The Functions of Nucleic Acids
- Nucleic acids are responsible for the transmission of inherent characters from parent to offspring.
- They are responsible for the synthesis of protein in our body
- DNA fingerprinting is a method used by forensic experts to determine paternity. It is also used for the identification of criminals. ...
What are nucleic acids and why are they important?
Nucleic acids are responsible for the transmission of inherent characters from parent to offspring. They are responsible for the synthesis of protein in our body DNA fingerprinting is a method used by forensic experts to determine paternity.
What do nucleic acids do for the body?
Thus, nucleic acids are defined as large macromolecules that store, encode and transmit genetic data from one generation to another. Let us find out more about nucleic acids and their structure and properties. Nucleic Acids Structure. These vital macromolecules are typically made of oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, phosphorus, and most importantly, carbon.
What are some interesting facts about nucleic acids?
May 12, 2022 · Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that play essential roles in all cells and viruses. A major function of nucleic acids involves the storage and expression of genomic information. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, encodes the information cells need to make proteins. A related type of nucleic acid, called ribonucleic acid (RNA), comes in different molecular …
What is the role of nucleic acids in the body?
Nucleic acid is a natural chemical compound that can be broken down to produce phosphoric acid, sugars and a combination of organic bases (nucleotide, purines, and pyrimidines). They are the cell's main information-carrying molecules and they ultimately determine the inherited traits of every living organism by guiding the entire process of protein synthesis.
What are the 3 main functions of nucleic acids?
What is the function of a nucleic acid example?
What are the 4 functions of nucleotides?
Why are nucleic acids called acids?
1. What are the main components of nucleic acids?
Ans. A nucleic acid is a long-chain polymer made of monomeric units called nucleotides. A nucleotide, in turn, consists of three primary components...
2. What is a nucleic acid?
Ans. Nucleic acids can be defined as large macromolecules that store, encode and transmit genetic information from one generation to another. These...
3. Which nucleic acids are present in viruses?
Ans. Viruses, usually have either DNA or RNA as their genetic material. These can be double-stranded or single-stranded.
4. What are the functions of nucleic acids?
Ans. Nucleic acids help synthesise proteins in the body. The RNA is an especially important factor in the synthesis of proteins. The DNA never leav...
What are the elements in nucleic acids?
Nucleic Acids Structure. These vital macromolecules are typically made of oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, phosphorus and most importantly, carbon. They are long-chain polymers that consist of monomeric units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide comprises a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar and a specific nitrogen base. Image will be uploaded soon.
What is a nucleic acid test?
A nucleic acid test or NAT is a burgeoning technique used in medical science as well as other fields of molecular biology and research, to detect strains of unknown bacteria, viruses and other microbes. In this test, a particular sequence of nucleic acids is investigated and detected. This helps to identify or eliminate various strains of viruses and bacteria, or other pathogens in the blood. They are unique to the field of pathology, in the sense that, unlike most tests that detect antibodies or antigens, the NAT focuses more on the genetic components of the microbes.
What is the name of the polymer that contains sugar?
In a nucleotide, if the sugar happens to be a ribose, then the polymer is called ribonucleic acid or RNA. Likewise, if the sugar is deoxyribose, it is called deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. These are the most vital of all biomolecules present in living organisms.
What are the four types of nucleobases?
These further assemble into chains of base-pairs of nucleobases. Nucleobases are prominently of four types: adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil and thymine. Note that uracil is found only in RNA while, thymine is present only in DNA.
Do prokaryotes have DNA?
Prokaryotic organisms, however, do not have their DNA enclosed in a membranous coat. In such organisms, the DNA is found freely-floating in the cytoplasm. The genetic machinery of each cell, in its entirety, is known as a genome. The study of genomes, on the other hand, is known as genomics.
Where is DNA found in an organism?
In such organisms, the DNA is found freely-floating in the cytoplasm. The genetic machinery of each cell, in its entirety, is known as a genome. The study of genomes, on the other hand, is known as genomics. Activity: Find out from the Internet how each DNA or RNA strand in a cell is packed.
