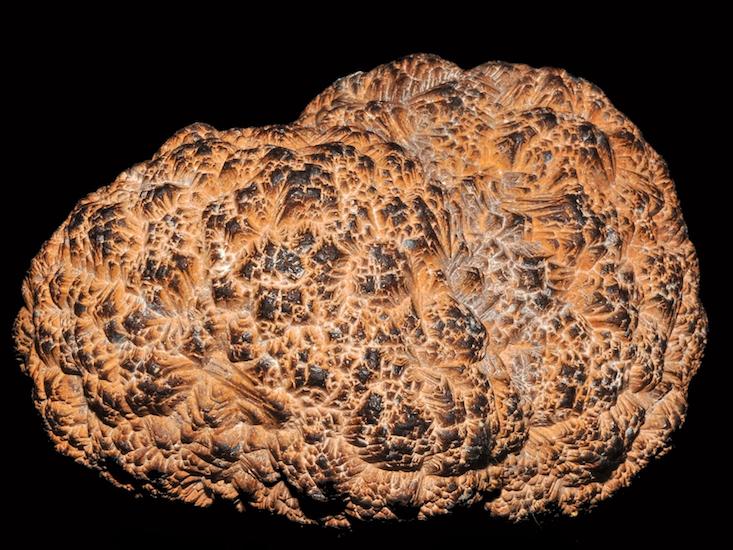
Manganese-nodule fields are among the more spectacular features that have been discovered on the deep-sea floor ( Fig. 9.31 ). They vary largely in size (from micronodules to more than meter size), shape (from spherical to ellipsoidal to tabular), surface texture (from smooth to botryoidal to rough) and abundance ( Glasby, 2006 ).
Volume 5
Deep ocean manganese nodules, iron-manganese crusts and deep sea muds are all potential future marine sources of REE (Hein et al., 2013 ).
Sampling Methods
Deep ocean floor mineral resources include polymetallic nodules, manganese crusts, active/extinct hydrothermal sulfide vents, and diamonds. They cover large areas between 4000 and 6000 m below the ocean's surface. The polymetallic nodules contain mainly nickel, copper, cobalt, and manganese.
Marine Manganese Deposits
Ranadhir Mukhopadhyay, ... Sridhar D. Iyer, in The Indian Ocean Nodule Field (Second Edition), 2018
What is Manganese?
Manganese is a silver metallic element with an atomic number of 25 and a chemical symbol of Mn. It is not found as an element in nature. It occurs in many minerals such as manganite, sugilite, purpurite, rhodonite, rhodochrosite, and pyrolusite. It is also found in many mineraloids such as psilomelane and wad.
What is Steel Made From?
Many people would correctly respond that steel is made of iron. Far fewer know that it is also made of manganese. Although the amount of manganese used to make a ton of steel is small, it is just as essential as iron to produce this fundamental building block of modern societies.
Other Uses of Manganese
Manganese is used also as an alloy with metals such as aluminum and copper. Important nonmetallurgical uses include battery cathodes, soft ferrites used in electronics, micronutrients in fertilizers, micronutrients in animal feed, water treatment chemicals, colorant for automobile undercoating, bricks, frits, glass, textiles, and tiles.
Where Does Manganese Come From?
Elemental manganese readily combines with oxygen, carbon, and silicon to form a long list of manganese minerals. Manganese ores generally contain 25 to 45 percent manganese, mostly in oxide (or hydroxide) and carbonate minerals.
Manganese Ores
Some manganese minerals and mineraloids are considered “primary ores,” because they are rich enough in manganese to be of ore grade. Others are “secondary ores.” These occur in zones where the original manganese content of the sediments has been naturally enriched by younger geologic processes.
Manganese Nodules
An additional potential source of manganese is the ferromanganese nodules and crusts that occur on the seafloor in many parts of the world’s oceans. These bean- to potato-sized nodules are currently the target of exploration and research, mostly focused on the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
Manganese Supply and Demand
Most of the world's manganese ore is produced by a few countries that include South Africa, Australia, China, and Gabon. Ninety percent of proven manganese reserves are also in these four countries, plus Brazil and Ukraine.
Manganese nodule formation
MNs are essentially a conglomerate of minerals that are thought to accumulate in one of two ways: 1) hydrogenetic nodules accumulate chemicals via precipitation directly from seawater, and 2) diagenetic nodules accumulate minerals from within a few centimetres of the ocean floor sediments, metals being derived from interstitial pore water.
Manganese nodule growth rates
Figure 2. The Glomar Challenger scientific vessel used on the Deep Sea Drilling Project. Image courtesy of www.wikipedia.org
Spatial distribution of manganese nodules
As one peruses the literature on MNs, one finds a large consensus concerning the spatial distribution of MNs on the ocean floor. Images of MNs (see figure 1) reveal a rather strange accumulation of what look like potatoes littering the sea floor in every direction for several kilometres.
Where are all the sub-surface manganese nodules?
The almost complete absence of MNs below the ocean sediment surface is completely unexpected when the ocean floor is assumed to be many tens of millions of years old.
Manganese nodule growth rates revisited
The issue of MN growth rates still, of course, remains, even without a viable nodule-growth hypothesis. The issue for the uniformitarian is which rate is the rate to stand by: current growth rates or current sedimentation rates?
Conclusions
Manganese nodules are mostly found at the sediment-water interface, although it is not uncommon to find them buried within the first 50 m of marine sediment. That nodules are rarely found at greater depths has raised legitimate concerns as to their origin and rates of growth.
Acknowledgement
I would like to thank John Whitmore of Cedarville University. This paper was originally submitted as an Oceanography research paper to Dr. Whitmore who encouraged me to see it published in a mainline journal. I appreciate too the work of the Journal of Creation editors.
Occurrence, uses, and properties
Manganese combined with other elements is widely distributed in Earth’s crust. Manganese is second only to iron among the transition elements in its abundance in Earth’s crust; it is roughly similar to iron in its physical and chemical properties but is harder and more brittle.
Compounds
Of the wide variety of compounds formed by manganese, the most stable occur in oxidation states +2, +6, and +7. These are exemplified, respectively, by the manganous salts (with manganese as the Mn 2+ ion ), the manganates (MnO 42− ), and the permanganates (MnO 4− ).
Overview
Growth and composition
On the seabed the abundance of nodules varies and is likely controlled by the thickness and stability of a geochemically active layer that forms at the seabed. Pelagic sediment type and seabed bathymetry (or geomorphology) likely influence the characteristics of the geochemically active layer.
Nodule growth is one of the slowest of all known geological phenomena, on th…
Occurrence
Nodules lie on the seabed sediment, often partly or completely buried. They vary greatly in abundance, in some cases touching one another and covering more than 70% of the sea floor surface. The total amount of polymetallic nodules on the sea floor was estimated at 500 billion tons by Alan A. Archer of the London Geological Museum in 1981.
Polymetallic nodules are found in both shallow (e.g. the Baltic Sea ) and deeper waters (e.g. the c…
Proposed mining
Interest in the potential exploitation of polymetallic nodules generated a great deal of activity among prospective mining consortia in the 1960s and 1970s. Almost half a billion dollars was invested in identifying potential deposits and in research and development of technology for mining and processing nodules. These initial undertakings were carried out primarily by four multinational consortia composed of companies from the United States, Canada, the United Kin…
Ecology
Very little is known about deep sea ecosystems or the potential impacts of deep-sea mining. Polymetallic nodule fields are hotspots of abundance and diversity for a highly vulnerable abyssal fauna, much of which lives attached to nodules or in the sediment immediately beneath it.
Nodule mining could affect tens of thousands of square kilometers of these deep sea ecosystems, and ecosystems take millions of years to recover. It causes habitat alteration, direc…
See also
• Global Sea Mineral Resources (GSR) – Belgian dredging company
• Glomar Explorer – Deep-sea drillship platform used by the CIA to recover sunken Soviet submarine
• International Seabed Authority – Intergovernmental body to regulate mineral-related activities on the seabed
Further reading
• Abramowski, T.; Stoyanova, V. (2012). "Deep-Sea Polymetallic Nodules: Renewed Interest as Resources for Environmentally Sustainable Development". Proc 12th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM 2012. pp. 515–522.
• Abramowski, T. (2016). Value chain of deep seabed mining, Book: Deep sea mining value chain: organization, technology and development, pp 9–18, Interoceanmetal Joint Organization
External links
• Report on a World Almanac 1997 documentary Universe Beneath the Sea claiming evidence of rapid formation
• The International Seabed Authority
Chemistry
Construction
- Many people would correctly respond that steel is made of iron. Far fewer know that it is also made of manganese. Although the amount of manganese used to make a ton of steel is small, it is just as essential as iron to produce this fundamental building block of modern societies.
Significance
- Manganese constitutes roughly 0.1 percent of the Earths crust, making it the 12th most abundant element. Its early use was mainly in pigments and oxidants in chemical processes. The significance of manganese to human societies exploded with the development of modern steelmaking technology in the 1860s. Manganese is essential and irreplaceable in steelmaking, …
Uses
- Manganese is used also as an alloy with metals such as aluminum and copper. Important nonmetallurgical uses include battery cathodes, soft ferrites used in electronics, micronutrients in fertilizers, micronutrients in animal feed, water treatment chemicals, colorant for automobile undercoating, bricks, frits, glass, textiles, and tiles. The product manganese violet is used for th…
Properties
- Elemental manganese readily combines with oxygen, carbon, and silicon to form a long list of manganese minerals. Manganese ores generally contain 25 to 45 percent manganese, mostly in oxide (or hydroxide) and carbonate minerals.
Geology
- Manganese ores are widespread, but most of the worlds supply is from a small number of manganese mining districts. Most manganese ores are from extensive layers of manganese-rich sedimentary rocks that formed in ancient oceans under specialized conditions. These occurred when changes in the oxidation state of ocean water first caused high concentrations of dissolve…
Future
- Some researchers speculate that plots of seafloor could be harvested, left fallow, then harvested again decades into the future. Parts of the world's seafloor might produce a sustainable yield of ferromanganese ore.
Availability
- Important amounts of ferromanganese imports are from South Africa, China, Ukraine, and the Republic of Korea. Silicomanganese is imported from South Africa, Georgia, Norway, and Australia. Demand for manganese historically closely follows steel production and is expected to do so in the future.
Distribution
- Although there are large resources of manganese-enriched rock in the United States, mostly in Maine and Minnesota, their manganese content is substantially below manganese ores readily available from other parts of the world, so they are presently uneconomic to mine.
Resources
- Globally, there is no shortage of manganese ore. Land-based manganese deposits are dominated by the great Kalahari manganese district of South Africa, which accounts for roughly 70 percent of known manganese resources of the world (reserves plus identified material that has yet to be fully proven to be economic). As a result, South Africa is expected to continue to play a dominant rol…