
What are fallout shelters made of?
Safecastle prefabricated Fallout Shelters are made of steel up to 7/16" thick. The primary differences between our storm shelters and our fallout shelters are found in modifications to the door, steps, and air vents to make them virtually impervious to radiological, biological, or chemical contamination.
Should you build a nuclear fallout shelter?
While experts say nuclear war is unlikely, building a fallout shelter can still help provide peace of mind during these uncertain times. A nuclear fallout shelter, also called a bomb shelter, protects you and your family after a nuclear attack or disaster.
How is a nuclear shelter built?
The shelter is built from a single living space (which can divide into separate rooms) and the “machine room” adjacent to the generator and the air and water filtering systems. A nuclear shelter needs to be equipped with the necessary supplies to accommodate the entire family for a week.
What is a fallout shelter?
A fallout shelter is a specially designed enclosure that safeguards occupants from radioactive waste in case of a nuclear war. Underground fallout shelters are made of steel and were built in the past as civil defense systems during the cold war.
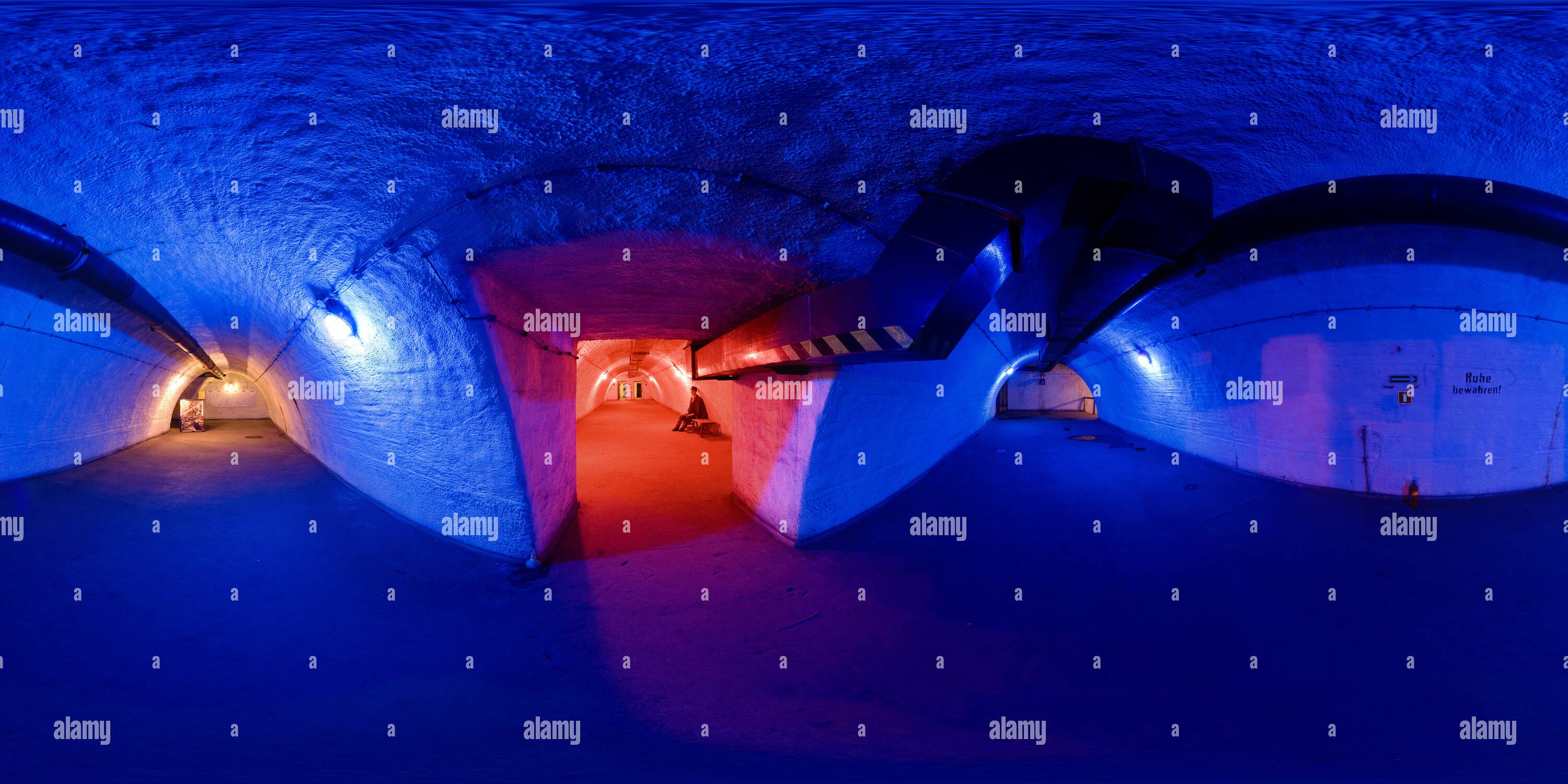
What are nuclear bunkers made out of?
