
Drug Action: Pharmaceutics, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamic Phases
- STIMULATION OR DEPRESSION
- REPLACEMENT
- INHIBITION OR KILLING OF ORGANISMS
- IRRITATION
What is the pharmaceutic phase of drug action?
d."The pharmaceutic phase is the process by which the drug becomes available to body fluids and tissue." A. To achieve drug action, drugs are moved by four processes
What are the three major processes for drug absorption?
Three major processes for drug absorption Passive absorption, Active absorption and pinocytosis 8. A student nurse is studying the phases of drug action. Which statement by the student indicates to the nursing instructor that the student understands the pharmaceutic phase? a."To achieve drug action, drugs are moved by four processes."
What are the stages of drug development?
Phases Stages Step 1: Discovery & Development Step 2: Preclinical Research Step 3: Clinical Development Step 4: FDA Review Step 5: Post-market Monitoring Other Relevant Drug Development Concepts Overview & Definition
What are the three stages of drug tolerance?
1. the onset of drug action 2.peak action 3. duration of action Tolerance decreased responsiveness over the course of therapy Toxic effects or Toxicity occurs when a drug level exceeds the therapeutic range causing overdosing or drug accumulation Trough drug level
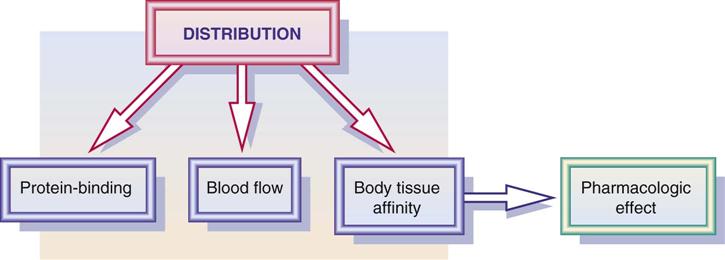
What are the types of drug action?
As a result, they cause the human body to react in a specific way. Based on drug action on receptors, there are 2 different types of drugs: Agonists – they stimulate and activate the receptors. Antagonists – they disable the agonists from stimulating the receptors.
What are the phases of pharmacology?
Think of pharmacokinetics as a drug's journey through the body, during which it passes through four different phases: absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME).
What are the 4 categories of drug actions?
There are four types of ligand that act by binding to a cell surface receptor, agonists, antagonists, partial agonists, and inverse agonists (Figure 1).
What is pharmacokinetics phase?
Pharmacokinetic Phase. This phase describes the time course and disposition of a drug in the body, based on its absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination. Definitions. • Pharmacokinetics: – describes what the body does to a drug.
What are the 3 phases of FDA approval?
There are three primary phases of the approval process: pre-clinical trials, clinical trials, and new drug application review.
How many phases are in a drug trial?
3There are 3 main phases of clinical trials – phases 1 to 3. Phase 1 trials are the earliest phase trials and phase 3 are later phase trials. Some trials have an earlier stage called phase 0, and there are some phase 4 trials done after a drug has been licensed.
What are the principles of drug action?
Principles of drug action encompass three major topic areas: drug administration, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics.
What is the meaning of drug action?
In medicine, a term used to describe how a drug or other substance produces an effect in the body. For example, a drug's mechanism of action could be how it affects a specific target in a cell, such as an enzyme, or a cell function, such as cell growth.
What is onset of drug action?
Listen to pronunciation. (... AK-shun) The length of time it takes for a medicine to start to work.
What is pharmacokinetics vs pharmacodynamics?
In simple words, pharmacokinetics is 'what the body does to the drug'. Pharmacodynamics describes the intensity of a drug effect in relation to its concentration in a body fluid, usually at the site of drug action. It can be simplified to 'what the drug does to the body'.
What are the differences between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics?
The difference between pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) can be summed up pretty simply. Pharmacokinetics is the study of what the body does to the drug, and Pharmacodynamics is the study of what the drug does to the body.
What is the process of drug absorption?
The most common mechanism of absorption for drugs is passive diffusion. This process can be explained through the Fick law of diffusion, in which the drug molecule moves according to the concentration gradient from a higher drug concentration to a lower concentration until equilibrium is reached.
What is the third stage of addiction?
Third Stage: Withdrawal/Negative Affect. In addition to the way addiction takes over a person’s life, substances also change a person’s brain affecting his moods and behavior. When he stops taking the drug or drinking alcohol, he may experience withdrawal symptoms.
What are the signs of a second stage of drug use?
Warning signs of the second stage include the following: Missing days at work or school or showing up late because of recovering from a drug or alcohol binge. Continued use in spite of threats of getting fired or expelled. Schedulingentire day around obtaining, using or recovering from drug use.
How does addiction treatment work?
This highly individual process works by going through talk therapy. Facilities that offer evidence-based therapies, such as Skywood Recovery, give patients the best outcomes.
What is the first sign that addiction is taking hold?
Constant cravings for a drug are the first sign addiction is taking hold.An overwhelming urge to use the drug of choice preoccupies the user despite other events, responsibilities or relationships in her life.
How do addictions develop?
How Addictions Develop. No one sets out to develop an addiction. A complicated mix of genetics and environmental factors determine if one person is at greater risk for addiction than another. Researchers know some people’s brains react differently to certain substances.
What are the symptoms of withdrawal?
Nausea, vomiting, chills, cramps. Shakes, sweats, tremors. Psychotic reactions. At this stage, the only motivation in a user’s life is to avoid the agonizing symptoms of withdrawal.< All other conventional activities cease to have meaning beyond finding and continuing to use his chosen substances.
How to know if you are a drug addict?
Warning signs of the second stage include the following: 1 Missing days at work or school or showing up late because of recovering from a drug or alcohol binge 2 Continued use in spite of threats of getting fired or expelled 3 Schedulingentire day around obtaining, using or recovering from drug use 4 Choosing to attend events or spend time with friends only if drugs or alcohol will be available 5 Unexplained personality changes 6 Sudden need for money 7 Excessive need for privacy 8 Possession of drug paraphernalia
How many steps are there in drug development?
There are five critical steps in the U.S. drug development process, including many phases and stages within each of them. We will discuss these different phases and stages to develop an in-depth understanding of the entire process. The five steps are –. Step 1: Discovery and Development.
How many volunteers are needed for the Phase 1 drug test?
This phase is the first time the drug is tested on humans; less than 100 volunteers will help researchers assess the safety and pharmacokinetics, absorption, metabolic, and elimination effects on the body, as well as any side effects for safe dosage ranges.
What is drug discovery?
Today drug discovery involves screening hits, medicinal chemistry, and optimization of hits to reduce potential drug side effects (increasing affinity and selectivity). Efficacy or potency, metabolic stability (half-life), and oral bioavailability are also improved in this step of the drug development process.
Why is stability important in drug development?
Stability is important in determining human drug efficacy, and biological samples are required. Drug and drug metabolites are susceptible to degradation, which can lower drug concentration over the life of the drug.
What is an API in medicine?
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are biologically active ingredients in a drug candidate that produce effects. All drugs are made up of the API or APIs and excipients. (Excipients are inactive substances that deliver the drug into the human system.).
