The philosophy of mission command is guided by six interdependent principles: build cohesive teams through mutual trust, create shared understanding, provide a clear commander’s intent, exercise disciplined initiative, use mission orders, and accept prudent risk. What are the 5 components of Mission Command?
What are the 6 principles of Mission Command?
MISSION COMMAND PRINCIPLES The philosophy of mission command is guided by six interdependent principles: build cohesive teams through mutual trust, create shared understanding, provide a clear commander's intent, exercise disciplined initiative, use mission orders, and accept prudent risk.
What is a mission command?
"Mission command is the exercise of authority and direction by the commander using mission orders to enable disciplined initiative within the commander's intent to empower agile and adaptive leaders in the conduct of unified land operations."1
How can everyday tasks be used to develop mission command?
By employing these principles, everyday tasks can be used to teach and develop the philosophy of mission command and build leaders willing and able to take disciplined initiative within their commander's intent. Commanders must have the confidence that all required tasks for a properly functioning organization are being carried out.
How do you develop the philosophy of Mission Command?
Exercise disciplined initiative. Use mission orders. By employing these principles, everyday tasks can be used to teach and develop the philosophy of mission command and build leaders willing and able to take disciplined initiative within their commander's intent.

What are the 5 components of mission command?
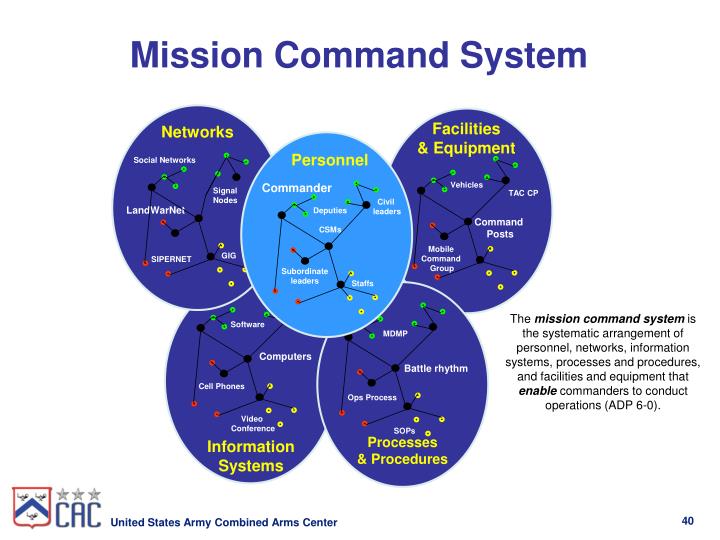
24 Cards in this Set(MC WFF or PHL) Mutual trust and a shared understanding and purpose between commanders and subordinatesMission Command PhilosophyWhat are the 5 Components of the Mission Command System?Personnel, Networks, Information Systems, Processes and Procedures, Facilities and Equipment22 more rows
What are the principles of mission command?
According to Army Doctrine Publication (ADP) 6-0, Mission Command: Command and Control of Army Forces, commanders and subordinates must build a relationship centered upon the seven principles of mission command: Competence, mutual trust, shared understanding, commander's intent, mission orders, disciplined initiative, ...
What is the most important principle of mission command?
Commander's Intent remains a critical component and arguably the most important principle of mission command. Too many times, the staff plans and develops operations without the commander's input.
What are the four elements of command?
The elements of command are authority, responsibility, decision making, and leadership.
What is mission command defined?
Mission command is the conduct of military operations through decentralized execution based upon mission-type orders. - Mission command exploits the human element…, emphasizing trust, force of will, initiative, judgment, and creativity.
What is the purpose of mission command?
Mission command is the exercise of authority and direction by the commander using mission orders to enable disciplined initiative within the commander's intent to empower agile and adaptive leaders in the conduct of unified land operations. of mission command.
Which statement best defines what is essential to the success of mission command?
For mission command to be successful, which statement best describes what is demanded by subordinate leaders? The exercise of disciplined initiative at all echelons. Regardless of when or where employed, the Armed Forces of the United States abide by U.S. values, the standards for the profession of arms, and .
What are the three components to commander's intent?
Commander's Intent It includes the operation's purpose, key tasks, and the conditions that define the end state. It links the mission, concept of opera- tions, and tasks to subordinate units.
