What are the steps in the semiconservative DNA replication process?
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
What are the 3 steps to semi-conservative replication?
The three steps in the process of DNA replication are initiation, elongation and termination.
What are the 3 steps of replication?
Replication occurs in three major steps: the opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands, the priming of the template strand, and the assembly of the new DNA segment. During separation, the two strands of the DNA double helix uncoil at a specific location called the origin.
What is the process of Semiconservative replication?
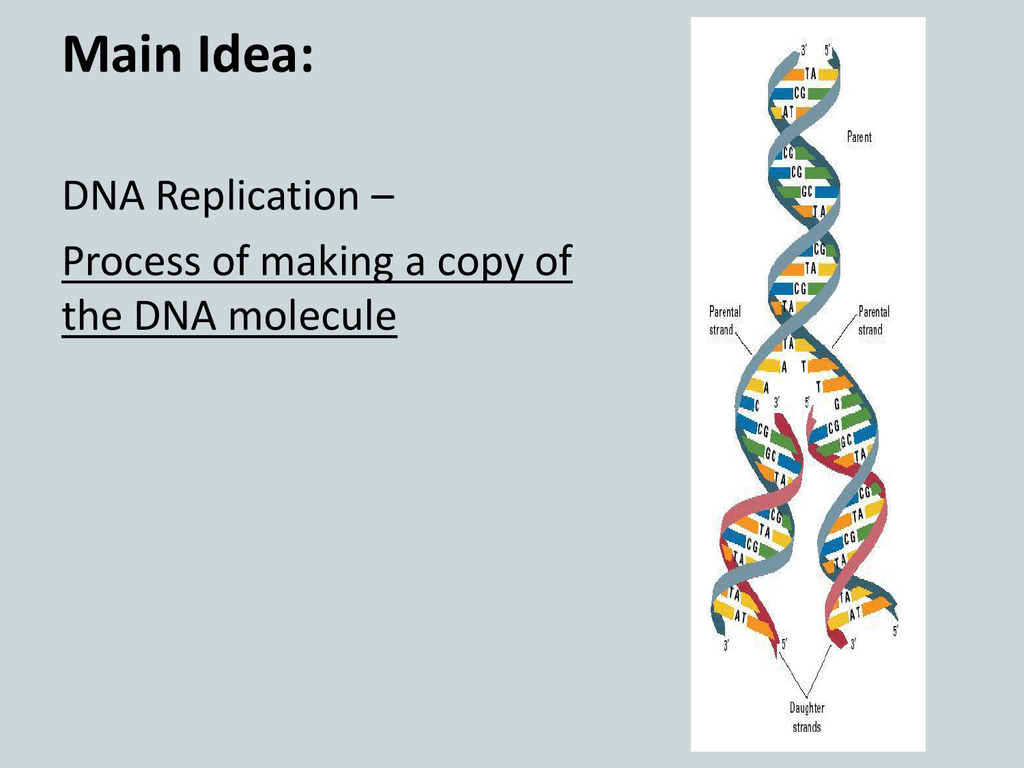
Semi-conservative replication. In this model, the two strands of DNA unwind from each other, and each acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. This results in two DNA molecules with one original strand and one new strand.
What happens during the 3rd step of DNA replication?
Step 3: Elongation In bacteria such as E. coli, polymerase III is the main replication enzyme, while polymerase I, II, IV and V are responsible for error checking and repair. DNA polymerase III binds to the strand at the site of the primer and begins adding new base pairs complementary to the strand during replication.
What are the 4 stages of DNA replication?
Step 1: Replication Fork Formation. Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into two single strands. ... Step 2: Primer Binding. The leading strand is the simplest to replicate. ... Step 3: Elongation. ... Step 4: Termination.
Why is DNA replication Semiconservative?
Semiconservative replication is so named because one of the strands of DNA in each of the two copies of DNA is ancient and conserved while the other is newly produced at the moment of replication.
What is meant by semi conservative replication of DNA quizlet?
Semiconservative DNA replication means that: each strand of a double-stranded DNA molecule is replicated differently. each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand. the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only part of the time.
Why is replication called Semiconservative quizlet?
DNA replication is said to be semiconservative because each newly made DNA molecule has one original and one new strand of DNA.
What is the first step of DNA replication?
The first step in DNA replication is to 'unzip' the double helix structure of the DNA? molecule. This is carried out by an enzyme? called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds? holding the complementary? bases? of DNA together (A with T, C with G).
What is the 2nd step in DNA replication?
