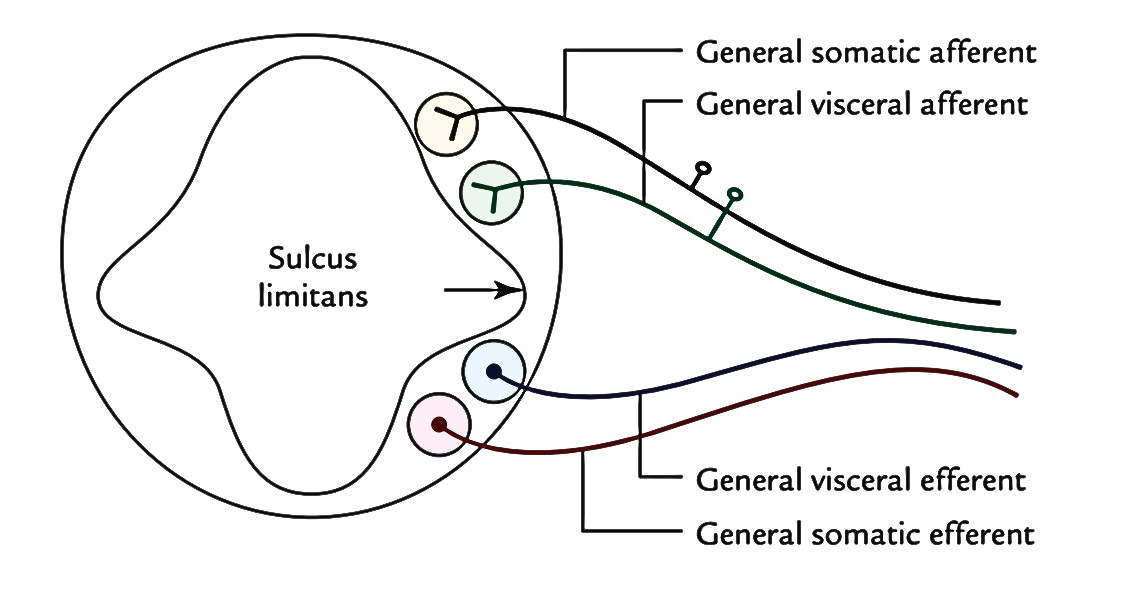
What are the different patterns of the medulla? Terms in this set (5) Continuous. one unbroken line of color. Interrupted/Intermittent. pigmented line broken at regular intervals. None. no separate pigmentation in the medulla. Fragmented/Segmented. pigmented line unevenly spaced. Solid. pigmented area filling both the medulla and the cortex.
What are the types of medulla patterns?
This preview shows page 1 - 4 out of 4 pages. 3. Medulla patterns can be these four types: Continuous, interrupted, fragmented and no medulla 4. Non-human medulla patterns are always continuous and can be divided further into these four types: Uniserial, multiserial, vacuolated and lattice 5.
What is the medulla oblongata?
Thanks, medulla! The medulla oblongata, also known just as the medulla, is part of your brainstem, which is literally the stem that extends from your brain. The medulla sits below the pons and above the spinal cord and is a major relay point for information going to and from your brain and spinal cord.
What does the medulla do?
In addition to the functions already outlined, your medulla controls the following autonomic reflexes: Blood vessel dilation to increase or decrease oxygen flow and respond to heart functions. Digestion to turn on or off digestion during 'fight or flight' scenarios.
What is the lowest part of the brainstem that connects the brain to the spinal cord?
What does the Medulla oblongata do?
What happens if the medulla is damaged?
How many cranial nerves are there?
Why does my heart beat so fast?
Where do the last seven pairs of cranial nerves originate?
Which nerves are responsible for swallowing?
See 4 more
About this website
What are the 4 main types of medulla found in hair?
Not all hairs have a medulla, but when it is present in humans, it is one of three different types: fragmented, interrupted, or continuous.
