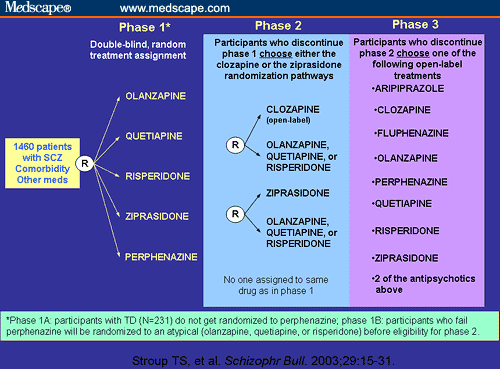
Summary of clinical trial phases
| Phase | Primary goal |
| Phase I | Testing of drug on healthy volunteers fo ... |
| Phase II | Testing of drug on patients to assess ef ... |
| Phase III | Testing of drug on patients to assess ef ... |
What are the 4 stages of clinical trials?
Clinical trials of a new precision ... mild or subjective-cognitive impairment—what Bredesen describes as essentially the first two of a four-stage disease—underwent 5-24 weeks of the MEND Protocol. “The therapeutic approach used was programmatic ...
What are the stages of a clinical trial?
Phases of Clinical Trials Preclinical Trial (Usually done on animals to determine the drug is safe enough for human testing) Phase I (Determine Pharmacological actions and Tolerability*) Phase II (Evaluate Safety and Efficacy) Phase III (Evaluate Effectiveness** and risk-benefit ratio) Phase IV (Monitor long term effects and effectiveness)
What are the 4 phases of the therapeutic process?
- Engagement. The client and therapist begin to establish the therapeutic relationship. ...
- Assessment. The therapist works to learn more about the client's background, including early memories and family dynamics. ...
- Insight. The therapist offers an interpretation of the client’s situation. ...
- Reorientation. ...
How long do clinical trial phases take?
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides an estimate for each clinical trial phase: Phase 1 trials, which examine the safety and dosage of a treatment, typically last several months. Phase 2 trials, which examine the efficacy and side effects of a treatment, typically last several months to two years.
What is Phase 4 of a drug trial?
In a phase 4 trial, any rare or long-term effects of the drug can be observed in a much larger population of patients and over a much longer period of time. If safety surveillance does indeed reveal concerns about the drug, it may be withdrawn from the market and no longer made available on prescription.
How long is a Phase 4 clinical trial?
two yearsSince phase IV trials aim to study how a treatment will perform in the long run, it shouldn't come as a surprise that they're quite long. Typically they're conducted for a minimum of two years.
What are Phase 5 clinical trials?
Phase 5 Clinical Trial means a post-registration clinical trial that is not required as a condition to, or for the maintenance of, any Marketing Approval or Pricing and/or Reimbursement Approval for a Licensed Product. Phase 5 Clinical Trials are commonly referred to as “post-marketing clinical trials”.
What are Phase 3 and 4 clinical trials?
Phase 3 is the final phase before a treatment receives FDA approval. Following FDA approval, a treatment goes through Phase 4. This phase involves the largest group of participants. It can last for several years as researchers continue to monitor the efficacy and safety of the treatment.
What is Phase 4 FDA approval?
Phase 4 Trials. This phase occurs post-marketing, meaning after a drug has been shown to work and the treatment has received FDA approval. Studies done at this stage are designed to evaluate the long-term risks and benefits of a medication.
What are the 4 stages of drug development?
Information ForStep 1: Discovery and Development.Step 2: Preclinical Research.Step 3: Clinical Research.Step 4: FDA Drug Review.Step 5: FDA Post-Market Drug Safety Monitoring.
What is a Phase 3 study?
A study that tests the safety and how well a new treatment works compared with a standard treatment. For example, phase III clinical trials may compare which group of patients has better survival rates or fewer side effects.
Why do most clinical trials never go to Stage 3?
Hwang et al. [58] noted that 22% of the failed phase 3 studies they examined failed due to lack of funding. The costs required to complete the entire development process from discovery to bringing a drug to market vary, and so do estimates of these costs; however, they have been reported in excess of $2.5 billion [34].
How long do Phase 3 clinical trials last?
between one and four yearsPhase 3 trials, which examine the efficacy of a treatment and monitor adverse reactions, typically last between one and four years.
What is a Phase 3b clinical trial?
Phase 3b Clinical Trial means a human clinical trial of a product that is initiated after the NDA is filed, but before such product obtains Regulatory Approval, the goal of which trial is to provide additional data for marketing support and the launch of such product in the Territory.
What are the 4 phases of clinical trials UK?
What is a clinical trial?Phase I. Trials aim to test the safety of a new treatment. ... Phase II. Trials test the new treatment. ... Phase III. Trials involve larger numbers of patients. ... Phase IV. Trials are done after a drug has been approved.
What phase of clinical trials is the Covid vaccine in?
A Global Phase III Clinical Trial of Recombinant COVID- 19 Vaccine (Sf9 Cells)Condition or diseaseIntervention/treatmentPhaseCOVID-19Biological: Recombinant COVID-19 vaccine (Sf9 cells) Other: Placebo controlPhase 3May 27, 2021
What is phase 4 of clinical trials?
First of all, once preclinical trials (on animals in a laboratory) have produced satisfying results, the clinical trials can begin. These clinical trials are conducted in 4 phases, here is a reminder of the first 3:
What is pharmacovigilance (PV)?
Pharmacovigilance lasts the whole duration of the drug's existence. It begins at the time when marketing of the latter occurs and ends during its withdrawal from the market. It is known as post-AMM (marketing authorisation). The main objective of PV is determining rare or long-term undesirable effects.
What event leads to the development of pharmacovigilance?
In the 1950s, a molecule known as " thalidomide " arrives on the market. This drug is used as a non-barbiturate sedative. Showing few side effects during the tests carried out at the time, thalidomide become the sedative molecule of choice.
You will also like
What are the dangers associated with the over-the-counter sale of certain medicines?
How long does phase 3 of a clinical trial last?
Trials in this phase can last for several years. The purpose of phase III is to evaluate how the new medication works in comparison to existing medications for the same condition.
How many people are in phase 1 of a clinical trial?
During phase I of a clinical trial, investigators spend several months looking at the effects of the medication on about 20 to 80 people who have no underlying health conditions. This phase aims to figure out the highest dose humans can take without serious side effects.
Why do we need a phase 3 trial?
This helps to eliminate bias when interpreting results. The FDA usually requires a phase III clinical trial before approving a new medication. Due to the larger number of participants and longer duration or phase III, rare and long-term side effects are more likely to show up during this phase. If investigators demonstrate ...
Why do investigators use a very small dose of medication?
Investigators use a very small dose of medication to make sure it isn’t harmful to humans before they start using it in higher doses for later phases . If the medication acts differently than expected, the investigators will likely to do some additional preclinical research before deciding whether to continue the trial.
What do investigators do before conducting clinical trials?
Before doing a clinical trial, investigators conduct preclinical research using human cell cultures or animal models. For example, they might test whether a new medication is toxic to a small sample of human cells in a laboratory.
What happens in phase 2?
What happens in phase II? Phase II of a clinical trial involves several hundred participants who are living with the condition that the new medication is meant to treat. They’re usually given the same dose that was found to be safe in the previous phase.
How long do investigators monitor participants?
Investigators monitor participants for several months or years to see how effective the medication is and to gather more information about any side effects it might cause. While phase II involves more participants than earlier phases, it’s still not large enough to demonstrate the overall safety of a medication.
