.jpg)
What Causes Low Sodium in Blood?
- Excess Water Intake. The sodium levels in our blood become depleted as we sweat, and we may overcompensate by drinking too much water.
- Dehydration. On the flip side, we can easily become dehydrated by not drinking sufficient amounts of water. ...
- Hormonal Changes. ...
- Drugs. ...
- Severe Diarrhea or Vomiting. ...
- Chronic Illness. ...
- Certain medications. ...
- Heart, kidney and liver problems. ...
- Syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH). ...
- Chronic, severe vomiting or diarrhea and other causes of dehydration. ...
- Drinking too much water. ...
- Hormonal changes. ...
- The recreational drug Ecstasy.
What are the dangers of low sodium?
Those include:
- Bowel diseases — People with ulcerative colitis, celiac disease and irritable bowel syndrome do not absorb salt well. ...
- Adrenal insufficiency — This is also called Addison’s disease and happens when the adrenal glands do not make enough cortisol. ...
- Hypothyroidism — Thyroid hormones help control metabolism and the kidneys’ ability to resorb salt. ...
What happens if low sodium is not corrected?
While your body works to maintain tight control over its sodium level, you can sometimes lose too much sodium via sweat or due to illness. Low sodium can have life-threatening effects if left untreated. Seeking medical attention before the problem becomes severe can help keep your body functioning optimally. Sodium Levels
How does low sodium affect a person?
You may experience low sodium symptoms daily or just once in a while. At times any of these low sodium symptoms can be severe: Abdominal pain or cramping; Bloating; Body aches; Changes in mood, personality or behavior; Difficulty with memory, thinking, talking, comprehension, reading or writing; Dizziness; Headache; Impaired balance and coordination
What to do if you have low sodium levels?
What to Do If You Have Low Sodium Levels?
- Causes and Symptoms. The most common causes of low sodium levels in healthy individuals are excessive sweating, vomiting and diarrhea.
- Restrict Fluid Intake. If you exhibit signs of hyponatremia, the first treatment step is to monitor fluid intake. ...
- Intravenous Fluids. ...
- Medication. ...
- Monitor Drugs. ...
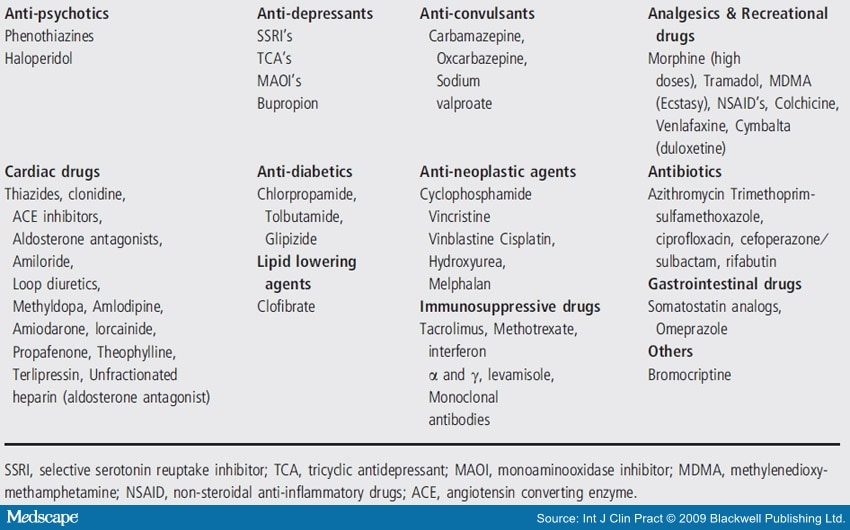
How do you raise your sodium level?
Options include:Intravenous fluids. Your doctor may recommend IV sodium solution to slowly raise the sodium levels in your blood. ... Medications. You may take medications to manage the signs and symptoms of hyponatremia, such as headaches, nausea and seizures.
What disease is associated with low sodium?
In hyponatremia, the level of sodium in blood is too low. A low sodium level has many causes, including consumption of too many fluids, kidney failure, heart failure, cirrhosis, and use of diuretics. Symptoms result from brain dysfunction.
Should I eat more salt if my sodium is low?
Our bodies need a small amount of salt for a variety of functions, such as the working of nerves and muscles. However, there is enough sodium present in all foods that a lack of sodium does not generally cause any problems in these areas. It is rarely necessary to add extra salt to food.
What happens when body is low on sodium?
When sodium levels in the blood become too low, it leads to hyponatremia, causing symptoms that include lethargy, confusion, and fatigue. Hyponatremia is the most common electrolyte disorder — research suggests that approximately 1.7% of people in the United States have the condition.
What causes sodium to be lowered?
Heart, kidney and liver problems. Congestive heart failure and certain diseases affecting the kidneys or liver can cause fluids to accumulate in your body, which dilutes the sodium in your body, lowering the overall level. Syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH).
What happens when the sodium in your blood is abnormally low?
Hyponatremia occurs when the concentration of sodium in your blood is abnormally low. Sodium is an electrolyte, and it helps regulate the amount of water that's in and around your cells.
What is the normal sodium level?