What is the function of each chromosome?
Each chromosome of a living organism is a repository of thousands of hundreds of genes, dictating the organism’s identity, behaviour, habit and other functions. Most genes contain the information that can code for protein products in the body. Some of these can also code for RNA products.
What are nucleic acids?
Regina Bailey. Updated January 25, 2020. Nucleic acids are molecules that allow organisms to transfer genetic information from one generation to the next. These macromolecules store the genetic information that determines traits and makes protein synthesis possible.
Where are nucleic acids found?
These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides held together by covalent bonds. Nucleic acids can be found within the nucleus and cytoplasm of our cells .
What are the two molecules that make up nucleic acids?
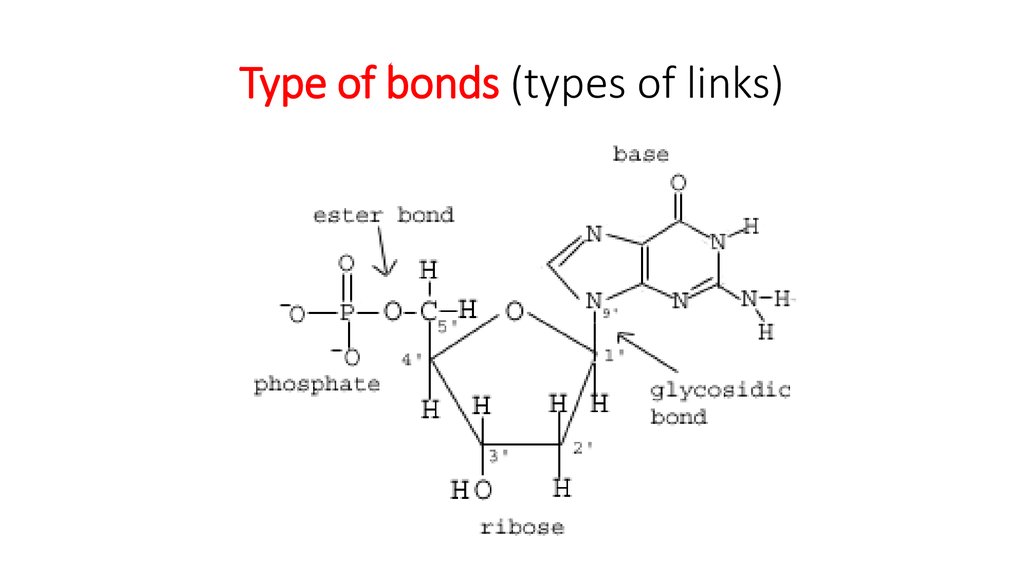
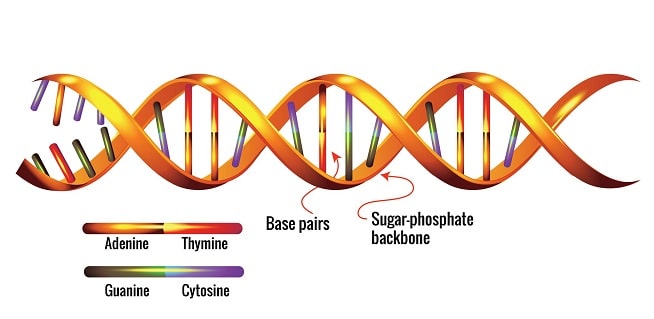
Nucleic acids include DNA and RNA. These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA is composed of a phosphate-deoxyribose sugar backbone and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
What is the sugar in DNA?
In DNA, the five-carbon sugar is deoxyribose, while ribose is the pentose sugar in RNA. Nucleotides are linked together to form polynucleotide chains. They are joined to one another by covalent bonds between the phosphate of one and the sugar of another. These linkages are called phosphodiester linkages.
How are nucleotides linked?
Nucleotides are linked together to form polynucleotide chains. They are joined to one another by covalent bonds between the phosphate of one and the sugar of another. These linkages are called phosphodiester linkages. Phosphodiester linkages form the sugar-phosphate backbone of both DNA and RNA.
