
Passive fire protection systems are intended to:
- Contain a fire to the compartment of fire origin
- Slow a fire from spreading from the compartment of fire origin
- Slow the heating of structural members
- Prevent the spread of fire through intentional openings (e.g., doors, HVAC ducts) in fire rated assemblies by the use of a fire rated closure (e.g., fire door, fire damper)
How does passive fire protection work?
Passive fire protection works to slow down or prevent the spread of fire by containing it as best as possible. Slowing down the fire may mean containing it by room, floor, or a combination of both. Passive fire protection creates a safer environment by allowing the building’s occupants to either reach a safe area or evacuate the building entirely.
What is passive fire protection (PFP)?
What is Passive Fire Protection (PFP)
- Responsibility, In the UK, passive fire protection must meet Building Regulations that ensure people can escape safely from a building that will itself not collapse in the event of fire.
- PFP products. ...
- Passive Fire Protection. ...
- PFP products also include: The building envelope, e.g. ...
What are the types of fire protection systems?
What are the different types of fire protection systems?
- Wet Fire Sprinkler Systems. – The wet-pipe system employs automatic sprinklers attached to a piping system connected to a water supply.
- Dry Pipe Systems.
- Special Hazard Fire Protection Systems.
- Dry Chemical Fire Suppression Systems.
- Gaseous Fire Suppression Systems.
- Foam Fire Suppression Systems.
What are fire suppression systems used for?
Fire protection system is one of the most important systems required to be installed in any building or establishment. It is used to detect, control, and safeguard inhabitants in a building or an establishment from fire hazards. These systems help ...

What is an example of a passive fire protection system?
Fire walls are another form of passive fire protection that are used to prevent the spread of fire and the exposure of adjacent equipment to thermal radiation.
What is active and passive fire protection systems?
In basic terms, Active fire protection is about detecting, stopping and escaping fire. Whereas passive fire protection means containing the fire and preventing it from spreading further.
Which of the following are methods of passive fire protection?
Passive Fire Protection productsFire doors.Fire-resisting walls, floors, ceilings, and ducts.Firestopping and fire protection for structural members.Fire-resistant epoxy coatings that can be spray applied.PFP sheet.Fire-protective boxes or wardrobes.More items...•
What are the passive fire elements?
Passive Fire Protection SystemsFire doors.Fire walls.Fire floors.Emergency exit lights.Dampers.Flame shields.Intumescent paint.Mortar coating.More items...•
Why is passive fire protection important?
Passive fire protection measures help to limit the spread of fire and can therefore save lives. If a fire starts, through passive measures, it should be relatively contained in a compartment, allowing those around to escape the area and leave the building.
What is active fire protection system?
An active fire protection system is a dormant system that needs to be activated in the case of a fire to perform its function (activation of water spray systems, deluge systems, sprinkler systems, fire water monitors, and steam rings around flanges).
Is passive fire protection a legal requirement?
PFP provision is required in all buildings, whether domestic or non-domestic.
What is passive fire protection PDF?
The aim for passive fire protection systems is typically to demonstrate in fire testing the ability to maintain the item or the side to be protected at or below either 140°C (for walls, floors and electrical circuits required to have a fire-resistance rating) or ca.
Is a fire door passive fire protection?
So, what role do fire doors play in passive fire protection? An effective passive fire protection product, fire doors fulfil a life-saving role in preventing the spread of smoke and fire for a period of time dependent on their fire classification.
How is passive fire protection expressed?
These are typically expressed in Classes. For example – Fire Resistance in terms of Load Bearing Capacity / Thermal Insulation; Integrity, for a given period of time; and Reaction to Fire, in terms of Euroclass A-F.
What are the different types of fire protection systems?
The Most Common Types of Fire Suppression SystemsWater-Based Fire Suppression Systems. One of the most common types of fire protection systems uses water to knock out fires. ... Chemical Foam Suppression Systems. ... Pneumatic Heat Detection Tube. ... Pressurized Gas System. ... Foam Deluge Systems.
What is a passive fire inspection?
FRS Passive Fire Inspection Reports provide the following: details on the non-compliant items in relation to non-compliant fire rated materials used, unsealed penetrations through fire rated elements, and areas of concern for fire separation.
What are two types of fire protection?
Fire-protection systems fall into two main categories — passive fire protection and active fire protection. Passive fire protection involves the use of building components to control or limit a fire. Walls, floors, and ceilings can be designed and constructed to resist the passage of fire and smoke.
