4 Stages of Demographic Transition Theory – Explained!
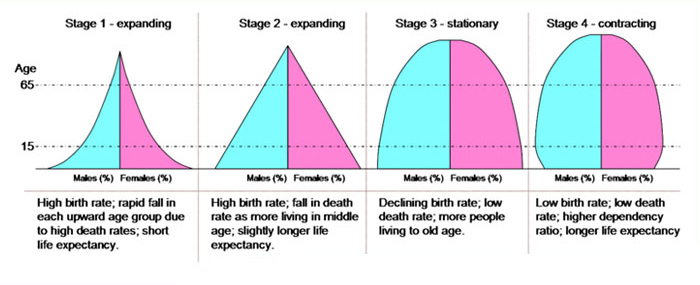
- High Stationary: High Birth Rate of High Death Rate: The first stage is characterised by high birth rate & high death rate, giving a low growth rate of population. ...
- Early Expanding Stage: Rapidly Falling Death Rate & High Birth Rate: The second stage is characterised by a sharp decrease in death rate, but the birth rate remains almost ...
- Later Expanding Stage: Sharply Falling Birth Rate and Low Death Rate: The third stage is characterised by sharp decrease in birth rate, with death rate remaining constant or falling ...
- Low Stationary Stage: Low Birth Rate and Low Death Rate:
What countries are in Stage 4 of demographic transition?
What are countries in demographic transition? Examples of countries in Stage 4 of the Demographic Transition are Argentina, Australia, Canada, China, Brazil, most of Europe, Singapore, South Korea, and the U.S. Since the middle of the 19th Century, Argentina has maintained a strong economy, keeping on par with Western Europe and North America.
What are the 4 stages of population growth?
What can we do to stop overpopulation?
- Have fewer children!
- Consider adoption!
- Read, educate yourself about population issues – read more here.
- Reduce your personal consumption: go vegan, limit flying, share your household with others, and more.
- Educate your teenage child (ren) about sex and contraception early, without taboos.
What are the 4 stages of the economic cycle?
The economic cycle goes through four stages:
- Expansion
- Peak
- Contraction
- Trough
What are the 4 stages of evolution?
The theory emphasized the following points:
- Natural Selection
- Variation
- Struggle To Exist
- Survival of the Fittest
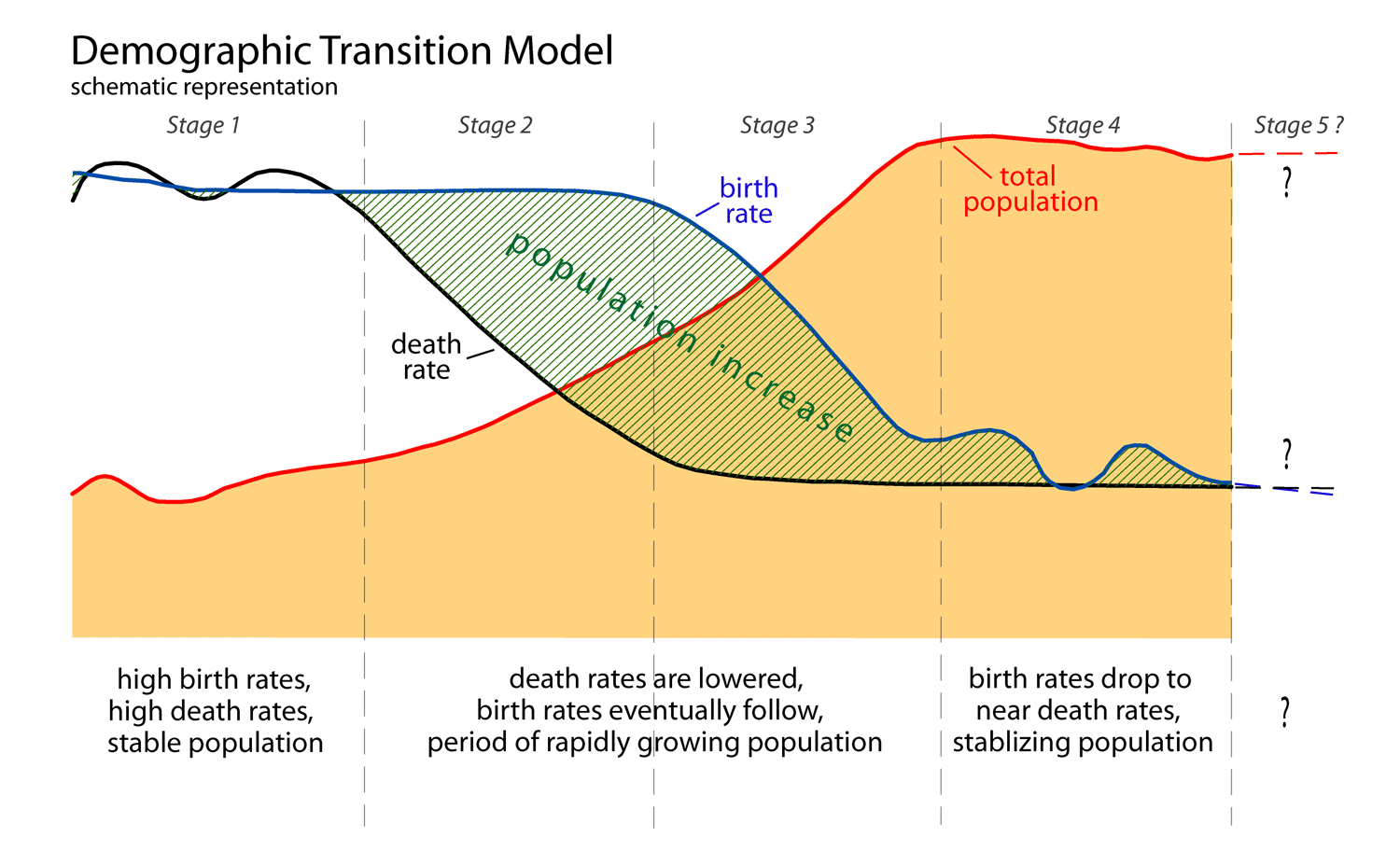
What is Stage 4 of the demographic transition model?
STAGE 4: LOW GROWTH RATE. A nation enters Stage 4 of the demographic transition model when CBRs equal to or become less than CDRs. When CBRs are equal to CDRs, a nation will experience zero population growth (ZPG). It should be noted that sometimes a nation could have a slightly higher CBR, but still experience ZPG.
What are the four stages of the demographic transition quizlet?
There are four stages in the demographic transition. Low growth, high growth, moderate growth, and low growth.
What causes stage 4 of the demographic transition model?
Low birth rates and low death rates characterize the countries in Stage 4 of the Demographic Transition Model. Not since Stage 1 of the DTM have birth rates and death rates been so equal in value, the main difference being that in Stage 4 total population is already high.
What are the 5 stages of demographic transition?
Demographic cycle(1) FIRST STAGE (High stationary) It is characterized by both. ... (2) SECOND STAGE (Early expanding) It begins with the. ... (3) THIRD STAGE (Late expanding) *Death rate declines further and. ... (4) FOURTH STAGE (Low stationary) This stage is characterized with. ... (5) FIFTH STAGE: (Declining)
What country is in stage 5 of the demographic transition?
Possible examples of Stage 5 countries are Croatia, Estonia, Germany, Greece, Japan, Portugal and Ukraine.
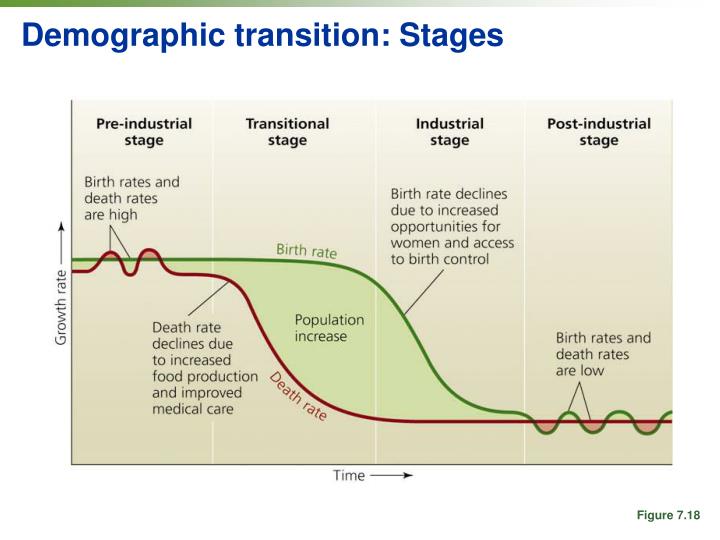
What is the pre-industrial stage?
Pre-industrial society refers to social attributes and forums of political and cultural organization that were prevalent before the advent of the Industrial Revolution, which occurred from 1750 to 1850. Pre-industrial refers to a time before there were machines and tools to help perform tasks en masse.