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
DNA is composed of a phosphate-deoxyribose sugar backbone and the four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). OpenStax/Wikimedia Commons/CC BY-SA 3.0. DNA is the cellular molecule that contains instructions for the performance of all cell functions.
Where is DNA found?
DNA is organized into chromosomes and found within the nucleus of our cells. It contains the "programmatic instructions" for cellular activities. When organisms produce offspring, these instructions are passed down through DNA. DNA commonly exists as a double-stranded molecule with a twisted double-helix shape.
What is the purpose of DNA?
It is the source of information for the synthesis of all cell and organism protein molecules, and it provides the information that daughter cells or offspring have inherited . Both of these functions require the DNA molecule to represent as a template — in the first case for the transcription of the information into RNA and in the second case for the daughter DNA molecules. The complementarity of the double-stranded DNA model Watson and Crick strongly suggests that semi-conservative replication of the DNA molecule occurs. Thus, when each strand of the double-stranded parental DNA molecule separates during replication from its complement, each serves as a template for synthesizing a new complementary strand. The two newly created double-stranded daughter DNA molecules are then sorted between the two daughter cells (Figure 35–5), each containing one strand (but complementary rather than identical) from the parent dual - stranded DNA molecules (Figure35–5). Each daughter cell contains DNA molecules with specific information remarkably similar to that possessed by the parent; however, the parent cell's DNA molecule was only semi-conserved in each daughter cell.
Why is DNA important?
DNA functions are vital to inheritance, protein coding, and life's genetic blueprint. It is not surprising, given the enormity of the functions of DNA in the human body and its responsibility for the growth and maintenance of life that the discovery of DNA has led to so many developments in the treatment of various types of diseases. DNA is guided by the development and reproduction of an organism - ultimately, it’s survival.
When was DNA first used?
In a series of experiments by Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty, the demonstration that DNA contained the genetic information was first made in 1944. They showed that by introducing purified DNA from the former coccus into the latter, the genetic determination of the character (type) of the capsule of specific pneumococcus could be transmitted to another capsular type. These scholars actually referred to the agent (later shown to be DNA) that accomplished the change as a "transforming factor." Thereafter, this form of genetic manipulation became commonplace. Recently, similar studies have been conducted using yeast, cultivated mammalian cells, and insect and mammalian embryos as recipients and cloned DNA as a donor of genetic material.
What are the roles of messenger RNAs?
Many other cytoplasmic RNA molecules (ribosomal RNAs; rRNAs) have major structural roles in which they contribute to the formation and function of ribosomes (organellar protein synthesis machinery) or serve as adapter molecules (transfer RNAs; tRNAs) for translating RNA information into specific polymerized amino acid sequences.
Does RNA contain DNA?
Though RNA in most cells do not really serve as genetic information, for many viruses that do not contain DNA, RNA holds this function. Therefore, RNA clearly has the extra ability to serve as genetic information. Although RNA is typically single cell stranded, there is considerable diversity in viruses. Rhinoviruses causing a common cold; influenza viruses; and one - stranded RNA viruses are Ebola viruses. Examples of double-stranded RNA viruses are rotaviruses that cause severe gastroenteritis in children and other immunocompromised individuals. Because in eukaryotic cells double-stranded RNA is uncommon, its presence serves as an indicator of viral infection. Viruses analyze in more detail the implications for a virus having an RNA genome instead of a DNA genome.
How do cells respond to their environment?
By taking signals from hormones or other external chemical signals, cells respond to their environment. The interaction between these extracellular chemical signals ("first messengers") and cell surface receptors often leads to the production of second messengers inside the cell, which in turn leads to adaptive changes inside the cell. The second messenger is often a nucleotide. Adenosine 3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic AMP, or cAMP), formed from ATP in a reaction catalyzed by adenylyl cyclase, an enzyme associated with the plasma membrane's inner face, is one of the most common. In virtually every cell outside the plant kingdom, Cyclic AMP serves regulatory functions. In many cells, Guanosine 3 ', 5 ' - cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) occurs and also has regulatory functions.