The 1st step is the unwinding of the double stranded structure of DNA that results to formation of the replication bubble. The second step is the binding of the RNA primer for the initiation of DNA synthesis.
What is the DNA replication process?
DNA replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell.
What is process of replication?
DNA replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell.
What are the different types of replication?
Types of data replicationFull table replication.Transactional replication.Snapshot replication.Merge replication.Key-based incremental replication.
What is the first step of DNA replication?
The first step in DNA replication is to 'unzip' the double helix structure of the DNA? molecule. This is carried out by an enzyme? called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds? holding the complementary? bases? of DNA together (A with T, C with G).
What are the steps in DNA replication with enzymes?
Step 1: Unzipping. The first step in DNA replication is the unzipping of DNA by the enzyme helicase. ... Step 2: Elongation. During the elongation stage the enzyme primase creates a small complementary sequence of RNA nucleotides called a primer. ... Step 3: Termination. During termination, DNA replication comes to an end.
What are the phases of replication?
The three phases of replication process are: (1) Initiation (2) Elongation and (3) Termination. Replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes occurs by very similar mechanisms, and thus most of the information presented here for bacterial replication applies to eukaryotic cells as well. ADVERTISEMENTS:
Where does DNA replication begin?
In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations in the genome, called “origins”. In case of E. coli the origin of replication is a sequence of approximately 245 base pairs (bp) called oriC. Origins contain DNA sequences recognized by replication initiator proteins (e.g. DnaA in E. coli and the Origin Recognition Complex in yeast), ...
How many repeats are in E. coli DNA?
We know substantially more about DNA synthesis in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes. As we have discussed that oriC of E.coli spans 245 bp of DNA. Sequence analysis of this segment shows that it contains two short repeat motifs, one of nine nucleotides and the other of 13 nucleotides. The five copies of nine nucleotide repeat motif are presented dispersedly throughout oriC.
What happens when DNA is negatively super-coiled?
Attachment occurs only when the DNA is negatively super-coiled, as is the normal situation for the E. coli chromosome. ADVERTISEMENTS: The result of DnaA binding is that the double helix opens up (melts) within the tandem array of three AT-rich, 13 nucleotide repeats located at one end of the oriC sequence.
Why does E. coli have termination sequences?
Because bacteria have circular chromosomes, termination of replication occurs when the two replication forks meet each other on the opposite end of the parental chromosome. E coli regulate this process through the use of termination sequences which, when bound by the Tus protein, enable only one direction of replication fork to pass through.
What is the structure of DNA that forms when DNA is replicated?
Unwinding of DNA at the origin, and synthesis of new strands, forms a replication fork. The replication fork is a structure which forms when DNA is being replicated. It is created through the action of helicase, which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the two DNA strands together. The resulting structure has two branching “prongs”, ...
Where do replication forks meet?
As a result, the replication forks are constrained to always meet within the termination region of the chromosome. Eukaryotes initiate DNA replication at multiple points in the chromosome, so replication forks meet and terminate at many points in the chromosome; these are not known to be regulated in any particular manner.
Where does replication begin?
Replication begins at a location on the double helix known as “oriC” to which certain initiator proteins bind and trigger unwinding. Enzymes known as helicases unwind the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs, while other proteins keep the single strands from rejoining.
What is the process of DNA replication?
A DNA strand is composed of a long backbone of sugar and phosphate units . One of our different nucleotide bases -- A, T, C or G -- hang off each sugar unit. The sequence of the bases encodes genetic information. The three steps in the process of DNA replication are initiation, elongation and termination.
What is the last primer sequence removed from the end of the lagging strand?
During termination, the last primer sequence must be removed from the end of the lagging strand. This last portion of the lagging strand is the telomere section, containing a repeating non-coding sequence of bases. Enzymes snip off a telomere at the end of each replication, leading to shorter strands after each cycle.
How does DNA replication work?
The A base can only bind to a T, and a C can only bind to a G. In the DNA double helix, the bases of one strand face across and bind to those of the other strand. Therefore, the base sequence of each strand complements that of the other -- the sequences are antiparallel and serve as templates for each other’s replication. The two strands are labelled by the location of certain chemical bonds in the DNA backbone. The cell can replicate the “leading strand" as a single unit, but must replicate the “lagging strand" in small pieces.
How are the two strands of DNA labelled?
The two strands are labelled by the location of certain chemical bonds in the DNA backbone. The cell can replicate the “leading strand" as a single unit, but must replicate the “lagging strand" in small pieces.
