What is the significance of stains in microscopy?
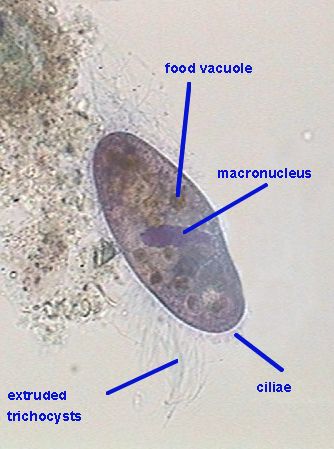
Jun 24, 2020 · Microscope cell staining is a technique used to enable better visualization of cells and cell parts under the microscope. By using different stains, a nucleus or a cell wall are easier to view. Most stains can be used on non-living (fixed) cells, while only some types of stain can be used on living cells. Also Know, what are stains used for in biology?
Why do use stain for light microscopy?
Nov 01, 2021 · Staining is a technique used in microscopy to enhance contrast in a microscopic image. Stains and dyes are frequently used to highlight structures in microbes for viewing, often with the aid of different microscopes. Sullivan ⭐ Answeregy Expert Preparation of Different Stains | Microscopy The stain is ready for use.
Why is stain used to study specimens under the microscope?
4 rows · The technician decides to make a Gram stain of the specimen. This technique is commonly used as ...
What is importance does staining serve in microscopy?
The most basic reason that cells are stained is to enhance visualization of the cell or certain cellular components under a microscope. Cells may also be stained to highlight metabolic processes or to differentiate between live and dead cells in …

What are the purposes of staining bacteria?
Introduction: Gram staining is a method commonly used to determine the chemical make up of the cell wall of bacteria. The cell wall can stain either positive or negative, depending on its chemistry. Knowing the chemical make up makes it easier to manipulate the bacteria for various purposes.
What are the different stains used in microscopy?
A variety of staining techniques can be used with light microscopy, including Gram staining, acid-fast staining, capsule staining, endospore staining, and flagella staining.
What are stains used for in biology?
Biological stains are used for the medical and biological industries to aid in detection of structures within tissues. This can include the detection of abnormalities, but is not limited to that. The stains are used to define and examine cell populations within the tissues, to mark cells, or to flag proteins.
What is the purpose of the stain?
The purpose of staining is to increase the contrast between the organisms and the background so that they are more readily seen in the light microscope.May 26, 2021
Why are stains used in light microscopy quizlet?
Why are stains used in light microscopy? Stains increase contrast as different components take up stains to different degrees. This allows components to become visible so they can be identified. They can also be used for differential staining.
What is stain in biology class 12?
Staining is an auxiliary technique used in microscopy to enhance contrast in the microscopic image. Stains and dyes are frequently used in biology and medicine to highlight structures in biological tissues for viewing, often with the aid of different microscopes.
What is a stain in science?
staining A technique in which cells or thin sections of biological tissue that are normally transparent are immersed in one or more coloured dyes (stains) to make them more clearly visible through a microscope. Staining heightens the contrast between the various cell or tissue components.
Which stain is used to stain chloroplast?
Visualizing the Integrity of Chloroplast Envelope by Rhodamine and Nile Red Staining. Chloroplasts are essential organelles in plant cells with many important functions. Chloroplasts isolated by Percoll density gradient centrifugation are widely used in the study of chloroplasts.Apr 26, 2021
How do stains work in microbiology?
In preparation for staining, a small sample of microorganisms is placed on a slide and permitted to air dry. The smear is heat fixed by quickly passing it over a flame. Heat fixing kills the organisms, makes them adhere to the slide, and permits them to accept the stain.
What are the advantages of using stains in microbiology?
The Advantages of Stained BacteriaBetter Visualization. Bacterial organisms are so small that most of them are visible only under a microscope with a magnification power of 1000X. ... Identification and Classification. ... Detection of Viability. ... Identification of Cellular Structures.Apr 25, 2017
Why is simple staining important?
Simple staining allows one to observe the morphology and arrangement of the bacterial cells. Morphology refers to “form” or shape. We can use terms like spiral, bacilli (rod shaped), and cocci (spherical) to describe cell shapes.
What is the purpose of stain quizlet?
What is the purpose of Staining? to make the bacteria, which are otherwise nearly transparent, visible.
What are the two types of staining techniques used in clinical settings?
Differential staining techniques commonly used in clinical settings include Gram staining, acid-fast staining, endospore staining, flagella staining, and capsule staining.
What is staining used for?
In addition to fixation, staining is almost always applied to color certain features of a specimen before examining it under a light microscope. Stains, or dyes, contain salts made up of a positive ion and a negative ion.