The most common purpose-built structure is a buried, steel reinforced concrete vault or arch. Most expedient blast shelters are civil engineering structures that contain large buried tubes or pipes such as sewage or rapid transit tunnels.
What material is used in bomb shelters?
United States Safe Room fallout shelters are designed to provide multiple layers of protection, including earth, concrete and solid-plate steel. Abundant space: Radioactive fallout is most harmful in the first few weeks, after which levels are diminished to a fraction of what they initially were.
How deep does a bunker have to be to survive a nuke?
Most experts say to withstand nuclear blasts, bombs, natural disasters, and radiation; you need to build a bunker at least 10 ft deep.
How do you build a radiation shelter?
1:565:35How to build a Home Fallout Shelter in the Cold War - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe entrance no more than two feet wide was strictly built with a right angle turn to prevent mostMoreThe entrance no more than two feet wide was strictly built with a right angle turn to prevent most of the radiation rays getting in as radiation travels in a straight line.
How do I seal my house from nuclear fallout?
To seal a room:Seal all windows, rooms and air vents in one room with 2-4 mil. thick plastic sheeting and duct tape. ... Cut the plastic sheeting at least six inches wider than the openings and label each sheet.Duct tape plastic at corners first and then tape down all edges.
How do you get fresh air in a bomb shelter?
0:554:58ARK TWO #2 How to bring air into shelter - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe simplest way to bring in air heavy steel great let me lock the top and bottom of every entrance.MoreThe simplest way to bring in air heavy steel great let me lock the top and bottom of every entrance. We might put up what sheet go through the air.
What is the safest place during a nuclear war?
Page 1In the event of a radiation emergency, such as a nuclear power plant accident or the explosion of a dirty bomb, you may be asked to stay home and take shelter rather than try to evacuate. ... The safest place in your home during an radiation emergency is a centrally located room or basement.More items...
How long should you stay underground after a nuclear bomb?
24 hoursStay inside for 24 hours unless local authorities provide other instructions.
How long do you have to stay inside after a nuclear bomb?
24 hoursThe walls of your home can block much of the harmful radiation. Because radioactive materials become weaker over time, staying inside for at least 24 hours can protect you and your family until it is safe to leave the area.
How do you make a homemade nuclear bunker?
How to Build an Underground Bunker in 9 StepsGet Permission. The most important thing to do is to get the proper permits. ... Choose the Location. ... Develop a Blueprint. ... Pick the Right Bunker Building Material. ... Choose the Right Excavating Equipment. ... Acquire Key Living Materials. ... Start Digging. ... Reinforce the Shelter.More items...•
Would a basement protect you from nukes?
When a nuclear explosion occurs, the best location to seek shelter is in the basement or the in middle of a room in one of these places to avoid radiation exposure.
Can you survive a nuclear bomb in a house?
You must protect yourself from the fallout or you'll have a short life. If you're in a stable structure such as a basement or fire staircase, you can shelter in place for a few days, if necessary. If your building is destroyed, you'll need to move to a nearby intact structure. Block all the doors, windows and air gaps.
Can you survive a nuke underground?
It's even possible to survive a nuclear blast near ground zero if you happen to be inside a robust building, such as a fortified structure or an underground facility, says Brooke Buddemeier, a certified health physicist at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in Livermore, California.
Can you survive a nuke in a basement?
Can you Survive A Nuclear Bomb by sheltering in a Basement. Yes and no. Surviving a direct hit from a nuclear strike is unlikely; however, the actual area of that damage is quite small, and it is highly likely that going into the basement will allow you to survive a nuclear bomb.
