What does stratified epithelium do?
The primary function of stratified epithelium is protection. As the epithelium has multiple layers, it protects the underlying tissues and internal organs against several physical and microbial damages. The columnar epithelium in the eyes protects the conjunctiva of the eyes and other delicate structures in the eyes.
What are two ways to classify epithelium tissue?
Types of epithelium tissue:
- simple epithelium tissue
- compound epithelium tissue
- Specialized Epithelium
What are the 4 types of epithelial tissue?
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscle Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
What are the four essential functions of epithelial tissue?
Further, they are of three types:
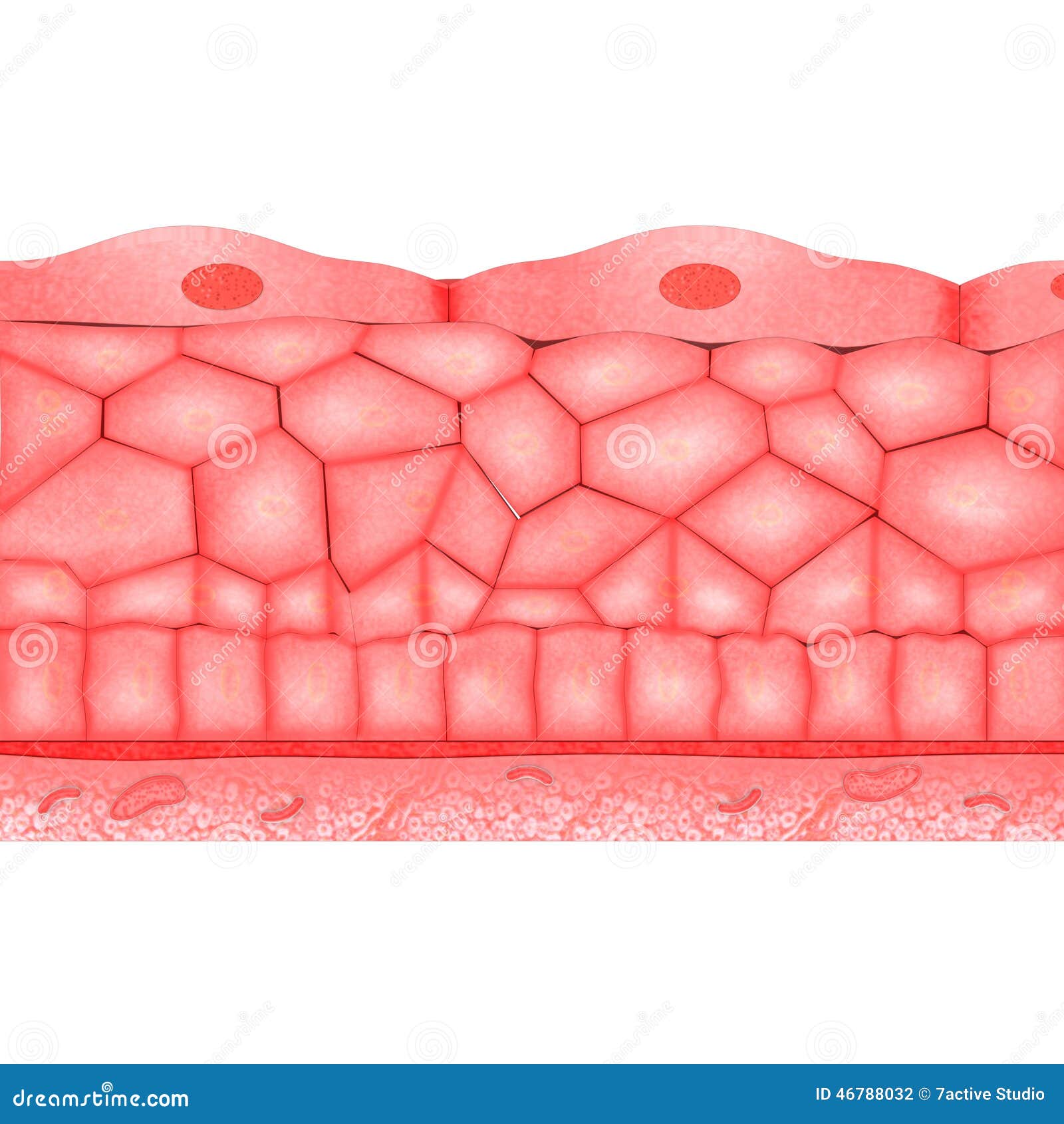
- Stratified Squamous Epithelium: They mainly provide protection against abrasion and water loss. They are mainly found in the oral cavity, esophagus, larynx, etc. ...