What is nucleic acid?
Nucleic acid refers to both DNA and RNA. In 1938, the first x-ray diffraction pattern of DNA was published by Astbury and Bell. In 1953, Watson and Crick described the structure of DNA. While discovered in eukaryotes, over time scientists realized a cell need not have a nucleus to possess nucleic acids.
Do all cells have nucleic acids?
While discovered in eukaryotes, over time scientists realized a cell need not have a nucleus to possess nucleic acids. All true cells (e.g., from plants, animals, fungi) contain both DNA and RNA. The exceptions are some mature cells, such as human red blood cells.
What are the two types of polymers in DNA?
Both DNA and RNA are polymers made up of monomers called nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of three parts: 1 a nitrogenous base 2 a five-carbon sugar (pentose sugar) 3 a phosphate group (PO 43-)
Where are nucleic acids found?
These large molecules are called nucleic acids because they were first identified inside the nucleus of cells, however, they are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts as well as bacteria and viruses.
Who discovered nucleic acids?
Considerable research in the 19th and 20th centuries led to the understanding of the nature and composition of the nucleic acids. In 1869, Friedrick Miescher discovered nuclein in eukaryotic cells. Nuclein is the material found in the nucleus, consisting mainly of nucleic acids, protein, and phosphoric acid.
Where is DNA found in a cell?
DNA and RNA Comparison. Sponk. DNA is a double-stranded molecule organized into chromosome found in the nucleus of cells, where it encodes the genetic information of an organism. When a cell divides, a copy of this genetic code is passed to the new cell. The copying of the genetic code is called replication .
What is the process of copying DNA?
A type of RNA called messenger RNA or mRNA reads DNA and makes a copy of it, through a process called transcription. mRNA carries this copy from the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, ...
What is the purpose of nucleic acids?
All life on Earth uses nucleic acids as their medium for recording hereditary information – that is nucleic acids are the hard drives containing the essential blueprint or “source code” for making cells.
What is the role of nucleic acids in living things?
By far the most important function of nucleic acids for living things is their role as carriers of information. Because nucleic acids can be created with four “bases,” and because “base pairing rules” allow information to be “copied” by using one strand of nucleic acids as a template to create another, these molecules are able to both contain ...
What is a nucleic acid?
Typically, a nucleic acid is a large molecule made up of a string, or “polymer,” of units called “ nucleotides .”. All life on Earth uses nucleic acids as their medium for recording hereditary information – that is nucleic acids are the hard drives containing the essential blueprint or “source code” for making cells.
Where are nucleic acids found?
Nucleic acids have been found in meteorites from space, proving that these complex molecules can be formed by natural causes even in environments where there is no life. Some scientists have even suggested that such meteorites may have helped create the first self-replicating nucleic acid “life” on Earth.
What is the name of the chain of nucleotides that stores genetic information?
A nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems. It creates DNA and RNA, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. This information is stored in multiple sets of three nucleotides, known as codons.
Where is DNA found in the cell?
Scientists eventually found the answer in the form of DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid – a molecule located in the nucleus of cells, which was passed down from parent cells to “daughter” cells. When the DNA was damaged or passed on incorrectly, the scientists found that cells did not work properly.
Why is DNA important to a cell?
Because the DNA source code is just as vital to a cell as your operating system is to your computer, DNA must be protected from potential damage. To transport DNA’s instructions to other parts of the cell, copies of its information are made using another type of nucleic acid – RNA. It’s these RNA copies of genetic information which are sent out ...
What are the components of a nucleic acid?
A nucleotide contains 3 components: a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group and a 5-carbon sugar.
What are the different types of nucleic acids?
There are different types of nucleic acids with different characteristics and functions. 1. DNA. DNA holds the genetic information which is important in the functioning and development of all living things. The genetic information carried on the DNA segments is called genes.
Who discovered nucleic acids?