What are the two vital components of command?
The two components of command and control are the commander and the command and control system.
What are the elements of proper command?
Correct commands have three important elements: tone, cadence, and snap, and they demand a willing, accurate, and immediate response by everyone in the unit. In contrast to commands, directives are oral orders given by commanders to direct or cause subordinate leaders or a lead element to take action.
What are the four types of command relationships?
There are five Army command relationships: organic, assigned, attached, operational control (OPCON), and tactical control (TACON).
What is the most important component of the command and control system?
The most important element of the C2 system is people-soldiers who assist commanders and exercise control on their behalf. Personnel dedicated to C2 systems include staffs, deputy commanders, and seconds-in-command.
What are the principles of mission command?
They are build cohesive teams through mutual trust, create shared understanding, provide clear commander's intent, exercise disciplined initiative, use mission orders, and accept prudent risk. Much like the CJCS white paper, ADP 6-0 does not ...
What is mission command?
"Mission command is the exercise of authority and direction by the commander using mission orders to enable disciplined initiative within the commander's intent to empower agile and adaptive leaders in the conduct of unified land operations."1
Why is trust important in mission command?
Because trust is the glue that binds mission command, leaders must understand the dimensions of trust and its impact on Soldiers and units. In executing mission command, sustainment commanders must have a broad perspective, understanding, and knowledge of activities throughout the operational area. They must share their vision ...
Who was the first Prussian general to use mission command?
Mission command, as a recognized methodology, traces its roots back to Prussian Generals Johann David von Scharnhorst , August Graf Neidhardt von Gneisenau, and Carl von Clausewitz.4 Following the Prussian defeat at the battles of Jena and Auerstedt, Germany, in 1806, the generals began an in-depth review of Prussian doctrine and, in 1837, updated the Prussian field service regulation.
Who wrote the evolution of command approach?
3 Keith G. Stewart, "The Evolution of Command Approach" (Paper 192), paper presented at the International Command and Control Research and Technology Symposium, Santa Monica, Calif., June 2010, p. 10.
What is mission command?
Army Doctrine Reference Publication 6.0, Mission Command, defines this philosophy as: "The exercise of authority and direction by the commander using mission orders to enable disciplined initiative within the commander's intent to empower agile and adaptive leaders in the conduct of unified land operations." 1
What is mission order in war?
In the warfighting function, mission orders come in the form of Warning Orders, Operation Orders, and Fragmentary Orders. In our scenario, this can be as simple as "go sweep the hangar floor." Again, the level of detail required depends upon the experience level of the subordinate in charge.
What is the commander's intent?
The commander's intent, one of the six guiding principles of mission command, should be concise and to the point. The "conciseness" depends upon your target audience. For example, "go sweep the hangar floor" is enough for a sergeant who has swept many a hangar floor.
Is there another article on mission command?
Yes, another article on mission command. Before you click the "back button," let me explain why embracing the philosophy of mission command is critical to the development of the noncommissioned officer Corps. "Mission command" has been the buzz phrase of choice since its adoption as official Army doctrine in 2012.
Who embodied mission command?
Nelson embodied Mission Command before the Battles of Jena-Auerstadt that led to the thinking that formed into the German concept of Mission Command. “To say that an officer is never, for any object, to alter his orders, is what I cannot comprehend.
What is the purpose of the commander's intent?
The commander’s intent is a clear and concise expression of the purpose of the operation and the desired military end state that supports mission command, provides focus to the staff, and helps subordinate and supporting commanders act to achieve the commander’s desired results without further orders , even when the operation does not unfold as planned. The higher echelon commander’s intent provides the basis for unity of effort throughout the force. Each commander’s intent nests within the commander’s intent two levels up. During planning, the initial commander’s intent drives course of action development. During execution, the commander’s intent establishes the limits within which a subordinate may exercise initiative.
How does training and education help commanders?
Training and education that occurs in both schools and units provides commanders and subordinates with the experiences that allow them to achieve professional competence. Repetitive, realistic, and challenging training creates common experiences that develop the teamwork, trust, and shared understanding that commanders need to exercise mission command and forces need to achieve unity of effort. Leaders supplement institutional and organizational training and education with continuous self-development. Self-development is particularly important for the skills that rely on the art of command, which is further developed by reading and studying the art of war. These skills can also be developed through coursework, simulations and experience.