How many medulla patterns are there?
Five different patterns of medulla are identified in forensic hair analysis.
What is the medulla pattern of human hair?
The medulla, when present in human hairs, is amorphous in appearance, and the width is generally less than one-third the overall diameter of the hair shaft. The medulla in animal hairs is normally continuous and structured and generally occupies an area of greater than one-third the overall diameter of the hair shaft.
What are 5 types of medulla?
what are the 5 types of medulla?continuous - one unbroken line of color.interrupted (intermittent) - pigmented line broken at regular intervals.fragmented or segmented - pigmented one unevenly spaced.solid - pigmented area filled both the medulla and cortex.none - no separate pigmentation in the medulla.
What are the types of medulla patterns?
Medulla are generally classified as continuous, interrupted, fragmented, or absent. Human head hairs have fragmented patterns or are absent. Most animals have either a continuous or interrupted pattern.
What is a medullary pattern?
Medullary pattern is a histological pattern that can be applied to an invasive breast carcinoma of no special type that contains pushing borders, syncytial growth, high grade nuclei and prominent lymphoid infiltrate.
What are the 4 formations of hair?
Read on to learn more.Anagen: Growing phase. The stages of hair growth begin with the anagen phase. ... Catagen: Transition phase. The catagen phase starts when the anagen phase ends, and tends to last about 10 days or so. ... Telogen: Resting phase. The telogen phase typically lasts around 3 months. ... Exogen: Shedding phase.
What are the three possible medulla patterns in humans?
Human medulla may be continuous, fragmented, or absent.
What are the 4 parts of hair?
The hair follicle is made up of four parts:Hair Bulb. The hair bulb is located at the base of the hair follicle. ... Sebaceous Gland. The sebaceous gland produces an oily substance called sebum that moisturizes both the hair shaft and the skin.The Inner and Outer Root Sheath. ... Arrector Pili Muscle.
What are the three basic medullary types?
When the medulla is present in human hairs, its structure can be described as fragmentary or trace, discontinuous or broken, or continuous. Figure 95 is a diagram depicting the three basic medullary types.
What medulla pattern is most common in humans?
Human hairs generally have no medulla or one that is fragmented, however a continuous medulla is frequently found in the hairs of Native Americans and Asians.
What are the 3 structure of hair?
Each hair shaft is made up of two or three layers: the cuticle, the cortex, and sometimes the medulla.
What are the three possible medulla patterns in humans?
Human medulla may be continuous, fragmented, or absent.
Does every hair have the same medulla pattern?
The molecular structure of hair will vary from person to person depending on their genetics. People with thin hair may not even have a medulla, while thick hair types normally have all three layers. But it can also differ on the same person, with some hairs having all three layers and some only having two.
Does everyone have the same medulla pattern?
Only one medulla pattern type is found in human hair.
How many medulla are in the kidney?
Between seven and eighteen pyramids exist in the innermost part of the kidney, which is called the renal medulla; in humans, there are usually only seven of the pyramids.
Medulla Oblongata Function, Definition & Location | Body Maps - Healthline
The medulla oblongata helps regulate breathing, heart and blood vessel function, digestion, sneezing, and swallowing. This part of the brain is a center for respiration and circulation.
Medulla Oblongata: What It Is, Function & Anatomy - Cleveland Clinic
Function What does the medulla oblongata do? Your medulla oblongata (med-oo-la ob-long-ah-ta), often just called the medulla, is a key part of your nervous system.It’s key not only because of its location but also because of what it controls.
What is the lowest part of the brainstem that connects the brain to the spinal cord?
The medulla is the lowest part of the brainstem that connects the brain to the spinal cord. Learn about the definition, location, and function of the medulla, and explore autonomic nervous system control, cranial nerves, and motor functions. Updated: 10/27/2021
What does the Medulla oblongata do?
Your medulla directly controls many ANS responses, in addition to playing an accessory role in the control of certain areas of your body. It also has a stake in your overall major motor functions, or body movement. Let's take a moment to explore each of these functions in detail.