What is Stage 4 of the epidemiological transition?
In the “fourth stage” of epidemiological transition, the distribution of non-communicable diseases is expected to shift to more advanced ages, but age-specific changes beyond 80 years of age have not been reported.
How many stages are there for demographic transition?
four stagesThe original Demographic Transition model has just four stages, but additional stages have been proposed. Both more-fertile and less-fertile futures have been claimed as a Stage Five. Some countries have sub-replacement fertility (that is, below 2.1–2.2 children per woman).
What is an example of demographic transition?
The world and most countries are going through a period of unprecedentedly rapid demographic change. The most obvious example of this change is the huge expansion of human numbers: four billion have been added since 1950.
What is Stage 2 of the demographic transition?
Stage 2 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM) is characterized by a rapid decrease in a country's death rate while the birth rate remains high. As such, the total population of a country in Stage 2 will rise because births outnumber deaths, not because the birth rate is rising.
What happens in Stage 3 of the demographic transition model?
In Stage 3 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM), death rates are low and birth rates decrease, usually as a result of improved economic conditions, an increase in women's status and education, and access to contraception.
What is a Stage 3 country?
Stage three countries start to become more industrialized, which means they are more urbanized and the total fertility rate goes down. Countries that are currently in stage three are Mexico, India, Colombia, and South Africa.
What is the demographic transition quizlet?
is the general pattern of demographic change from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates, and observed in the history of more-developed countries. The theory behind the demographic transition is that industrial development causes economic and social progress that then affects population growth rates.
What is the demographic transition model quizlet?
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
What happens in each stage of the demographic transition?
In stage 1 the two rates are balanced. In stage 2 they diverge , as the death rate falls relative to the birth rate. In stage 3 they converge again, as the birth rate falls relative to the death rate. Finally in stage 4 the death and birth rates are balanced again but at a much lower level.
Which of the following is are the stage of demographic transition?
The concept of demographic transition has four stages, including the pre-industrial stage, the transition stage, the industrial stage, and the post-industrial stage.
What is the third stage of growth?
The third stage is characterised by sharp decrease in birth rate, with death rate remaining constant or falling by small number. As a result the gap between the birth rate and death rate high, so, overall the rate of growth goes on diminishing.
What is the first stage of the human development?
1. High Stationary: High Birth Rate of High Death Rate: The first stage is characterised by high birth rate & high death rate, giving a low growth rate of population. This stage is associated with undeveloped, low output and agricultural dominated conditions. Death rate is high during this stage for a number of reasons.
Why does the death rate fall slowly at the second stage of birth control?
On the other hand, death rate falls slowly at this stage because the major decrease in death rate had taken place from the second stage.
What is the second stage of economic development?
The second stage is characterised by a sharp decrease in death rate, but the birth rate remains almost stable resulting in a very high rate of growth of population. This stage emerges when the process of economic development staris in a country.
How does economic development affect the death rate?
Economic development leads to a fall in death rate because of its direct & indirect effects on death rate . First, economic development enables people to have adequate & balanced diet, adequate clothing & proper health-care. This improves the health condition and reduces the chances of falling sick.
Is the death rate high during famine?
Death rate is generally high and it becomes exceptionally high during the period of famines and epidemics. Image Source: timedotcom.files.wordpress.com. ADVERTISEMENTS: The birth rate also is very high during the first stage due to variety of reasons.
Is the birth rate higher than the death rate?
Furthermore, since all are interested in continuation of families and races, it is essential that birth rate must be higher than the death rate. Thus, in the final stage the birth rate and death rate becomes stationary at low levels resulting in very low and almost constant steady rate of population.
What is the fifth stage of fertility?
Some theorists include a fifth stage in which fertility rates begin to transition again to either above or below that which is necessary to replace the percentage of the population that is lost to death. Some say fertility levels decrease during this stage while others hypothesize that they increase. Rates are expected to increase populations in Mexico, India and the U.S. in the 21st century, and to decrease populations in Australia and China. Birth and death rates largely plateaued in most developed nations in the late 1900s.
What is the definition of demographic transition?
Demographic transition is a model used to represent the movement of high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system. It works on the premise that birth and death rates are connected to and correlate with stages of industrial development.
What are the stages of transition?