What does trust do to a commander?
When a commander exercises initiative, trust gives other commanders the same level of confidence to synchronize their actions with those of that commander.
When considering how much risk to accept with a course of action, what are the commanders?
When considering how much risk to accept with a course of action, commanders consider risk to the force and risk to the mission against the perceived benefit. They apply judgment with regard to the importance of an objective, time available, and anticipated cost.
Who was the commander of the Royal Navy Mission Command?
The Battle of Cape St Vincent is his first famous disobediences, using his understanding of the situation, specific the view he has of how the battle is unfolding at the rear of the line and disobeys orders in order to meet the intent of his Commander, Admiral Sir John Jervis.
How does trust affect commanders?
At the lowest tactical levels the ability to trust subordinate formations to execute their collective tasks and battle drills is essential. Building that trust is critical to rapid decision making in high-pressure situations; commanders should be focused more on the problem to be solved when giving guidance than the methods that their subordinates might use. Subordinates must trust that commanders will employ mission orders to the maximum extent possible once they have demonstrated the attributes and competencies expected. Commanders must also trust their colleagues who are commanding adjacent and supporting forces, and they must earn their trust as well. When a commander exercises initiative, trust gives other commanders the same level of confidence to synchronize their actions with those of that commander. Such actions synchronize operations without requiring detailed instructions from higher echelons. Once established and sustained, trust allows each echelon to focus on operations as a whole instead of on the actions of individual subordinates.
What is mission command?
Army Doctrine Publication (ADP) 6-0, Mission Command, defines mission command as "the exercise of authority and direction by the commander using mission orders to enable disciplined initiative within the commander's intent to empower agile and adaptive leaders in the conduct of unified land operations.". For the sake of clarity and ...
Why do sustainment commanders use mission command?
Sustainment commanders use mission command to create a balance between the art of command and the science of control as they integrate the sustainment warfighting function with the other warfighting functions to achieve objectives. Joint doctrine and Army doctrine have different definitions for the term mission command.
How did the JTF commander build a cohesive team?
To overcome this challenge, the JTF commander used a collaborative approach and worked to build a cohesive team by conducting frequent on-site visits, establishing interpersonal relationships, and placing senior-ranking liaison officers (LNOs) in the supported units. The LNOs gave the supported commanders a level of comfort and trust because they showed that the JTF was committed to the team.
How does mission command work?
Mission command works when its guiding principles are followed. The use of mission command principles as a framework facilitated the JTF's ability to build a cohesive team that had a shared understanding of the commander's intent and what needed to be accomplished. Continuous collaboration with unified action partners, the exercise of disciplined initiative, the use of mission orders, and the JTF commander's willingness to accept prudent risk enhanced the JTF's ability to overcome challenges.
Why is trust important in a mission?
Trust is an imperative for accepting calculated risk and for exercising disciplined initiative without fear of reprisal. Effective mission command also requires mission orders that create a shared understanding of the commander's intent and the objectives to be accomplished.
Who is the commander of the 593rd Sustainment Brigade?
The Soldiers of B Company, 113th Special Troops Battalion, form up for an awards ceremony to recognize the high performers of their unit. Col. Douglas McBride, the commander of the 593rd Sustainment Brigade, U.S. Central Command Materiel Retrograde E... (Photo Credit: U.S. Army) VIEW ORIGINAL
Who was the staff and functional lead for base camp closure?
For example the staff and functional lead for base camp closure was the Marine Corps contingent of the JTF. The Air Force led the contracting efforts, while the Navy assumed the lead for customs. Other organizations in the JTF were also tasked based on strengths and functional capabilities.
What does the Civilian Corps Creed say?
The Civilian Corps Creed states, "I will provide stability and continuity during peace and war." Which accurately addresses the deployability of Army Civilians?
Why are army civilians considered combatants?
Because Army Civilians take the same oath as the uniformed Officer members, Army Civilians station in overseas areas during times of war automatically are converted to a combatant status.
Do civilians support the military?
While most Army Civilians historically support military forces at home stations, Army Civilians may also deploy with military forces to sustain theater operations.