Johann Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895), a Swiss biochemist, discovered nucleic acids in 1869. He found out that the cell nuclei contained a rather unusual compound and he named it nuclein. The unusual nature of the compound was brought about by the presence of phosphorus and nitrogen, as well as oxygen, hydrogen and carbon.
Can nucleic acids be fatal?
Nucleic acids are so vital in the body that if any form of mutation occurs, it can be fatal. There are several conditions that can result from mutations of nucleic acids. Examples of the most common mutations include:
What is DNA made of?
The genetic information carried on the DNA segments is called genes. DNA is made up of two polymers that are formed by smaller units called nucleotides . The polymers have backbones made of phosphate and sugar combined by ester bonds. The polymers are not parallel as they run in opposite directions.
What are the two molecules that make up DNA?
The polymers are not parallel as they run in opposite directions. Each sugar has one out of 4 molecules called bases (nucleobases) attached to it.
What are the backbones of polymers?
The polymers have backbones made of phosphate and sugar combined by ester bonds. The polymers are not parallel as they run in opposite directions. Each sugar has one out of 4 molecules called bases (nucleobases) attached to it. Information is encoded by the sequence of the 4 neuclobases.
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids are long chainlike molecules composed of a series of nearly identical building blocks called nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogen-containing aromatic base attached to a pentose (five-carbon) sugar, which is in turn attached to a phosphate group.
What are the two classes of nucleic acids?
They play an especially important role in directing protein synthesis. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) and ribonucleic acid ( RNA ).
How are nucleotides synthesized?
The ribose phosphate portion of both purine and pyrimidine nucleotides is synthesized from glucose via the pentose phosphate pathway. The six-atom pyrimidine ring is synthesized first and subsequently attached to the ribose phosphate. The two rings in purines are synthesized while attached to the ribose phosphate during the assembly of adenine or guanine nucleosides. In both cases the end product is a nucleotide carrying a phosphate attached to the 5′ carbon on the sugar. Finally, a specialized enzyme called a kinase adds two phosphate groups using adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as the phosphate donor to form ribonucleoside triphosphate, the immediate precursor of RNA. For DNA, the 2′-hydroxyl group is removed from the ribonucleoside diphosphate to give deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate. An additional phosphate group from ATP is then added by another kinase to form a deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate, the immediate precursor of DNA.
What is the chemical compound that is capable of being broken down to yield phosphoric acid, sugars, and
Nucleic acid, naturally occurring chemical compound that is capable of being broken down to yield phosphoric acid, sugars, and a mixture of organic bases (purines and pyrimidines). Nucleic acids are the main information-carrying molecules of the cell, and, by directing the process of protein synthesis, they determine the inherited characteristics ...
Nucleic Acid Monomers
DNA Structure
- DNA is the cellular molecule that contains instructions for the performance of all cell functions. When a cell divides, its DNA is copied and passed from one cellgeneration to the next. DNA is organized into chromosomes and found within the nucleusof our cells. It contains the "programmatic instructions" for cellular activities. When organisms produce offspring, these inst…
RNA Structure
- RNA is essential for the synthesis of proteins. Information contained within the genetic code is typically passed from DNA to RNA to the resulting proteins. There are several types of RNA. 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the RNA transcript or RNA copy of the DNA message produced during DNA transcription. Messenger RNA istranslated to form proteins. 2. Transfer RNA (tRNA)has a t…
DNA and RNA Composition
- The nucleic acids DNA and RNA differ in composition and structure. The differences are listed as follows: DNA 1. Nitrogenous Bases:Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine 2. Five-Carbon Sugar:Deoxyribose 3. Structure: Double-stranded DNA is commonly found in its three-dimensional, double-helix shape. This twisted structure makes it possible for DNA to unwind for DNA replicati…
More Macromolecules
- Biological Polymers: macromolecules formed from the joining together of small organic molecules.
- Carbohydrates: include saccharides or sugars and their derivatives.
- Proteins: macromolecules formed from amino acid monomers.
- Lipids: organic compounds that include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes.