While animals stop growing in size once they become adults, cells produced by meristems ensure that plants continue to grow in height and width throughout their life:
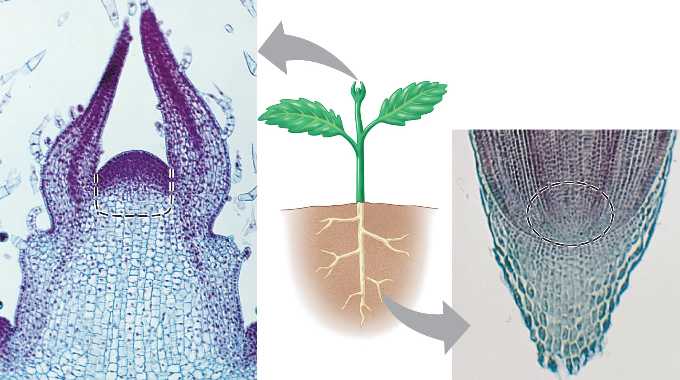
- Meristems at the tips of roots provide a constant supply of new cells allowing roots to grow longer
- Meristems at the tips of shoots allow a plant to keep growing taller and spread wider
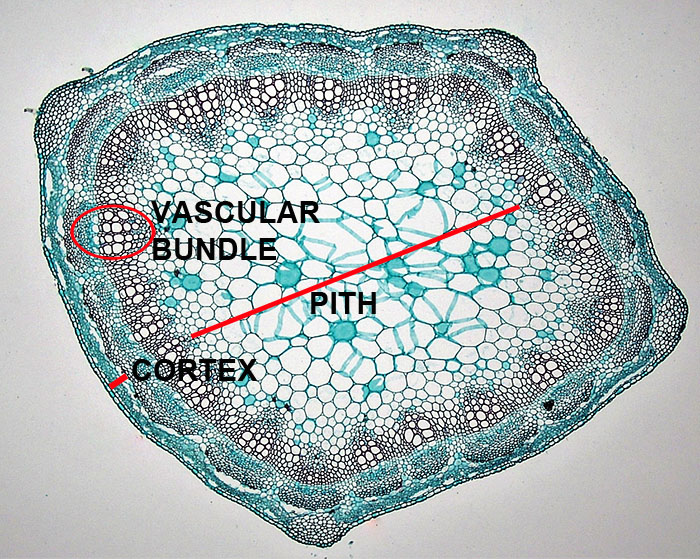
- Meristems between the xylem and phloem increase the width of a plant. These result in the annual growth rings in trees.
How do meristems differ from other plants?
Other cells in the plant are fully differentiated (meaning that they are specialized in both form and function) and do not divide. Cells in the meristem, however, divide and produce all of the new cells in a plant.
How do meristems assist in plant growth?
- Meristems at the tips of roots provide a constant supply of new cells allowing roots to grow longer
- Meristems at the tips of shoots allow a plant to keep growing taller and spread wider
- Meristems between the xylem and phloem increase the width of a plant. These result in the annual growth rings in trees.
What happens in the meristem region of plants?
Lateral Meristem
- It is located in the stems and roots on the lateral side.
- It increases the thickness of the plant.
- Vascular cambium and cork cambium are the two lateral meristems.
- These divide preclinically or radially and give rise to secondary permanent tissues.
Are meristematic tissues present in plants?
There is a special name for these cells, which are called the meristem cells. The tissue that these meristem cells form in plants is called as the meristematic tissue. Meristematic tissue or meristems, as they are also called are tissues that have the ability to enlarge, stretch and differentiate into other types of cells as they mature.

What are meristems and their functions?
Meristems form anew from other cells in injured tissues and are responsible for wound healing. Unlike most animals, plants continue to grow throughout their entire life span because of the unlimited division of meristematic regions.
Where are the meristems in plants?
Meristems are regions of unspecialised cells in plants that are capable of cell division. Meristems make unspecialised cells that have the potential to become any type of specialised cell. They are only found is certain parts of the plant such as the tip of roots and shoots and in between the xylem and phloem.
What are meristems easy definition?
mer·i·stem ˈmer-ə-ˌstem. : a formative plant tissue usually made up of small cells capable of dividing indefinitely and giving rise to similar cells or to cells that differentiate to produce the definitive tissues and organs.
What is meristem in plant tissue?
The cells have no intercellular space. The zone where these cells exist is known as meristem. The cells of the meristematic tissue divide actively to form specialized structures such as buds of leaves and flowers, tips of roots and shoots, etc. These cells help to increase the length and girth of the plant.
Are meristems stem cells?
Meristem cells are a group of cells that reside at the shoot and root tips of plants. As undifferentiated (or slightly differentiated cells) they are considered as stem cells given that they are the origin of many of the cells that go on to rapidly differentiate/specialize and form various parts of the plant.
How do plants grow meristems?
They grow through a combination of cell growth and cell division (mitosis). The key to plant growth is meristem, a type of plant tissue consisting of undifferentiated cells that can continue to divide and differentiate. Meristem allows plant stems and roots to grow longer (primary growth) and wider (secondary growth).
What are meristems in roots?
The root meristem is a layered organized stem cell system. Its core, the quiescent center, consists of four nondividing cells between two files of stem cells. Daughter cells generated by the upper tier extend the cell files of the root.
What are the 4 meristems?
A plant has four kinds of meristems: the apical meristem and three kinds of lateral—vascular cambium, cork cambium, and intercalary meristem. These are located at opposite ends of the plant axis in the tips of roots and shoots.
What are examples of meristems?
The growth tissues of plants are meristems; they have rapidly dividing cells that enlarge (grow) to provide the bulk of the plant. Examples of several meristematic tissues will be considered here: the root tip (radical), the terminal bud (apical meristem), and the cambium.
Why is meristem tissue important for plants?
Meristem tissue is important because it allows for plants to grow and repair damaged tissue. For example, the buds on the ends of leaves are the product of the meristem. This allows for plants to push new growth. There are different types of meristems, called meristematic tissue.
Where are the meristems in roots?
The root apical meristem, or root apex, is a small region at the tip of a root in which all cells are capable of repeated division and from which all primary root tissues are derived. The root apical meristem is protected as it passes through the soil by an outer region of living parenchyma cells called the root cap.
Where is the meristem located in the leaf?
The plate meristem consists of parallel layers of cells dividing anticlinally to play a major role in leaf growth. The marginal meristem, which is located at the edge of the leaf between the adaxial and abaxial surfaces, contributes to the establishment of tissue layers within the leaf.
Where are meristems first found?
Primary meristems are found in the tips of the main and lateral shoots and roots, and hence they are called apical meristems. The apical meristems of the branches arise from the first shoot apical meristem, whereas the apical meristems of the secondary roots develop from the root endodermis.
What is meristematic tissue where it is located?
Meristematic tissues are found at all growing points in a plant, like the tip of roots,stems and branches,where growth in length occurs. The growth in the thickness of stem is also due to meristematic tissue.
What Is a Meristem?
Have you ever given any thought as to how exactly we grow taller when we are kids? Children and adolescents have a special tissue at the end of the long bones in their arms and legs referred to as the growth plate. The growth plate contains osteogenic cells whose sole job is to divide, adding more bone to the bone that is already there. Through this process the bone gets longer, and we grow!
What is the lateral meristem of a plant?
These plants also have a lateral meristem, from the Latin latus, or 'side. ' As opposed to only being located in the tips of plants, this meristem runs up and down the length of the stem.
What is the difference between a cork cambium and a vascular cambium?
There are two types of lateral meristem, the vascular cambium and the cork cambium. The vascular cambium creates new vascular tissue, while the cork cambium replaces the outer layer, or epidermis of the plant.
What is the periderm of cork oak?
This process forms a new layer of bark for the tree or plant. The periderm of the cork oak can grow quite thick. This is the cork that we harvest to make bulletin boards and stoppers for wine bottles.
What are meristematic cells?
Meristematic cells have often been compared to stem cells in humans. They divide rapidly, and their end role in the plant (leaf, stem, flower or root) has yet to be determined. Since they are unspecialized, their cell structure is very basic. They are small and tightly packed with small vacuoles, rudimentary chloroplasts, and thin cell walls. There are two types of meristem in plants: the apical meristem allows the plant to grow taller, while the lateral meristem allows the plant to grow wider.
What is the tissue that grows in plants?
Just like you and me, as plants get older, they grow! The tissue where this growth occurs in plants is called meristem. The meristem is filled with unspecialized meristematic cells, whose job is to divide so that the plant gets bigger. The apical meristem is found at the tips of the plant's roots and shoots and helps the plant get longer. The lateral meristem is located in the stem of trees and woody plants and allows the plant to grow wider.
What is the role of the vascular cambium?
As the plant grows, it requires more food and water, as well as the means to transport that food and water. This is the role of the vascular cambium. It adds new rings of xylem and phloem outside the pre-existing rings. This is the process that creates the rings that we see in the trunks of trees.
What is the meristem in plants?
Meristem. In plants, the meristem is the area of tissue from which new growths are formed. At the meristem, the plant cells are continually proliferating and are not yet differentiated. Depending on where on the plant the meristem is, and on which signals it receives, the meristem tissue can give rise to new leaves, flowers, or roots.
What is the function of the meristem?
The meristem is integral in plant growth —without it, plants would have no source for the production of new cells.
What is the name of the tissue that forms the epidermal tissue of a plant?
The protoderm will go on to form the epidermal tissues of the plant; the ground meristem will form the cortext and pith of the plant; and the procambium will become xylem and phloem, the vascular tissues of the plant. The shoot of a plant also includes its leaves, which grow from the sides of the apical meristem.
What is the function of lateral root meristems?
Lateral root meristems account for the lateral growth of roots from the main root, into vastly branched root systems. Lateral root growth help to increase the plant’s efficiency in water and nutrient absorption, nutrient storage, and stability for aerial growth.
What is the tissue that protects the apical meristem?
One tissue comprises the main roots of the plant that supply proliferative, undifferentiated cells for continued growth, and the other forms a root cap that protects the apical meristem and the source of new cells. Because the roots are growing and the root cap is continuously being ground down into the soil, cells of the root cap are constantly ...
What is the basal meristem?
Also known as an intercalary meristem, the basal meristem is found between mature, differentiated tissues. Although located relatively near an apical meristem and also composed of mostly undifferentiated cells, the intercalary meristem is distinctly different. It works independently of the apical meristem to promote the vertical growth of the plant.
What is the shoot apical meristem?
Shoot Apical Meristem. The shoot apical meristem, found above ground, is composed of undifferentiated cells that have one of three destinies. They can develop to become one of three primary meristems: the protoderm, ground meristem, or procambium.