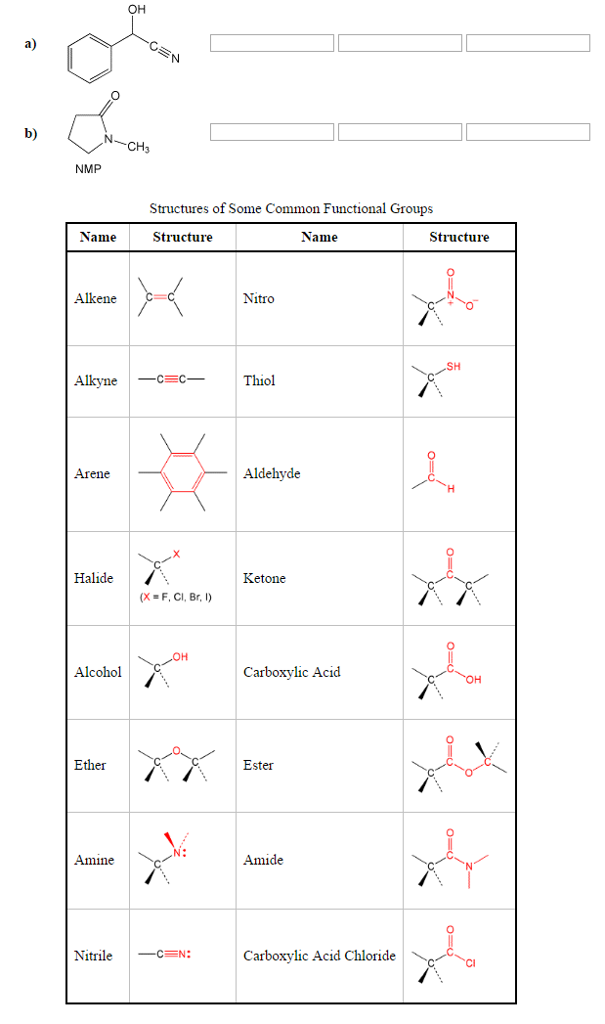
3. Oxygen-Containing Functional Groups
| Functional Group and Formula | Suffix | Example |
| Alcohol, R-OH | -ol | Methanol |
| Ketone, R- (CO)-R’ | -one | Butanone |
| Aldehyde, R-CHO | -al | Ethanal (acetaldehyde) |
| Acyl Halide, R- (CO)-X | -oyl halide | Ethanoyl Chloride (acetyl chloride) |
Full Answer
What functional groups are found in all?
There are 7 important functional groups in the chemistry of life: Hydroxyl, Carbonyl, Carboxyl, Amino, Thiol, Phosphate, and aldehyde groups.
What do all functional groups have in common?
functional groups is used to describe the pieces or parts of a drug molecule. The key point here is that each individual group within a drug molecule can serve to provide one or more specifi c roles, tasks, or functions. As evidenced by functional groups A and B, the same functional group—a carboxylic acid in this case—can serve different roles
What are functional groups and their properties?
Functional Groups and Their Properties. What is a functional group? • A structural arrangement of atoms which determines the physical and chemical properties in a given molecule • Organic molecules are grouped into organic families based on the functional groups present
What are the characteristics of functional groups?
Key Takeaways: Functional Groups
- In organic chemistry, a functional group is a set of atoms within molecules that function together to react in predictable ways.
- Functional groups undergo the same chemical reactions no matter how large or small the molecule is.
- Covalent bonds link the atoms within functional groups and connect them to the rest of the molecule.

What are the examples of functional groups?
Examples of functional groups include the hydroxyl group, ketone group, amine group, and ether group.Hydroxyl Functional Group. ... Aldehyde Functional Group. ... Ketone Functional Group. ... Amine Functional Group. ... Amino Functional Group. ... Amide Functional Group. ... Ether Functional Group. ... Ester Functional Group.More items...•
What are the 5 common functional groups?
Hydroxyl, sulfhydryl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino and phosphate groups.
What are the 7 most common functional groups?
Properties of Functional Groups Some of the important functional groups in biological molecules include: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl groups. These groups play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
What are functional groups 3 examples?
An atom/group of atoms joined in a specific manner which is responsible for the characteristics chemical properties of the organic compounds is called a functional group. Examples are hydroxyl group (-OH), aldehyde group(-CHO), Ketonic group (-CO-),Carboxlic acid group(-COOH) etc. Was this answer helpful?
What are functional groups in chemistry?
A functional group is defined as an atom or group of atoms within a molecule that has similar chemical properties whenever it appears in various compounds. Even if other parts of the molecule are quite different, certain functional groups tend to react in certain ways.
What are called functional groups?
A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds.
What are the four functional groups?
An atom/group of atoms joined in a specific manner which is responsible for the characteristics chemical properties of the organic compounds is called a functional group. Examples are hydroxyl group (-OH), aldehyde group(-CHO), Ketonic group (-CO-),Carboxlic acid group(-COOH) etc.
Is alcohol a functional group?
An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl (OH) functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom. Because OH is the functional group of all alcohols, we often represent alcohols by the general formula ROH, where R is an alkyl group.
How do you identify functional groups?
1:446:0910.1 Identifying functional groups (SL) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis molecule contains an alkyne a functional group if we look at the condensed structural formulaMoreThis molecule contains an alkyne a functional group if we look at the condensed structural formula we can see that we have one carbon atom that is not bonded to any hydrogen atoms.
How do you write a functional group?
1:012:4210.1 Functional groups (SL) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe functional group is called the hydroxyl group an example is methanol the carboxylic acids have aMoreThe functional group is called the hydroxyl group an example is methanol the carboxylic acids have a carboxyl group an example is propanoic acid the aldehydes and the ketones.
Is alkane a functional group?
Alkane sequences form the inert framework of most organic compounds. For this reason, alkanes are not formally considered a functional group. When a hydrocarbon chain is connected as a substituent to a more fundamental structural unit, it is termed an alkyl group.
What are functional groups of organic compounds?
A functional group is a group of atoms or bonds within a substance that is responsible for the substance's distinctive chemical reactions. The halo group, alcohol group, aldehyde group, ketone group, carboxylic acid group, alkene group, alkyne group are some of the most important functional groups in organic chemistry.
What are functional groups?
Functional groups. Large biological molecules are generally composed of a carbon skeleton (made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms) and some other atoms, including oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Often, these additional atoms appear in the context of functional groups. Functional groups are chemical motifs, or patterns of atoms, ...
What are some examples of less hydrophilic groups?
An example of a less hydrophilic group is the carbonyl group (C=O), an uncharged but polar (contains partial positive and partial negative charges) functional group. Carbonyls are found in many different biological molecules, including proteins, peptides, and carbohydrates.
What are the two types of fuels that are made up of carbon and hydrogen?
Hydrocarbons, made up entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms, make wonderful combustion fuels (such fuels include propane, butane, and the bulk of commercial gasoline).
Which group is hydrophilic?
One example of a strongly hydrophilic group is the carboxyl group (COOH), which can act as an acid and lose a proton to form a negatively-charged carboxylate ion (COO ). Carboxyl groups are commonly found in amino acids, fatty acids, and other biomolecules. An example of a less hydrophilic group is the carbonyl group (C=O), an uncharged but polar (contains partial positive and partial negative charges) functional group. Carbonyls are found in many different biological molecules, including proteins, peptides, and carbohydrates.
Is a charged group positive or negative?
more. A charged group is either positive or negative (gains or loses an electron) and a polar group contains atoms that have a difference in electronegativity. Comment on Citrus's post “A charged group is either...”. Button opens signup modal.
Is a carboxyl group acidic?
Charged (forms R-COO) at the pH of most biological systems. Since carboxyl groups can release H into solution, they are considered acidic.
Chemistry Glossary Definition of Functional Groups
Benzyl acetate has an ester group (red). Wikimedia Commons/Public Domain
Functional Groups Definition
A functional group or moiety is a specific group of atoms within a molecule that is responsible for characteristic chemical reactions of that molecule. No matter what size a molecule is, a functional group participates in chemical reactions in a predictable manner.
Functional Group Examples
Examples of common functional groups include alcohol (-OH), aldehyde (-COH), and nitrile (-CN).
Nomenclature
The naming convention for moieties describes whether it is saturated or unsaturated and whether it contains single, double, or triple bonds.
What is functional group?
Key Takeaways: Functional Groups. In organic chemistry, a functional group is a set of atoms within molecules that function together to react in predictable ways. Functional groups undergo the same chemical reactions no matter how large or small the molecule is. Covalent bonds link the atoms within functional groups and connect them to the rest ...
What are functional groups in chemistry?
Functional groups are collections of atoms in organic chemistry molecules that contribute to the chemical characteristics of the molecule and participate in predictable reactions. These groups of atoms contain oxygen or nitrogen or sometimes sulfur attached to a hydrocarbon skeleton. Organic chemists can tell a lot about a molecule by ...
What are some examples of covalent bonds?
Examples of functional groups include the hydroxyl group, ketone group, amine group, and ether group.
What is the structure of a hydroxyl group?
Also known as the alcohol group or hydroxy group, the hydroxyl group is an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom. Hydroxy groups link biological molecules together via dehydration reactions.
What is an ether group?
An ether group consists of an oxygen atom forming a bridge between two different parts of a molecule.
How can organic chemists tell a lot about a molecule?
Organic chemists can tell a lot about a molecule by the functional groups that make up a molecule. Any serious student should memorize as many as they can. This short list contains many of the most common organic functional groups. It should be noted that the R in each structure is a wildcard notation for the rest of the molecule's atoms.
What are some examples of compounds that contain hydroxyl groups?
Examples of common compounds containing hydroxyl groups are alcohols and carboxylic acids.
Table of Contents
What Are Functional Groups?
- Two molecules having different sizes but the same functional groups will take part in chemical reactions that are similar or exactly the same. The presence of a functional group in a molecule implies that the behaviour and the chemical reactions of the molecule in question can be predicted in a systematic fashion. The process of chemical synthesis, in which chemical reactio…
Nomenclature of Common Functional Groups
- The common functional groups, along with the prefix and the suffix which must be used in their nomenclature is provided in this subsection. Additionally, a brief description of the constitution of each of these groups is also provided.