Myofilament - Types of Myofilaments
- Thick filaments consist primarily of the protein myosin. Each thick filament are approximately 15 nm in diameter, and each is made of several hundred molecules of myosin.
- Thin filaments, 7 nm in diameter, consist primarily of the protein actin. All thin filaments are attached the Z disc.
- Elastic filaments, 1 nm in diameter, are made of titin, a large springy protein. ...
What is the structure of a myofilament?
Structure. There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments. Thick filaments consist primarily of the protein myosin. Each thick filament is approximately 15 nm in diameter, and each is made of several hundred molecules of myosin. A myosin molecule is shaped like a golf club,...
How many Myofibrils are in a muscle fiber?
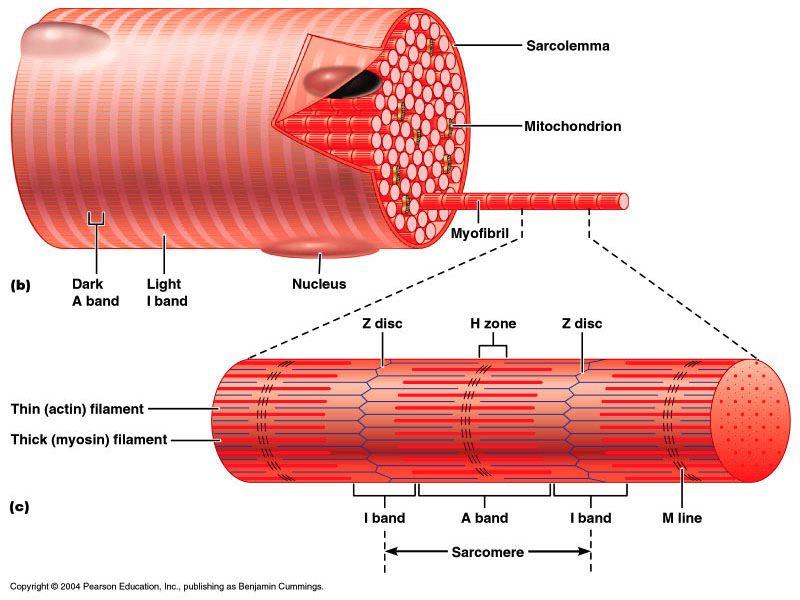
Within each muscle fiber are hundreds of parallely arranged myofibrils. Each myofibril is made up of bundles of the protein filaments (myofilaments) that are responsible for muscle contraction. The 2 types of myofilaments are: thin filaments: made of the protein actin , and thick filaments: made of the protein myosin .
What are the two types of filaments in muscle tissue?
The two filaments are a thick one composed mostly of myosin, and a thin one composed mostly of actin. Types of muscle tissue are striated skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, obliquely striated muscle (found in some invertebrates ), and non-striated smooth muscle.
What is the structure of myosin filaments?
The thick filament, myosin, has a double-headed structure, with the heads positioned at opposite ends of the molecule. During muscle contraction, the heads of the myosin filaments attach to oppositely oriented thin filaments, actin, and pull them past one another.

What are the two types of myofilaments quizlet?
There are two types of myofilaments: thick (myosin) filaments and thin (actin) filaments.
What are the 2 types of myofilaments in a sarcomere?
Sarcomeres. A sarcomere is the functional unit (contractile unit) of a muscle fiber. As illustrated in Figure 2-5, each sarcomere contains two types of myofilaments: thick filaments, composed primarily of the contractile protein myosin, and thin filaments, composed primarily of the contractile protein actin.
What are the 2 protein myofilaments?
The myofilament contractile proteins consist of thick filament myosin and thin filament actin proteins.
What are the types of myofilament?
There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments.
What are the two myofilaments involved in muscle contraction?
Muscle contraction thus results from an interaction between the actin and myosin filaments that generates their movement relative to one another.
What is the thin myofilament called?
The myofibrils are made up of thick and thin myofilaments, which help give the muscle its striped appearance. The thick filaments are composed of myosin, and the thin filaments are predominantly actin, along with two other muscle proteins, tropomyosin and troponin.
What is myosin and actin?
The main difference between actin and myosin is that actin is a protein that produces thin contractile filaments within muscle cells, whereas myosin is a protein that produces the dense contractile filaments within muscle cells.
What is a myofilament quizlet?
A protein that forms filaments that slide between myosin filaments to contract a muscle.
What is thick and thin filament?
The thin filaments contain actin, tropomyosin, troponins C, I, and T and nebulin. The thick filaments are composed of myosin with the globular heads forming cross-bridges with thin filaments. Myosin-binding proteins, including MyBP-C, are associated with the thick filaments.
What do you mean by myofilament?
Definition of myofilament : one of the individual filaments of actin or myosin that make up a myofibril.
Which muscle type contains myofilaments?
-All muscle tissues contains the myofilaments actin and myosin, which generate contractile forces; the plasma membrane is called a sarcolemma; and the cytoplasm is called sacroplasm .
What is myosin and actin?
The main difference between actin and myosin is that actin is a protein that produces thin contractile filaments within muscle cells, whereas myosin is a protein that produces the dense contractile filaments within muscle cells.
What are sarcomeres made of?
The sarcomere consists of a bundle of myosin-containing thick filaments flanked and interdigitated with bundles of actin-containing thin filaments (Fig. 1). The striated appearance of muscle results from the alternation of thick-filament-containing (A-Band) and thin-filament-containing (I-band) regions.
What type of myofilaments are found in the I band?
actin filamentsThe arrangement of the thick myosin filaments across the myofibrils and the cell causes them to refract light and produce a dark band known as the A Band. In between the A bands is a light area where there are no thick myofilaments, only thin actin filaments. These are called the I Bands.
Which muscle type contains myofilaments?
-All muscle tissues contains the myofilaments actin and myosin, which generate contractile forces; the plasma membrane is called a sarcolemma; and the cytoplasm is called sacroplasm .
What are the two proteins in myofibrils?
FMA. 67897. Anatomical terms of microanatomy. Myofilaments are the two protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The two proteins are myosin and actin and are the contractile proteins involved in muscle contraction. The two filaments are a thick one composed mostly of myosin, and a thin one composed mostly of actin .
What changes occur in the myofilament in response to exercise?
The changes that occur to the myofilament in response to exercise have long been a subject of interest to exercise physiologists and the athletes who depend on their research for the most advanced training techniques. Athletes across a spectrum of sporting events are particularly interested to know what type of training protocol will result in maximal force generation from a muscle or set of muscles, so much attention has been given to changes in the myofilament under bouts of chronic and acute forms of exercise.
What are the proteins involved in muscle remodeling?
Other promising areas of research that may illumine the exact molecular nature of exercise-induced protein remodeling in muscle may be the study of related proteins involved with cell architecture, such as desmin and dystrophin. These proteins are thought to provide the cellular scaffolding necessary for the actin-myosin complex to undergo contraction. Research on desmin revealed that its presence increased greatly in a test group exposed to resistance training, while there was no evidence of desmin increase with endurance training. According to this study, there was no detectable increase in dystrophin in resistance or endurance training. It may be that exercise-induced myofilament alterations involve more than the contractile proteins actin & myosin.
What are the two types of muscle tissue?
Types of muscle tissue are striated skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, obliquely striated muscle (found in some invertebrates ), and non-striated smooth muscle. Various arrangements of myofilaments create different muscles.
What is the weakened contractile function of skeletal muscle?
The weakened contractile function of skeletal muscle is also linked to the state of the myofibrils. Recent studies suggest that these conditions are associated with altered single fiber performance due to decreased expression of myofilament proteins and/or changes in myosin-actin cross-bridge interactions. Furthermore, cellular and myofilament-level adaptations are related to diminished whole muscle and whole body performance.
How many nm are in a thin filament?
Thin filaments, are 7 nm in diameter, and consist primarily of the protein actin, specifically filamentous F-actin. Each F-actin strand is composed of a string of subunits called globular G-actin. Each G-actin has an active site that can bind to the head of a myosin molecule. Each thin filament also has approximately 40 to 60 molecules ...
How many molecules are in a filament?
Each thick filament is approximately 15 nm in diameter, and each is made of several hundred molecules of myosin. A myosin molecule is shaped like a golf club, with a tail formed of two intertwined chains and a double globular head projecting from it at an angle.
What are the two types of myofilaments?
The 2 types of myofilaments are: thin filaments: made of the protein actin , and thick filaments: made of the protein myosin . Myofilaments are arranged to form repeating units termed sarcomeres .
What are myofibrils made of?
Each myofibril is made up of bundles of the protein filaments ( myofilaments) that are responsible for muscle contraction. The 2 types of myofilaments are: thin filaments: made of the protein actin , and thick filaments: made of the protein myosin . Myofilaments are arranged to form repeating units termed sarcomeres .
Is calcium necessary for sliding filament?
Click here for an animation that will help explain this. Note that calcium is necessary for this action. sliding filament
