
Glass-ionomer cements are popular materials as they display the following clinical advantages:
- they are tooth-coloured
- they bond chemically to tooth substance and non-precious metals without the need for additional adhesives
- they release fluoride
- their coefficient of thermal expansion is equivalent to that of tooth structure
- they have good biocompatibility.
What is glass ionomer cement?
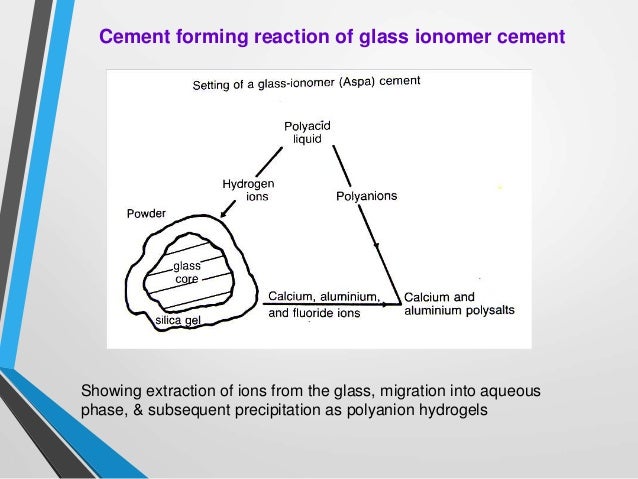
Glass ionomer cement [GIC], invented by Wilson and Kent, has been used as a dental restorative material for more than four decades and its properties are constantly improved to overcome its shortcomings.
What are the advantages of glass ionomer fillings?
Glass Ionomer Filling Advantages Closely matches the colour of your teeth. Often no preparation is needed before you are fitted with a glass ionomer filling. This means that it is a popular choice for use when children have cavities that need filling. They release fluoride over time, thus strengthening your tooth and maintaining good dental health.
What is ionomer luting cement used for?
Luting and bonding: Glass ionomer is commonly used for cementation of crowns, bridges, inlays, onlays and orthodontic appliances. The best glass ionomer luting cements will have high erosion resistance and excellent biocompatibility, such as DEHP Glass Ionomer Luting Cement.
What are the disadvantages of glass ionomer?
Glass Ionomer Filling Disadvantages The material is a lot weaker than other filling materials and is prone to quick wear and tear. Although the colour is close, it is not a perfect match to your original tooth colour. It takes a long time to complete Glass Ionomer, treatment as each layer has to be bonded individually.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of glass ionomer?
The advantages of glass-ionomer cements are offset by the following disadvantages: low fracture toughness, limiting applications in high load-bearing areas. some types cannot be finished and polished at the same visit they are placed. some types are vulnerable to acid erosion.
What is the principal advantage of using glass-ionomer cement?
Resin-modified glass-ionomer cements have significantly enhanced physical properties along with the great advantage of rapid, “on command” hardening by concentrated visible light exposure.
What is the main advantage of glass ionomer filling material?
As fluoride is part of the silicate glass-powder, glass ionomer fillings have the unique advantage of being able to slowly release fluoride over time to the surrounding area – helping prevent future cavities and protect your teeth. There are no negative health effects associated with the use of glass ionomers.
What is an advantage of glass ionomer restorative material?
Glass ionomer cements exhibit a number of advantages over other restorative materials. By bonding a restorative material to tooth structure, the cavity is theoretically sealed, protecting the pulp, eliminating secondary caries and preventing leakage at the margins.
What is the advantage of using glass-ionomer cement quizlet?
What are advantages and disadvantages of glass ionomer cements? Advantages: 1. Chemical adhesion to tooth and metal.
What are the properties of glass ionomers?
In contrast, glass-ionomer cements (GICs) have interesting properties such as biocompatibility, bioactivity, fluoride release, excellent coefficient of linear thermal expansion/contraction and modulus of elasticity, as well as being the only restorative material capable of chemically bonding to the tooth structure 6 .
What is Type 2 glass-ionomer cement?
RESTORATIVE+ Glass Ionomer Cement Type II is a radiopaque glass powder and organic polymer liquid Application: Glass Ionomer Cement Type II is used for restoration of primary teeth core build up and restoration of class III, V and limited class I cavities.
What is glass-ionomer cement made of?
Glass polyalkenoate cements, more commonly known as glass-ionomers, are made of calcium or strontium alumino-fluoro-silicate glass powder (base) combined with a water soluble polymer (acid). Glass-ionomers were invented in 1969 and reported by Wilson and Kent in the early 1970s.
What are the 9 types of GIC?