What are the different types of fire protection systems?
The Most Common Types of Fire Suppression SystemsWater-Based Fire Suppression Systems. One of the most common types of fire protection systems uses water to knock out fires. ... Chemical Foam Suppression Systems. ... Pneumatic Heat Detection Tube. ... Pressurized Gas System. ... Foam Deluge Systems.
Is fire hydrant passive or active?
Active fire protection equipment is made up of the following systems: Fire detection and alarm systems . Fire-fighting water supply systems. Fire hydrant system .
How is passive fire protection expressed?
These are typically expressed in Classes. For example – Fire Resistance in terms of Load Bearing Capacity / Thermal Insulation; Integrity, for a given period of time; and Reaction to Fire, in terms of Euroclass A-F.
What is passive fire protection?
Passive fire protection ( PFP) is an integral component of the components of structural fire protection and fire safety in a building. PFP attempts to contain fires or slow the spread, such as by fire-resistant walls, floors, and doors. PFP systems must comply with the associated listing and approval use and compliance in order to provide ...
What is fire prevention?
Fire prevention includes minimizing ignition sources, as well as educating the occupants and operators of the facility, ship or structure concerning operation and maintenance of fire-related systems for correct function, and emergency procedure s including notification for fire service response and emergency evacuation.
What is the best material for fireproofing steel?
There are mainly two types of materials that provide structural fire resistance: intumescent and vermiculite. Vermiculite materials cover the structural steel members in a relatively thick layer. Because of the porous nature of vermiculite, its use is not advisable if there is the possibility of water exposure. Steel corrosion is also difficult to monitor. Intumescent fireproofing is a layer of a material which is applied like paint on the structural steel members. The thickness of this intumescent coating is dependent on the steel section used. Intumescent coatings are applied in a relatively low thickness (usually 350- to 700- micrometer ), have a more aesthetic smooth finish, and help prevent corrosion.
What is a PFP system?
PFP systems are designed to "prevent" the spread of fire and smoke, or heating of structural members, for an intended limited period of time as determined by the local building code and fire codes. Passive fire protection measures such as firestops, fire walls, and fire doors, are tested to determine the fire-resistance rating of the final assembly, which is usually expressed in terms of hours of fire resistance (e.g., ⅓, ¾, 1, 1½, 2, 3, 4 hour). A certification listing provides the limitations of the rating.
What temperature should a fire protection system be tested at?
The aim for fire protection systems is typically demonstrated in fire testing the ability to maintain the item or the side to be protected at or below either 140 °C (for walls, floors and electrical circuits required to have a fire-resistance rating) or ca. 550 °C, which is considered the critical temperature for structural steel, above which it is in jeopardy of losing its strength, leading to collapse. This is based, in most countries, on the basic test standards for walls and floors, such as BS 476: Part 22: 1987, BS EN 1364-1: 1999 & BS EN 1364-2: 1999 or ASTM E119. Smaller components, such as fire dampers, fire doors, etc., follow suit in the main intentions of the basic standard for walls and floors. Fire testing involves live fire exposures upwards of 1100 °C, depending on the fire-resistance rating and duration one is after. More items than just fire exposures are typically required to be tested to ensure the survivability of the system under realistic conditions.
What is the purpose of a fire compartment?
Organization into smaller fire compartments, consisting of one or more rooms or floors, prevents or slows the spread of fire from the room of fire origin to other building spaces, limiting building damage and providing more time to the building occupants for emergency evacuation or to reach an area of refuge.
What is structural fire protection?
Fire protection in a building, offshore facility or a ship is a system that includes: Active fire protection can include manual or automatic fire detection and fire suppression. Passive fire protection includes compartmentalization of the overall building through the use of fire-resistance rated walls and floors.
What is passive fire protection?
Passive fire protection (PFP), also known as Built Fire Protection, is an important component of any fire safety strategy. It plays a vital, and increasingly significant, role in safeguarding people, as well as limiting damage to buildings and their contents from fire and smoke.
What is a comprehensive fire protection plan?
A comprehensive fire protection plan requires the implementation of both Active Fire Protection and Passive Fire Protection. While Passive Fire Protection is, as described above, a series of built-in fire resistant features, Active Fire Protection is essentially a collection of manual or automatic elements that need intervention to work – for example; fire detection and alarms, sprinklers (triggered by a sensor) and extinguishers (manual), gaseous suppression, door release mechanisms, dynamic fire shutters, etc.