Why is darkfield microscopy used?
Since fixation and staining would kill the cells, darkfield microscopy is typically used for observing live specimens and viewing their movements. However, other approaches can also be used. For example, the cells can be thickened with silver particles (in tissue sections) and observed using a light microscope.
What color is a positive stain?
Because cells typically have negatively charged cell walls, the positive chromophores in basic dyes tend to stick to the cell walls, making them positive stains. Thus, commonly used basic dyes such as basic fuchsin, crystal violet, malachite green, methylene blue, and safranin typically serve as positive stains.
What is the first step in the Gram stain process?
The steps of the Gram stain procedure are listed below and illustrated in Table 1. First, crystal violet , a primary stain, is applied to a heat-fixed smear, giving all of the cells a purple color. Next, Gram’s iodine, a mordant, is added.
Why do you use a single dye in simple staining?
In simple staining, a single dye is used to emphasize particular structures in the specimen. A simple stain will generally make all of the organisms in a sample appear to be the same color, even if the sample contains more than one type of organism.
What chemical can denature proteins?
Chemical agents such as acetic acid, ethanol, methanol, formaldehyde (formalin), and glutaraldehyde can denature proteins, stop biochemical reactions, and stabilize cell structures in tissue samples (Figure 1c). Figure 1. (a) A specimen can be heat-fixed by using a slide warmer like this one.
Working With Children Who Struggle With Reduced Dexterity
The definition of dexterity is defined as the ability and ease of using one’s fine motor skills to grasp or pinch objects. Tasks such as pinching require tiny muscles in the hand to be strengthened. These small muscles often strengthen after larger muscles, those that...
How to Become an Archeologist
Maybe you’re exploring a full-time career option or maybe you’re just really into archaeology, you're interested in becoming a professional archaeologist. What Do Archeologists Do? Anthropologists and archeologists study the origin, development, and behavior of...
How To: DIY Science Lab At Home
A DIY science lab at home is a wonderful way to foster science curiosity — creating that desire to learn and experience science in your kiddos! Building a science lab at home can be a bit of an intimidating thought, though. With the help of the tips you’ll find in...
CAREER PROFILE: ZOOKEEPER
Do you have a deep love for animals, a deep concern for the care of animals? Maybe you are considering a career as a zookeeper. This article will provide information about the requirements to become a zookeeper, what the job entails, and the steps you can take to...
Why do we use stains in microscopy?
Stains are used in microscopy to help view bacteria, which are normally colorless and hard to see in their natural state even with a microscope.
What is eosin y stain?
Eosin Y. Eosin Y Stain is a reversible, fluorescent red, acidic dye, commonly used in hospital histology labs. Eosin's most important medical uses are in blood and bone-marrow testing, including the PAP smear. It can also test for protein in plant, animal and blood specimens.
Why is histological staining important?
Histological staining and examination hold a very high clinical significance in medical diagnosis and treatment in almost every field of medicine. Histological examination is a gold standard for the diagnosis of many pathological diseases, for which staining is an essential component.
Why is an electron microscope useful?
The electron microscope is useful for viewing intracellular components not visible via light microscopy, which aids in clarifying the biology of abnormal tissues and cells. Electron microscopy commonly magnifies 100 to 300 times more than the highest magnification of light microscopy.[20] .
What is the difference between eosin and hematoxylin?
For example, one of the most common stains, Hematoxylin, is a basic dye that stains proteins a blue color, while Eosin stains proteins a pink color.
What is neutral buffered formalin?
Although several specialized fixatives are available, Neutral Buffered Formalin is a common choice for this step. The fixation step is vital to the rest of the histologic staining procedure because by retaining the chemical composition of the tissue, the sample is hardened and makes the sectioning phase easier.
What color is hematoxylin?
The hematoxylin is a basic dye that stains acidic structures. The resulting color is a purple/blue hue, and structures that are targeted with this dye are named Basophilic. Basophilic structures include DNA in cell nuclei, RNA in ribosomes, and the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the color of eosin?
Eosin is a counterstain done after hematoxylin and is an acidic dye that targets basic structures. The resulting color is a pink/red hue , and structures that attract eosin are called eosinophilic.[1] . The cytoplasm is an example of an eosinophilic structure. Gram Stain.
What is the purpose of adding ethanol to a sample?
Dehydration: The addition of ethanol accomplishes the dehydration of a sample. It removed water from the sample and further hardens the tissue for eventual light microscopy. After ethanol is applied, and following the completion of tissue dehydration, xylene is used to remove the ethanol. [1] .