- Stratified Columnar Epithelium: Their main functions are secretion and protection. ...
- Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Their main function is protective in nature. ...

What is the basis for the classification of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is classified based on the cell shape and the number of cell layers. Cell layers: simple (one layer), stratified (multiple layers).
How is stratified epithelium organized and classified?
2 – Cells of Epithelial Tissue: Simple epithelial tissue is organized as a single layer of cells and stratified epithelial tissue is formed by several layers of cells. Epithelial tissue is classified based on the shape of the cells present and the number of cell layers present. Figure 4.2.
What are the 4 factors considered in classifying epithelium?
The epithelium is classified according to the cells (squamous, cuboidal, columnar), the number of layers, and other unique characteristics either due to function (transitional epithelium allowing distention) or appearance (pseudostratified epithelium giving a false impression of multiple layers).
What are the characteristics of stratified epithelial tissue?
Stratified epithelia contain two or more layers of cells. The function of this type of epithelium is mostly protective - the higher the number of layers, the more protective it is. It is good at withstanding abrasion. This type of epithelium is constantly renewing itself.
How are stratified epithelia organized and classified quizlet?
epithelium is classified by arrangement as simple (one layer) or stratified (more than one layer) and by cell shape as squamous, cuboidal, or columnar. the terms donating the cell shape and arrangement are combined to describe the epithelium fully.
How would you classify epithelial cells?
The three principal shapes associated with epithelial cells are—squamous, cuboidal and columnar. Squamous epithelium is composed of cells that are wider than their height (flat and wide).
What is the main purpose of stratified epithelium?
It provides protection against germs invading beneath tissue and/or prevention of water loss are two of the protection mechanisms of stratified epithelium.
How do you tell if a tissue is stratified?
Structure. The biggest difference between simple and stratified tissue is that simple tissue is one layer thick while stratified tissue is multi-layered. All epithelial tissue rests on a basement membrane, which is a thin protective membrane located on the outside of the tissue.
Which of the following describes stratified epithelium?
Which of the following describes stratified epithelium? It is highly vascularized. It is located in areas where filtration is important. It is lines the urinary bladder.
How are epithelial cells classified by how they are layered?
The types of epithelia are classified by the shapes of cells present and the number of layers of cells. Epithelia composed of a single layer of cells is called simple epithelia; epithelial tissue composed of multiple layers is called stratified epithelia.
What level of Organisation is the epithelium?
The organ level of organization is when two or more tissues work together for a specific function. For example, the bladder consists of an inner lining of epithelial tissue, bound by various connective tissues to (smooth) muscle.
What is the structure and classification of tissue?
A tissue is a group of cells, in close proximity, organized to perform one or more specific functions. There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
1. What are Epithelial Tissues?
They are thin tissue that cover all the exposed surface of the body. They cover various surfaces of body parts like inner lining of mouth, digestiv...
2. Explain different Types of Epithelial Tissues?
Epithelial tissue is classified on the basis of shape, layer and function:A. On the Basis of Shape:Squamous EpithelialCuboidal EpithelialColumnar E...
3. Write Three Major Functions of Epithelial Tissue?
Epithelial tissue perform crucial functions, some of their major functions are:They help in the protection process.They help in the secretion proce...
4. Which epithelial tissue is not having a basement membrane?
It is the urothelium also known as the transitional epithelium, that is doesn’t have a basement membrane. The two unique features it possesses are...
5. From which germ layer is epithelial tissue derived?
For the exact case, we cannot classify or differentiate from which germ layer the epithelial tissue is derived. Since it is the epithelial tissue c...
6. Do epithelial tissues contain blood vessels?
Epithelial tissues don’t contain blood vessels. It is the connective tissues underlining the epithelial tissues possess blood vessels. We can say i...
7. What is the unique characteristic of epithelial tissue?
The epithelial tissue is considered the major functional cell in the glands. The tissue covers the body through lining body cavities. However, if w...
8. Where does cuboidal epithelium tissue located in our body?
There are two types of cuboidal epithelium tissue. They are:Simple cuboidal epithelium Stratified cuboidal epithelium Simple cuboidal epithelium ti...
What is the function of stratified columnar epithelium?
Stratified Columnar Epithelium: Their main function is secretive and protective process. They are present in the covering of conjunctiva of the eye. c. Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Their main function is protective in nature. They mainly line the excretory ducts of the sweat glands, large ducts of excretory glands.
What are some examples of cells that are secretive, absorptive, or excretory?
Examples: collecting ducts of the kidney, pancreas, and salivary gland. c. Simple Columnar Epithelium: These types of cells can be secretive, absorptive, or excretory in nature.Some of these tissues contain goblet cells and are referred to as simple glandular columnar epithelium.
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue perform crucial functions, some of their major functions are: 1 They help in the protection process. 2 They help in the secretion process. 3 They also act as the receptors during various sensational activities.
What are the structures that connect epithelial cells to each other called?
The cells which form epithelial tissue are closely attached to each other through a structure called tight junctions.
What is the function of receptors?
Receptor Function: Epithelial cells can receive receptor i.e sensory information and they convert them into neural signals. Example of such epithelial tissue is olfactory nasal mucosa, they detect the odors coming from outside and further transmit these information to the central nervous system.
Which type of tissue is taller in height than width?
c. Columnar Epithelium: This type of tissues are taller in height than width i.e column like shape. They are further classified into two types i.e ciliated columnar epithelium and glandular columnar epithelium.
Which epithelium is responsible for the absorption of nutrients?
Absorption Process: Absorption process is mainly performed by surface epithelia with the help of microvilli as they increase surface area for absorption process. Another example is columnar epithelium in the small intestine. Their main function in absorption of nutrients in the digestive tract.
How are cells in the epithelium arranged?
Polarity- Epithelium is arranged so there is one free surface ( apical surface) and one attached surface ( basal surface) Cellular nature – Cells in epithelium fit closely together side by side and sometimes atop each other to form sheets of cells. These sheets are held together by specialized junctions.
What is the tissue that covers the body?
epithelial tissue. An epithelium is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a cavity. Epithelium forms the coverings of surfaces of the body such as Skin, Mouth, Nasal cavity (Ectodermal), Lines internal body surface such as GI tract, Lungs, Urinary bladder and vagina (Endodermal) and Lining of blood vessels, ...
What is transitional epithelium?
Transitional epithelium: cells are rounded and can slide across one another to allow stretching. 2. Classification scheme of epithelial tissue on the basis of shape. i. Squamous epithelium: (Latin, squama- scale) flat, thin, scale-like cells, eg. Endothelium, mesothelium, pericardium, peritonium.
What is the classification scheme of epithelial tissue?
Classification scheme of epithelial tissue: Typically epithelial tissue is classified on the basis of arrangement and shape of cells. For naming the tissue types, the arrangement of the cells is stated first, then the shape, and is followed by “epithelium” to complete the naming. For example; Simple Squamous Epithelium.
Which layer of connective tissue is supported by the basal surface?
Supported by connective tissue – Attachment to a layer of connective tissue at the basal surface forms a layer called the basement membrane, an adhesive layer formed by secretions from the epithelial cells and the connective tissue cells. Avascular – Epithelium typically lacks its own blood supply. Regeneration – Epithelium cells can regenerate ...
Is pseudostratified epithelium single layer?
Pseudo-stratified epithelium: Pseudo-stratified epithelium appears to be more than one cell thick since the nuclei lie at different heights, but in fact it is single layer of cells, in contact with the basement membrane. iv. Transitional epithelium: 2. Classification scheme of epithelial tissue on the basis of shape.
What are the four types of tissues in animals?
Ans. There are four types of tissues in animals. These are the connective tissues, the muscle tissues, the nervous tissues and the epithelial tissues.
What are the four major categories of tissues?
The classification of tissues in animals falls under four major categories. These are: Connective tissues. Muscle tissues. Nervous tissues. Epithelial tissues. Before you learn more about what is the function of tissue, here’s a quiz for you to try:
What is connective tissue?
Connective Tissues. In connective tissue, a group of cells separated by a non-living extracellular matrix combine to form a tissue. Connective tissues help provide mechanical strength, shape and rigidity to the organs and keep them in place.
What are the three types of connective tissue?
Further, there are three types of connective tissues. These are: Skeletal Connective Tissue. Fluid Connective Tissue. Fibrous Connective Tissue. Connective tissues have several different functions in the human body, namely: They provide insulation and protection against cold to the body.
What is the tissue that covers the body?
Epithelial Tissue. Epithelial tissues consist of cells that form the external covering of the body. These covers the organ surfaces such as the skin, the airways, the inner walls of our digestive tract as well as the reproductive tract.
What is the epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissues consist of cells that form the external covering of the body. These covers the organ surfaces such as the skin, the airways, the inner walls of our digestive tract as well as the reproductive tract.
What are the epithelial tissues that protect us from pathogens?
Moreover, epithelial tissues such as the ones beneath our skin help us in sensory reception and protect us against pathogens and physical trauma. They also secrete hormones, mucus and enzymes from various endocrine organs.