What temperature does epoxy degrade?
Epoxy intumescent and subliming materials begin to degrade at temperatures above 80 degrees C , limiting their use on very hot surfaces. However, new dual layer systems are now available using phenolic foam bonded directly to the hot surface to provide an insulating layer, with a second layer of material bonded to it.
What is firestopping best practice?
It is imperative that any gaps in new installations from refurbishments also have an appropriate firestop in place, as building fire protection systems could be compromised if not carried out.
What does PFP mean in firefighting?
With AFP you are taking action to out a fire. PFP stops that fire from spreading. Their combined result means that people inside a building are alerted of a fire, safely containing that fire and allowing people to suppress the fire and/or evacuate.
What is a PFP sheet?
PFP sheet. Fire-protective boxes or wardrobes. Protection for vital equipment such as first-aid boxes, oil or gas tanks, or other volatile sites to prevent the risk of explosion. And also, as supplied by the The Association for Specialist Fire Protection (ASFP): Fire protection to the structural frame of the building.
What is a firewall?
A firewall is a fireproof barrier used to prevent the spread of fire between or through buildings or structures.
What is the Purpose of Passive Fire Protection?
Passive fire protection is all about limiting the reach of the dangers present when a fire breaks out. Namely preventing the spread of heat, flames, and smoke. When you consider that the last factor, smoke, accounts for the vast majority of fire deaths, it is easy to see why any system that stops its spread is particularly valuable.
What are fire doors?
Fire doors are thick, sturdy, and heat resistant. They act by keeping a fire compartmentalized. By limiting fire (and smoke) to one area, they effectively contain a fire. This has three key benefits:
Is a contained fire a fire?
A contained fire is easier to deal with and allows those residing in a home or business to escape to safety. It also limits damage and makes suppression easier. Today we will look at passive fire protection, what it is, and the benefits to your home or business.
Passive versus Active Systems
Passive fire protection (PFP) materials are typically built right into a building and include things like using fire retardant materials like cinder blocks in place of wood to build the walls of a building. Builders can also use materials like fire dampers, fire doors, wall assemblies, and fire-resistant coatings.
So Which System Should I Focus On?
The truth is that both systems are equally crucial for fire protection and deserve equal attention. If you can use passive fire protection materials during the construction of your commercial building, you should. Using fire retardant materials during the construction can save you a lot of money later should a fire break out in your building.
Thanks for making this project a success
On behalf of Executive Construction Inc. we would like to thank you and your team for all of their efforts in making the Zurich North America Headquarters project at 1229 Zurich Way a huge success. Zurich had their final move in last weekend and are now 100% occupied. You had a great crew out here with Chris S. as your lead technician.
What is Active Fire Protection (AFP)?
Active fire protection systems are those that require some action for them to be effective against a fire. When most people read this statement, they falsely believe that only manual actions (such as dowsing flames with a fire extinguisher) count as active fire protection.
What happens if one sprinkler system fails?
What is more, if one system fails, (frozen sprinkler pipes for instance) then a fire could spread uncontrollably without the help of its counterpart. You should always ensure both types of fire protection are in place and up to date with the latest codes of practice to adequately protect both your building and employees.
Why do you need both active and passive fire protection?
Why You Must Have Both. If the worst happens and a fire does break out in your building, both active and passive fire protection systems will activate . Active systems such as alarms, sprinklers and manual firefighting will begin immediately after detection. Passive protection systems will stop the fire’s spread and keep it contained ...
What are the elements of passive fire protection?
The key elements of passive fire protection systems are fire-resistant walls, fire-resistant glass, and heavy-duty fire doors . However, other assets can sometimes be passively protected through spray-applied fireproofing. These systems safeguard buildings by ensuring that the fire burns out quickly due to a lack of available fuel.
Why do buildings need fire protection?
Every building needs to have adequate fire protection in place to ensure the safety of the lives of employees and to maintain the integrity of business assets. When people envision fire protection, they think of sprinkler systems and fire extinguishers.
What happens when active systems kick in?
Active systems usually kick in once the occupants (and computerized systems) in the building are made aware that there is a fire, which allows people to evacuate the building while the active systems keep the fire at bay until members of the fire service arrive.
Why are fire doors important?
Items such as fire doors also play a crucial role in plotting a fire’s route through a building, thereby giving fire crews a better chance of putting it out quickly.
What is an active fire protection system?