What happens if the medulla is damaged?
What's more, if damage is high in the medulla (before the tracts cross over), it would affect muscles that control the opposite side of the body, whereas damage below the crossover would affect muscles on the same side as the damage. Lesson Summary. The medulla oblongata, also known as the medulla, directly controls certain ANS responses, ...
How many cranial nerves are there?
Cranial Nerves. You have 12 pairs of cranial nerves, which control everything from the movements and reflexes of your eyes to your sense of smell, tongue movement, and sense of balance. These nerves leave your central nervous system at various locations.
Why does my heart beat so fast?
Your heartbeat quickens to pump the extra oxygen (which your quickened breathing is now taking in) to your muscles so you can make a 'fight' (truly not recommended) or 'flight' decision. And, what's more, you have totally forgotten that urgent need to go to the bathroom that you had three seconds before meeting Yogi's giant cousin (thank goodness--what a terrible time to be stuck doing a bathroom dance!). All of these responses are due to your autonomic nervous system ( ANS ), which is, in part, controlled by your medulla oblongata. Thanks, medulla!
Where do the last seven pairs of cranial nerves originate?
The last seven pair of cranial nerves originate at either the junction between the pons and the medulla or directly through the medulla itself , meaning the medulla either plays an accessory role in conducting those signals or a direct role in controlling them.
Which nerves are responsible for swallowing?
9. The glossopharyngeal nerve, which receives sensations and sends motor signals to the tongue and pharynx. This nerve also enables sense of taste and pharyngeal contractions for actions such as swallowing and interacts with your inner ear. This is one of the three nerves that plays a direct role in the medulla's ANS control of swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and vomiting.
What is the lowest part of the brainstem that connects the brain to the spinal cord?
The medulla is the lowest part of the brainstem that connects the brain to the spinal cord. Learn about the definition, location, and function of the medulla, and explore autonomic nervous system control, cranial nerves, and motor functions. Updated: 10/27/2021
What does the Medulla oblongata do?
Your medulla directly controls many ANS responses, in addition to playing an accessory role in the control of certain areas of your body. It also has a stake in your overall major motor functions, or body movement. Let's take a moment to explore each of these functions in detail.
What happens if the medulla is damaged?
What's more, if damage is high in the medulla (before the tracts cross over), it would affect muscles that control the opposite side of the body, whereas damage below the crossover would affect muscles on the same side as the damage. Lesson Summary. The medulla oblongata, also known as the medulla, directly controls certain ANS responses, ...
How many cranial nerves are there?
Cranial Nerves. You have 12 pairs of cranial nerves, which control everything from the movements and reflexes of your eyes to your sense of smell, tongue movement, and sense of balance. These nerves leave your central nervous system at various locations.
Why does my heart beat so fast?
Your heartbeat quickens to pump the extra oxygen (which your quickened breathing is now taking in) to your muscles so you can make a 'fight' (truly not recommended) or 'flight' decision. And, what's more, you have totally forgotten that urgent need to go to the bathroom that you had three seconds before meeting Yogi's giant cousin (thank goodness--what a terrible time to be stuck doing a bathroom dance!). All of these responses are due to your autonomic nervous system ( ANS ), which is, in part, controlled by your medulla oblongata. Thanks, medulla!
Where do the last seven pairs of cranial nerves originate?
The last seven pair of cranial nerves originate at either the junction between the pons and the medulla or directly through the medulla itself , meaning the medulla either plays an accessory role in conducting those signals or a direct role in controlling them.
Which nerves are responsible for swallowing?
9. The glossopharyngeal nerve, which receives sensations and sends motor signals to the tongue and pharynx. This nerve also enables sense of taste and pharyngeal contractions for actions such as swallowing and interacts with your inner ear. This is one of the three nerves that plays a direct role in the medulla's ANS control of swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and vomiting.
