
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal.
What is an example of a reversible reaction?
What is a reversible reaction at equilibrium? Chemical equilibrium is the state of a reversible reaction where the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. While a reaction is in equilibrium the concentration of the reactants and products are constant. Click to see full answer.
When does a chemical reaction reach equilibrium?
Apr 08, 2011 · A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction where the reactants form products that, in turn, react together to give the reactants back. Reversible reactions will reach an equilibrium point where the concentrations of the reactants and products will no longer change.
How to improve balance and equilibrium?
May 08, 2017 · Firstly, let’s clarify what equilibrium is. When we have a reversible reaction taking place in a closed system – that is, one where no substances are being added or lost – at the beginning of the reaction we will have only the reactants.
What is equilibrium response?
A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions. In other words, the reactants and products of the reaction may reverse roles. Fact: Remember that → → implies that A goes to B and cannot become A again. ⇌ ⇌ implies that the reaction is reversible. A can go to B and B can go to A.
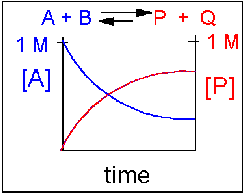
What is a reversible equilibrium reaction?
Reversible reactions that happen in a closed system eventually reach equilibrium. At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products do not change. But the forward and reverse reactions have not stopped - they are still going on, and at the same rate as each other.
What are the characteristics of a reversible reaction at equilibrium?
Chemical equilibrium exists in reversible reactions only. At equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction. At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant.Apr 1, 2020
What is a reversible reaction simple definition?
noun Chemistry. a reaction that, depending on ambient conditions, can proceed in either of two directions: the production of the reaction products from the reactants, or the production of the original reactants from the formed reaction products.
What is a reversible reaction BBC Bitesize?
In some chemical reactions, the products of the reaction can react together to produce the original reactants . These reactions are called reversible reactions .
What character is a reversible reaction?
A reversible reaction can never proceed to completion. This is because a reversible reaction is an equilibrium reaction in which both forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate. Was this answer helpful?
What is a forward reaction and reverse reaction in equilibrium?
Key Concepts and Summary A reaction is at equilibrium when the amounts of reactants or products no longer change. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic process, meaning the rate of formation of products by the forward reaction is equal to the rate at which the products re-form reactants by the reverse reaction.
What is a reversible reaction Class 10?
A reversible reaction is defined as a chemical reaction where the reactants and the products react together to give the reactants back.
What are the examples of reversible reaction?
A reversible reaction is a reaction in which the conversion of reactants to products and the conversion of products to reactants occur simultaneously. One example of a reversible reaction is the reaction of hydrogen gas and iodine vapor to from hydrogen iodide.
What happens when a reaction is reversible?
In a non-reversible reaction this would be about the long and short of it, but when a reaction is reversible the products can also react to produce the reactants again. After a time, a reversible reaction in a closed system can reach what we call a ‘dynamic equilibrium’.
What happens to equilibrium when pressure is decreased?
Conversely, if we decrease the pressure, the equilibrium will respond to increase the pressure, and will therefore favour the side of the reaction with more gas molecules. As a caveat, there are plenty of reactions where we actually have the same number of gaseous molecules shown in the balanced equation.
What is the difference between forward and backwards reaction?
This is where the forwards reaction (reactants reacting to produce the products) and the backwards reaction (products reacting to reform the reactants) are occurring at the same rate. This means that the amounts of the reactants and the products remain constant, despite the fact that both reactions are still ongoing.
Why do we use catalysts in chemical reactions?
Using one doesn’t affect the position of equilibrium in any way, however. This is because it speeds up both the forwards and backwards reaction by an equal amount, so overall neither side of the reaction is favoured by using one.
What happens when you increase the temperature?
When we increase the temperature, the reaction will favour whichever reaction is endothermic to take in heat and reduce the temperature. On the other hand, if we decrease the temperature, the exothermic reaction will be favoured, as this will give out heat and increase the temperature.
What is the Haber process?
It’s actually more important for non-chemists than you might think. The Haber process, a reaction in which hydrogen and nitrogen are combined to make ammonia, is an example of a reaction which takes advantage of some of the chemistry we’ve discussed here.
What happens to the size of the hole when both shovels are shoveling?
If both are shovelling at the same rate, then the size of the hole and the size of the pile of dirt outside the hole will remain constant , despite the fact that both of them are still shovelling dirt back and forth. Dynamic equilibrium is much the same.
Reversible Reactions
Some reactions can take place in two directions. In one direction the reactants combine to form the products. This is called the forward reaction forward reaction. In the other direction, the products react to form the reactants again. This is called the reverse reaction reverse reaction.
Definition: A reversible reaction
A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions. In other words, the reactants and products of the reaction may reverse roles.
What is a reversible reaction?
Reversible reactions. Many reactions are irreversible. But in a reversible reaction, the products can react to produce the original reactants. At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products do not change. Part of. Chemistry (Single Science) Chemical reactions and tests.
Why does a reaction reach equilibrium sooner?
If a catalyst is used, the reaction reaches equilibrium much sooner, because the catalyst speeds up the forward and reverse reactions by the same amount.
What happens when a chemical reaction happens in a closed system?
If a chemical reaction happens in a container where none of the reactants or products can escape , you have a closed system. Reversible reactions that happen in a closed system eventually reach equilibrium.
Do forward and reverse reactions stop?
But the forward and reverse reactions have not stopped - they are still going on, and at the same rate as each other. Imagine walking the wrong way on an escalator - at the same speed as the escalator but in the opposite direction. Your legs are still walking forwards, and the escalator continues to move backwards.
What does it mean when a reaction is going forward and backwards?
That means that the forward reaction and the backward/reverse reaction are happening at the same rate as each other. This is why we often refer to the state as dynamic equilibrium. Both reactions do continue at equilibrium, but there is no overall change to concentrations.
What happens when we start a reaction with the reactants?
Let’s consider what happens when we start the reaction with the reactants: hydrogen and nitrogen, both in the gas state. Under suitable conditions the reaction proceeds with some nitrogen and hydrogen molecules reacting to become ammonia molecules.
What is the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen to produce ammonia?
You probably recognise this reaction as the Haber process, the industrial process used to manufacture ammonia.
What happens to energy in reversible reactions?
Energy changes in reversible reactions. If a reaction is exothermic in one direction, it will be endothermic in the other direction. The same amount of energy is transferred in both the forwards and reverse reaction.
What happens when a reversible reaction happens in a closed container?
Dynamic equilibrium. When a reversible reaction happens in a closed container, it reaches a dynamic equilibrium. At equilibrium: the forward and backward reactions are still happening. the forward and backward reactions have the same rate of reaction. the concentrations of all the reacting substances remain constant.
What is the term for the reaction that produces the original reactants?
In some chemical reactions, the products of the reaction can react together to produce the original reactants. These reactions are called reversible reactions. They can be represented in the following way:
What is the name of the white solid that breaks down when heated?
Ammonium chloride is a white solid. It breaks down when heated, forming ammonia and hydrogen chloride. When these two gases are cool enough, they react together to form ammonium chloride again.
Which reaction goes to the right?
the forward reaction is the one that goes to the right. the backward reaction is the one that goes to the left. The reaction mixture may contain reactants and products, and their proportions may be changed by altering the reaction conditions.
Is a chemical reaction reversible?
Chemical reactions are reversible and may reach a dynamic equilibrium. The position of equilibrium of a reversible reaction can be altered by changing the reaction conditions. Part of. Combined Science. The rate and extent of chemical change.