Active fire protection measures , on the other hand, provide some way for people to respond to and actively stop a fire. Some active fire systems, like sprinkler systems, fire alarms or smoke detectors are automatic. Others, like fire extinguishers and fire blankets, are manual. You can even class firefighters as an active fire protection measure. Active fire protection systems can be broken down into 3 categories:
What are the two types of fire protection?
When you’re thinking about your businesses fire protection measures, it helps to divide them into two categories: active and passive fire protection. Both types of fire protection are essential for running a fire safety compliant business. The two systems work together to suppress and stop fires.
What is the definition of fire detector?
Detection – Smoke sensors, fire alarms etc. Anything that can detect heat, smoke or flames in a location and send a signal to alarms throughout a building falls into this category.
What is the purpose of ventilating a fire?
Ventilation – This type of active fire protection focuses on keeping escape routes free of smoke and other toxic fumes. Fire resistant emergency fans would fall into this category.
Can you use passive fire protection?
The short answer to this question is no. Both are essential for minimising the risks fire poses to your business and it’s only through effectively deploying both active and passive fire protection measures that you stand the best chance of dealing with a fire on your premises.
Passive and active fire protection
A balanced and systematic approach to building fire safety includes both active and passive fire protection systems.
Model codes and certification standards
Code compliance should be the responsibility of all stakeholders involved with building design, construction, operation and maintenance. Compliance does not rest solely with a plans examiner or building official.
Code requirements for special inspections and audits
The addition of model code requirements for special inspection of passive fire protection systems and components has changed the passive fire protection industry over the past several model code cycles.
Standards for fire stop system inspection practices
Standards have been developed to provide guidance for conducting on-site inspections of these passive fire protection systems, including:
Education and training
The development of new model code requirements, focused on proper firestop system specification, system certification (listing), competent installation and inspection for verification of code compliance, has increased the need for training, education and certification programs for designers, contractors and code authorities.
Plan review and field inspections
The importance of a thorough plan review is another critical step to help ensure code compliance for occupant fire and life safety.
Qualifications for contractors and manufacturers
Typically, unqualified contractors are prohibited from installing essential life safety systems such as fire sprinkler systems, fire alarm systems or building electrical systems because contractors/installers must be trained and competent in their trade.
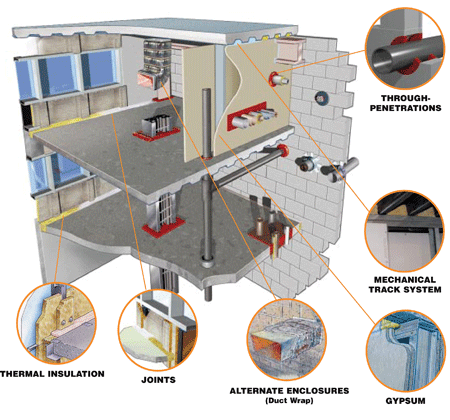
Overview
Passive fire protection (PFP) is components or systems of a building or structure that slows or impedes the spread of the effects of fire or smoke without system activation, and usually without movement. Examples of passive systems include floor-ceilings and roofs, fire doors, windows, and wall assemblies, fire-resistant coatings, and other fire and smoke control assemblies. Passive fire protection …
Main characteristics
Passive fire protection systems are intended to:
• Contain a fire to the compartment of fire origin
• Slow a fire from spreading from the compartment of fire origin
• Slow the heating of structural members
Examples
• Fire-resistance rated walls
• Firewalls not only have a rating, they are also designed to sub-divide buildings such that if collapse occurs on one side, this will not affect the other side. They can also be used to eliminate the need for sprinklers, as a trade-off.
Regulations
Examples of testing that underlies certification listing:
• Europe: BS EN 1364
• Netherlands: NEN 6068
• Germany: DIN 4102
• United Kingdom: BS 476
Prescriptive versus Listed
Prescriptive systems have been tested and verified by governmental authorities including DIBt, the British Standards Institute (BSI) and the National Research Council's Institute for Research in Construction. These organisations publish wall and floor assembly details in codes and standards that are used with generic standardised components to achieve the quantified fire-resistance ratings. Germany and the UK publish prescriptive systems in standards such as DIN4102 Part 4 …
Countries with optional certification
Fire tests in the UK are reported in the form of test results but building authorities do not require written proof that the materials that have been installed on site are actually identical to the materials and products that were used in the test. The test report is often interpreted by engineers as the test results are not communicated in uniformly structured listings. In the UK, and other countries which do not require certification, the proof that the manufacturer has not substituted o…
See also
• Pressurisation ductwork
• Smoke exhaust ductwork
• Combustibility and flammability
• Mortar (firestop)
External links
• Association for Specialist Fire Protection
• Burning down the house (a trial by fire)
• European Association for Passive Fire Protection
• AIA Approved Fire Rated Glass & Glazing Course
What Is Passive Fire Protection?