The Four Stages of Transition 1 Stage 1: Death rates and birth rates are high and are roughly in balance, a common condition of a pre-industrial society. Population growth is very slow, influenced in part by the availability of food. The U.S. was said to be in Stage 1 in the 19th century. 2 Stage 2: This is the "developing country" phase. Death rates drop rapidly due to improvements in food supply and sanitation, which increases life spans and reduces disease. Without a corresponding fall in birth rates, countries in this stage experience a large increase in population. 3 Stage 3: Birth rates fall due to access to contraception, increases in wages, urbanization, an increase in the status and education of women, and other social changes. Population growth begins to level off. Mexico is believed to be in this stage in the early decades of the millennium. Northern Europe entered this stage in the later part of the 19th century. 4 Stage 4: Birth rates and death rates are both low in this stage. People born during Stage 2 are now beginning to age and require the support of a dwindling working population. Birth rates may drop below replacement level, considered to be two children per family. This leads to a shrinking population. Death rates may remain consistently low, or they may increase slightly due to increases in lifestyle diseases linked to low exercise levels and high obesity. Sweden has reached this stage in the 21st century.
What is stage 3 birth rate?
Stage 3: Birth rates fall due to access to contraception, increases in wages, urbanization, an increase in the status and education of women, and other social changes. Population growth begins to level off. Mexico is believed to be in this stage in the early decades of the millennium.
What is the stage 1 of the development process?
Stage 1: Death rates and birth rates are high and are roughly in balance, a common condition of a pre-industrial society. Population growth is very slow, influenced in part by the availability of food. The U.S. was said to be in Stage 1 in the 19th century. Stage 2: This is the "developing country" phase.
Why do death rates drop?
Death rates drop rapidly due to improvements in food supply and sanitation, which increases life spans and reduces disease. Without a corresponding fall in birth rates, countries in this stage experience a large increase in population. Stage 3: Birth rates fall due to access to contraception, increases in wages, urbanization, ...
What is the stage of Mexico?
Mexico is believed to be in this stage in the early decades of the millennium. Northern Europe entered this stage in the later part of the 19th century. Stage 4: Birth rates and death rates are both low in this stage. People born during Stage 2 are now beginning to age and require the support of a dwindling working population.
How has population demographics evolved over the past 300 years?
Over the past 300 years, population demographics have continued to evolve as a result of the relationship between the birth and death rates within a country. The observation and documentation of this global phenomenon has produced a model, the Demographic Transition Model, which helps explain and make sense of changes in population demographics.
What is the Demographic Transition Model?
Using the Demographic Transition Model, demographers can better understand a country’s current population growth based on its placement within one of five stages and then pass on that data to be used for addressing economic and social policies within a country and across nations.
What stage are most developing countries in?
Most developing countries are in Stage 3. In Stage 4, birth and death rates are both low, stabilizing the population. These countries tend to have stronger economies, higher levels of education, better healthcare, a higher proportion of working women, and a fertility rate hovering around two children per woman.
What happens in stage 3?
In Stage 3, birth rates gradually decrease, usually as a result of improved economic conditions, an increase in women’s status, and access to contraception. Population growth continues, but at a lower rate. Most developing countries are in Stage 3. In Stage 4, birth and death rates are both low, stabilizing the population.
What happened in the late 1700s?
Beginning in the late 1700s, something remarkable happened: death rates declined . With new technologies in agriculture and production, and advancements in health and sanitation, a greater number of people lived through their adolescent years, increasing the average life expectancy and creating a new trajectory for population growth.
What happens in stage 2 of the population?
In Stage 2, the introduction of modern medicine lowers death rates, especially among children, while birth rates remain high; the result is rapid population growth.
Is every country in the DTM?
Every country can be placed within the DTM, but not every stage of the model has a country that meets its specific definition. For example, there are currently no countries in Stage 1, nor are there any countries in Stage 5, but the potential is there for movement in the future.
What is the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
The Demographic Transition Model is a model that studies population trends in every country across the globe.
What is Stage 1 of the DTM?
The first stage of the DTM is a stage where there are high birth rates and death rates. Many countries were here prior to the Industrial Revolution.
What is Stage 2 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
Stage 2 of the Demographic Transition Model is one that sees a decline in death rates, but birth rates are typically higher.
What is Stage 3 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
Stage 3 of the DTM includes lower birth rates and better conditions in the economy. Women are more involved in the economy, and there is improved access to health care and methods such as contraception.
Is there a Stage 5 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
Yes, there is Stage 5 of the Demographic Transition Model, though it is somewhat colloquial and not an official stage.
What is an example of a country in Stage 4 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
The United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada are all very common examples of a country in stage 4 of the DTM.
Do you understand the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) is a model that studies population patterns with factors specific to birth rates and death rates.