How much concrete do you need to survive a nuclear blast?
As close as 1,000 feet, a 32-inch concrete slab will insure survival. At 2,000 feet, 20 inches of concrete is sufficient. At 4,000 feet, only 6 inches of concrete is necessary, while, at 5,000 feet from the burst, no shelter is needed for survival from the explosion itself.
How much would it cost to build a doomsday bunker?
Doomsday Bunker Cost A doomsday or apocalypse bunker can cost anywhere from $35,000 to several million dollars. Some companies use “doomsday” bunkers interchangeably with nuclear or fallout bunkers but some people see these types of bunkers as different.
What was the untenability of the shelters?
In fact, the untenability of the shelters was public knowledge before they had even opened. A November 1961 story on the front page of The Washington Post bemoaned that most of the designated shelters would be little more than “cold, unpleasant cellar space, with bad ventilation and even worse sanitation.”.
How to protect Americans from nuclear attack?
A surer way to protect Americans from a nuclear attack—which, with the Berlin crisis of 1961, looked increasingly possible—was to build reinforced-concrete blast shelters around the nation that could actually withstand an explosion.
What paint did the 3M use to make the shelter signs?
As a test, Blakely had envisioned the signs put up in downtown Manhattan “when all the lights are out and people are on the street and don’t know where to go.” And since half of Americans at the time were smokers, Blakeley specified the use of yellow reflective paint to make the signs visible in the glow of a cigarette lighter. The 3M corporation (best known today as the maker of Scotch tape and Post-It notes) manufactured 400,000 shelter signs, for which Uncle Sam paid less than a penny apiece.
When did shelters end?
By 1971, the government decided to phase out the stocking of shelters. Eventually, it stopped keeping a list of them. Some building owners donated their shelter rations to the charity CARE, which shipped them to Africa and Bangladesh. In New York, some of the biscuits wound up with an upstate farmer, who fed them to his pigs. Looking back on the civil-defense program in 1976, The New York Times observed: “the only reminders of fallout shelters [now] are the yellow-and-black signs placed outside buildings.”
How many buildings were inspected by the Army Corps of Engineers?
The signs popped up everywhere. In New York alone, the Army Corps of Engineers contracted with 38 architectural firms to inspect 105,244 large buildings. Eventually, some 19,000 of them would become shelters.
When did fallout shelters start?
Americans got their first look at that protection in January of 1962, when fallout-shelter signs began appearing in 14 cities across the country. Designed by Robert W. Blakeley of the Army Corp of Engineers, the signs featured three yellow triangles inscribed in a black circle—an arresting image approved by government psychologists.
Do fallout shelters protect people?
While fallout shelters would do nothing to safeguard people from an actual bomb, they would, in the words of JFK’s civil-defense chief Steuart L. Pittman, give “our presently unprotected population some form of protection.”.
How long can you live inside a nuclear shelter?
According to some government manuals, you can live in a fallout shelter for approximately two weeks. However, the time it takes for radiation to fade varies between a few days to roughly two weeks.
What is fallout shelter?
A fallout shelter is a specially designed enclosure that safeguards occupants from radioactive waste in case of a nuclear war.
What should I do if the only fallout shelter near me is quite far away?
If you live in a high target area that may be prone to attack, consider constructing bomb bunkers.
What else should you do when stuck in fallout hideout locations?
Follow the latest updates through a hand crank emergency or battery-powered radio. Remember, making calls can be difficult during an emergency. Try communicating with your friends and loved ones through text messaging, social media platforms, or email.
How to survive a bombing?
The best way to survive a bombing is by hiding inside a nuclear shelter. To do that, you must know the basic fallout shelter signs. Overall, there are only three survival options when it comes to optimal protection: Underground Mines, Caves, and Government Bunkers. More helpful reading:
How did people die in the mines?
People have died from asphyxiation by going into an underground mine that lacks oxygen. Also, if the mine has been unused for a while, it could be in danger of collapsing from the explosion since it hasn’t been reenforced for some time.
Where are underground bunkers located?
There are several underground bunkers across the United States, in Washington D C the most, built during the cold war that are available in case of signs of war. Some of them were built in isolated mine shafts that have since been excavated.
How to build a shelter in the ground?
Plant a series of wooden stakes in the ground to outline the shelter’s perimeter. Then, use shovels, axes, and other tools to dig up grass, trees, rocks, and other debris in the area. Clear the land about 10 ft (3.0 m) beyond the shelter’s perimeter so you have plenty of space to work with.
How to make a shelter out of dirt?
Pile dirt near the entryway, then begin digging into it with a shovel. Shape the dirt into small steps. Lay threshold boards over each steps, connecting them to side boards with 10 in (25 cm) lag bolts. Always have a second exit in your shelter to guard against emergencies.
What do entryway poles hold?
These entryway poles hold back the dirt you will use to create the shelter ceiling. If you don’t have them in place, the dirt can slide into the entryways, blocking them.
How to make a hammock with a trench shelter?
With a pole-covered trench shelter, the best way to set up furniture is to make hammocks. Loop strong rope or wire around the ceiling poles. Connect the rope or wire to cloth to create strong but lightweight hammocks. You can also try assembling poles and boards together to create bunk beds.
How to make a log shelter?
Cover the logs with an 18 in (46 cm) earth dome. Begin moving the excavated dirt back on top of the logs. Make sure the dirt is unable to leak into the living space below the logs. As you pile up the dirt, shape it into a rounded mound ending right before the shelter’s entrances. The mound shape will give your shelter’s roof plenty of stability to prevent it from caving in.
What to do if you can't dig a trench shelter?
If you are unable to dig a trench shelter, look for alternatives. Underground areas are safest. Even a shelter built in a basement is a viable option in an emergency.
How to keep shelter safe?
It isn’t ideal, but it is an effective way to keep your shelter safe and sanitary. Seal the buckets and carry them to the surface as needed.
What is a fallout shelter made of?
Safecastle prefabricated Fallout Shelters are made of steel up to 7/16" thick. The primary differences between our storm shelters and our fallout shelters are found in modifications to the door, steps, and air vents to make them virtually impervious to radiological, biological, or chemical contamination. They are also referred to as NBC shelters (protecting from Nuclear, Biological, and Chemical contamination).
How tall is a fallout shelter?
Our fallout shelters come with a standard door base 30" tall. This will put the door entrance just above the ground level. The top of the shelter will be approximately 30" below ground. Any door base that extends above the top of the shelter more than the standard 30" base, has to be hauled separately from the shelter. This door base over 30" tall will have a door 32" wide and 32" long with ladder-type steps going down into the shelter.
How to know if you need a nuclear shelter?
These natural shelters will protect you only from the nuclear blast and the initial radiation burst. Chances are that you won’t be warned about a nuclear blast, but (just in case) here are 3 signs that you need to take “nuclear” cover: 1 – When your electronics stop working(most of them)
How to find the closest nuclear shelter?
But you can use a website to find the closest mine to your home. Just enter your location and make sure you’ve checked “underground” and a 50 miles radius. The results is your closest “nuclear shelter”.
How long can you live after a nuclear bomb explodes?
3 – When a Nuclear Bomb explodes a few miles away, but does not kill you. If you’re not killed in the first few minutes, you can live a lifetime or die of cancer in the next few days. The longer you expose yourself to radiation (in the radioactive area) the lowest the chances to survive.
What is salt mine used for?
The salt mine was used to mine table salt, but with the decline in salt prices the mine is now used to mine road salt for winter. The Michigan basin and the great lakes area (since there are also huge salt mines in Canada), used to be part of a sea which sank into the earth. The salt was left behind and formed the massive deposits that we mine today.
How many people can be sheltered in Detroit?
It’s the case in Detroit, where just 1200 Feet below there is a salt mine that can easily shelter the entire population of Detroit! Actually it can shelter over 5 million people.
Is there a nuclear shelter in the US?
But if you think about it , there are a lot of natural nuclear shelters in the US that are absolutely free.
Is there a map of underground mines?
Unfortunately, there isn’t a reliable map with all US underground mines. I tried to use Google Maps but it has a lot of other facilities with the name “mines” and also surface mines. You can see it here.
What is the worst thing about buried shelters?
But the worst problem with buried shelters is the fact that you have to go outside and open a hatch to get inside. The notoriety of bringing in a huge tank shelter on a semi-truck and burying it in your backyard with a crane guarantees that the whole neighborhood is going to know about it.
How To Prepare For and Survive a Nuclear Attack ?
First, let’s be clear about one thing: nuclear war is very survivable, even with minimal preparations, so don’t believe the “everyone is going to die” claims about nuclear winter and total destruction. 50% of Hiroshima survived without any preparations, though many were very sick.
What is a nuclear target map?
nuclear target map is an interesting and unique program unlike other nuclear target maps because it lets you pick the target and what size nuclear device that the area you chose is hit with and then shows the likely effects and range of damage and death that would be caused by that nuclear device if it hit and detonated on your chosen target area.
How much water is needed for nuclear protection?
Nuclear protection purists would demand a reduction in radiation that is almost total requiring 13.8 feet of water, 10 feet of earth, 6 feet of concrete, or about 1.3 feet of lead—a Protection Factor (PF) of a billion, all of which are very costly to achieve.
What happens to the electricity grid before a nuclear strike?
Because both Russian and Chinese nuclear doctrine dictates the use of high attitude Nuclear Electromagnetic Pulse weapons (EMP) just before a physical nuclear strike, the electric grid will go down —which guarantees a lot of panic as people are plunged into darkness, lack of communication, and the cessation of all government services, like sewer and water.

Why You Need A Shelter in Case of A Nuclear Blast?
Best Shielding Materials to Build A Nuclear Shelter
- Literally, all materials provide radiation protection to some extent, some might provide less protection and some provide more. You will have to use a sufficient quantity of any material to protect against the radiation. Barriers of lead, concrete, or water provide very good protection from all types of penetrating radiation. This is why certain ra...
Thickness of Shielding
- Shielding material’s effectiveness depends on its thickness and density. An ample thickness of shielding material will reduce the level of radiation to negligible amounts. The thickness required to weaken gamma radiation from fallout is far less than that needed to shield against initial gamma radiation. Fallout radiation has less energy than a nuclear detonation’s initial radiation. F…
Construction of Shelter Before A Nuclear Blast
- If you are just prepping for nuclear attack/blast, it’s better to build a shelter underground. Having thick concrete and brick walls is the best idea. If there is an exposed side of this basement, like a door or window, don’t forget to cover it with lead sheet. I highly recommend that you make some ventilation shaft that can be opened/shut from inside the shelter. If you get a nuclear blast warni…
Emergency Shelters After A Nuclear Blast
- You may not get an early warning about an imminent nuclear blast because of many factors involved in it. Therefore, you may not have the time to build a nuclear shelter. So you may have to resort to makeshift arrangements to survive for some initial time. In that case, ground that provides natural shielding and easy shelter construction is the ideal place for an emergency shel…
Trenches as Emergency Shelters
- In areas where there is no natural protection, and you don’t have time to build a nuclear shelter, digging a slit trench is the best bet. When digging a trench, work from inside the trench as soon as it is large enough to cover your body. This way you’ll not expose all your body to the radiation. In an open area, try to dig the trench from a prone position, stacking the dirt carefully and evenly ar…
Other Shelters
- While an underground shelter covered by 1 meter or more of dirt provides the best protection against fallout radiation, the following unoccupied structures (in the order listed) offer the next best protection: 1. Caves and tunnels covered by more than 1 meter of earth 2. Storm Shelters or storage cellars 3. Culverts 4. Basements or cellars of abandoned buildings 5. Buildings made of …
Roofs
- It is not mandatory that you build a roof when you build an emergency nuclear shelter. Build one only if the materials are readily available with only a brief exposure to outside contamination. If building a roof would require extended exposure to penetrating radiation, it would be wiser to leave the shelter roofless. A roof’s sole function is to reduce radiation from the fallout source to …
Decontamination
- Decontaminate any materials you bring into the shelter. These materials include grass or foliage that you use as insulation or bedding, and your outer clothing (especially footgear). If the weather permits and you have heavily contaminated outer clothing, you may want to remove it and bury it under a foot of earth at the end of your shelter. You may retrieve it later (after the radioactivity d…
Site Selection and Preparation
- To reduce your exposure time and thereby reduce the dosage received, remember the following factors when you select and build a nuclear shelter: 1. Where possible, seek a simple, existing shelter that you can improve. If none is available, immediately dig a trench. 2. Build the nuclear shelter deep enough to get good protection, then enlarge it as required for comfort. 3. Cover the …