How Does Passive Fire Protection Work?
- Passive fire protection works by: 1. Using fire-resistant walls and floors to limit the spread of fire, heat, and smoke by containing it in a single compartment in its area of origin 2. Protecting escape routes and providing vital escape time for occupants 3. Protecting a building’s critical structural members 4. Protecting a building’s assets Passive fire protection works in conjunction with activ…
Whose Responsibility Is Passive Fire Protection?
- In the UK, passive fire protection must meet Building Regulations that ensure people can escape safely from a building that will itself not collapse in the event of fire. Legislation places responsibility on building owners, managers, occupiers, and designers, to carry out regular fire risk assessments, which should include evaluation of the PFP provided. Experts advise that the …
Firestopping
- Firestopping best practice should always be followed from the start of any buildingdesignand its construction, as explained here in our nine-step guide to firestopping in new buildings. It is imperative that any gaps in new installations from refurbishments also have an appropriate firestopin place, as buildingfire protection systemscould be compromised if not carried out. The …
Fire Protection Surveys
- A Fire Protection Survey takes the findings of a Fire Risk Assessment to and develops a plan of works required throughout the property, protecting residents or employees in a building by removing potential hazards, making the escape routes clearer and proving equipment where needed, e.g. fire hoses and extinguishers. Particular attention should be paid to the safety of chil…
Passive Fire Protection Products
- The demands placed on passive fire protection have become increasingly complex in recent years, partly because of pressures to improve thermal insulation and reduce energy costs. PFP products that are installed in a building to improve its fire safety include: 1. Fire doors 2. Fire-resisting walls, floors, ceilings, and ducts 3. Firestopping and fire protection for structural membe…
Why Is Accreditation Important For The Products used?
- Independent, third-party accredited products will give the user a vital assurance that key standards are being met. Moreover, using an accredited fire protection company also guarantees that installing these products will be done to the required standard by appropriately trained staff, and third-party inspections will take place to verify that. A further benefit is that the user will be a…
The Difference Between Passive and Active Fire Protection
- A comprehensive fire protection plan requires the implementation of both Active Fire Protection and Passive Fire Protection. While Passive Fire Protection is, as described above, a series of built-in fire resistant features, Active Fire Protection is essentially a collection of manual or automatic elements that need intervention to work – for example; fire detection and alarms, sprin…
Active Fire Protection
Passive Fire Protection
- Passive fire protection is a little different. Unlike active fire protection, passive systems don’t require a response or motion to be effective. In simple terms? They are an inherent feature that requires no monitoring or response to reduce the danger of fire. They are always present, and they don’t need to be activatedto perform their role. Want ...
Fire Doors
- Fire doors are thick, sturdy, and heat resistant. They act by keeping a fire compartmentalized. By limiting fire (and smoke) to one area, they effectively contain a fire. This has three key benefits: 1. Reduces the immediate risk to people. 2. Buys time for people to get to safety. 3. Keeps a fire in a localized area, making it easier to suppress. All of the above is only beneficial if a fire door is cor…
Fire Damping
- Air conditioning ducts make heat transfer easy. After all, what works for cool air will also work for warm air, right? Damping systems close when they go beyond a certain temperature, preventing heat from traveling long distances to other rooms or even other floors!
Sealing
- Smoke is as dangerous as flames. It makes sense to limit its spread. Sealing is an excellent way to achieve this. If smoke is contained, it presents less of a risk.
Training
- You might not realize this, but passive fire protection isn’t allabout physical systems. What do we mean? How people behave and respond to a fire is just as effective as any fire door. Teaching people how to limit the risk and reduce fire spread is paramount to continued safety in any building. Consider consulting a local fire protection firm to see if they offer courses or briefings i…
Planning
- Anything that reduces the risk of fire spreading is a good thing. But the benefits can be limited if you are unsure as to what needs to be done. It is no use fitting a fire door between two rooms when heat can easily spread through internal wiring, or smoke can make its way through the grate above the door. The best solution to ensure complete fire protection is to recruit the help of an e…