Type 9 Glass Ionomer CementAmmdent GI Core Type 9 Glass Ionomer Cement.GC Fuji Gold Label Type 9 Glass Ionomer Cement Big Pack.GC Fujicem Resin Reinforced Glass Ionomer Luting Cement. ... Out of stock. ... DTech Restore Glass GIC Glass Ionomer Restorative Cement. ... Shofu Zirconomer Reinforced Glass Ionomer Cement.More items...
What is glass-ionomer cement in dentistry?
A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (calciumaluminofluorosilicate glass) and polyacrylic acid, an ionomer.
What are advantages to using a glass ionomer and what class restorations do you use it in?
One of the advantages of glass ionomers is the true bonding between materials and dentin/enamel; thus they have been widely used for Class V restorations which have high requirements in adhesion, for Class II and Class III restorations in deciduous teeth, for luting of crowns, and they also can be used as bases or ...
What is glass ionomer restorative material?
Glass-ionomer cements (GICs) are mainstream restorative materials that are bioactive and have a wide range of uses, such as lining, bonding, sealing, luting or restoring a tooth.
How long does a glass ionomer filling last?
Glass ionomers release fluoride, which can help protect the tooth from further decay. However, this material is weaker than composite resin and is more susceptible to wear and prone to fracture. Glass ionomer generally lasts five years or less with costs comparable to composite resin.
Which filling is best for teeth?
Composite fillings are the most widely used dental filling material. They're made of glass or quartz in resin. Your dentist may choose a composite filling if the size of your cavity is small to medium, or if your tooth gets a lot of chewing action.
What is a glass ionomer filling?
Glass Ionomer Fillings are a material made from acrylic and a component of glass – ‘flouroaluminosilicate’. They can be bonded to your tooth using a chemical reaction which makes the bond very strong. The filling is bonded straight onto the tooth, and no real preparation is required before you are fitted with one.
How long does a glass ionomer filling last?
Some dentists maintain that glass ionomer fillings are not very strong and last only 5 years or so.
Can you use glass ionomer fillings on children?
Often no preparation is needed before you are fitted with a glass ionomer filling. This means that it is a popular choice for use when children have cavities that need filling. They release fluoride over time, thus strengthening your tooth and maintaining good dental health.
Why is glass ionomer cement used?
Due to a number of qualities-such as biocompatibility and low toxicity, good adhesion to enamel and dentin, pulp protection, reduced volumetric shrinkage , and the release of fluoride ions (i.e., caries-protection)glass ionomer cements are used in wide applications in dental medicine [6, 7].
What is GIC cement?
Glass ionomer cements (GIC) also known as polyalkenoate cements have been used as dental luting material for decades. However, there are certain limitations with respect to its biomechanical properties. Therefore, the aim of current investigation was to synthesize and characterize silver nanoparticles (SNP) using a green approach and incorporating the synthesized SNP in commercially available GIC formulation. Methodology: SNP were synthesized using a green approach of chemical reduction and analysed by spectroscopy and Transmission Electron microscopy. SNP reinforced GIC in 10, 30 and 50% formulations were assessed for microhardness, compressive strength, color stability and Nano-computerized tomography was used for pore analysis. Results: Results from UV-Vis spectroscopy, Dynamic Light Scattering, Zeta potential, Transmission Electron Microscopy and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy revealed that the particles were spherical and polydisperse in nature with an average diameter of 122 nm. The synthesized particles had a positive surface charge of 74 mV. Their incorporation into the Glass ionomer cement (GIC) revealed non-significant results on microhardness and compressive strength. Significant color change was observed and Nano-CT revealed pores within the set cements. Conclusion: Nevertheless, the biosynthesized silver nanoparticles have much broader clinical application and can be used to reinforce properties of existing dental biomaterials. They can be conveniently synthesized by the biogenic route adapted in the current investigation. However, their addition to the luting cement still warrants further in-depth investigation.
What is dual cured cement?
Dual-cured cements are recommended for the cementation of thicker restorations where light curing alone would not be able to penetrate adequately.
What does powder do to dental cement?
The addition of powder to dental cement creates a secondary consistency that increases the viscosity and strength of the cement.
How long does zinc phospate cement take to mix?
Zinc phospate cements are dispensed in 4-6 portions on one end of a glass slab and are incorporated in small increments into the liquid, with each increment mixed for 10-15 seconds.
Which element has inferior strength and high solubility?
Cements have inferior strength and high solubility.
What is the thickness of a high strength base liners?
High strength base liners provide protection from the thermal conduction of metallic restorations. They are placed in a thickness of 0.5 mm or greater.