A normal blood sodium level is between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). Hyponatremia occurs when the sodium in your blood falls below 135 mEq/L. Many possible conditions and lifestyle factors can lead to hyponatremia, including: Certain medications. Some medications, such as some water pills (diuretics), ...
How to prevent low sodium?
Getting treatment for conditions that contribute to hyponatremia, such as adrenal gland insufficiency, can help prevent low blood sodium. Educate yourself. If you have a medical condition that increases your risk of hyponatremia or you take diuretic medications, be aware of the signs and symptoms of low blood sodium.
Why does my body lose sodium?
Chronic, severe vomiting or diarrhea and other causes of dehydration. This causes your body to lose electrolytes, such as sodium, and also increases ADH levels. Drinking too much water. Drinking excessive amounts of water can cause low sodium by overwhelming the kidneys' ability to excrete water.
Why do older people have hyponatremia?
Older adults may have more contributing factors for hyponatremia, including age-related changes, taking certain medications and a greater likelihood of developing a chronic disease that alters the body's sodium balance.
How long does it take for sodium to drop?
In chronic hyponatremia, sodium levels drop gradually over 48 hours or longer — and symptoms and complications are typically more moderate. In acute hyponatremia, sodium levels drop rapidly — resulting in potentially dangerous effects, such as rapid brain swelling, which can result in a coma and death.
What does it mean when your sodium is low?
The results of this test will help your doctor determine the cause of your low blood sodium: If your blood sodium levels are low but your urine sodium levels are high, your body is losing too much sodium. Low sodium levels in both your blood and your urine mean your body isn’t taking in enough sodium. There may also be too much water in your body.
How to treat low sodium?
It may include: cutting back on fluid intake. adjusting the dosage of diuretics. taking medications for symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and seizures. treating underlying conditions.
What is the sodium level in your blood?
In other words, there’s either too much water or not enough sodium in your blood. Normally, your sodium level should be between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter.
How to prevent low sodium levels?
Prevention of low blood sodium. Keeping your water and electrolyte levels in balance can help prevent low blood sodium. If you’re an athlete, it’s important to drink the right amount of water during exercise. You should also consider drinking rehydration beverages like Gatorade or Powerade.
Why is sodium important?
Sodium is an essential electrolyte that helps maintain the balance of water in and around your cells. It’s important for proper muscle and nerve function. It also helps maintain stable blood pressure levels. Insufficient sodium in your blood is also known as hyponatremia. It occurs when water and sodium are out of balance.
What happens if your sodium levels drop?
If they drop very quickly, your symptoms may be more severe. Losing sodium quickly is a medical emergency. It can cause loss of consciousness, seizures, and coma. Common symptoms of low blood sodium include: weakness. fatigue or low energy.
What is the best way to check for low sodium?
A blood test can help your doctor check for low sodium levels. Even if you don’t have symptoms of low blood sodium, your doctor may order a basic metabolic panel. This tests the amounts of electrolytes and minerals in your blood. A basic metabolic panel is often part of a routine physical.
What causes low sodium levels?
A number of medical conditions or circumstances can lead to low sodium levels including: Adrenal gland disease. Burns. Certain medications such as diuretics. Cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver. Congestive heart failure.
Why is my sodium level low?
There are several common causes of low sodium, including diarrhea, excessive sweating, and vomiting. Medications that are prescribed to treat high blood pressure or fluid retention, called diuretics, can lead to low sodium levels.
What are the risk factors for low sodium?
A number of factors increase the risk of developing low sodium. Not all people with risk factors will get low sodium. Risk factors for low sodium include:
What are the potential complications of low sodium?
Complications of untreated or poorly controlled low sodium can be serious, even life threatening in some cases. You can help minimize your risk of serious complications by following the treatment plan you and your health care provider design specifically for you. Complications of low sodium include:
What are the three types of hyponatremia?
Electrolytes are critical for proper functioning of all body systems. There are three types of hyponatremia: euvolemic, hypervolemic and hypovolemic. Euvolemic hyponatremia occurs when your body’s water content is normal but your sodium level declines. Hypervolemic hypona tremia is when water is increased relative to sodium levels.
How do you know if you have low sodium?
Common symptoms of low sodium. You may experience low sodium symptoms daily or just once in a while. At times any of these low sodium symptoms can be severe: Abdominal pain or cramping. Bloating. Body aches. Changes in mood, personality or behavior. Difficulty with memory, thinking, talking, comprehension, reading or writing.
What happens if you have low sodium?
Seek immediate medical care (call 911) if you have serious symptoms of low sodium, such as a change in mental status (con fusion or hallucinations ); a change in level of consciousness, ...
What does it mean when you have low sodium?
Low blood sodium (hyponatremia) occurs when you have an abnormally low amount of sodium in your blood or when you have too much water in your blood. Low blood sodium is common in older adults, especially those who are hospitalized or living in long-term care facilities.
What are the causes of hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia is more common in older adults because they're more likely to take medications or have medical conditions that put them at risk of the disorder. These risk factors include: 1 Drugs that make you urinate more (diuretics) 2 Some types of antidepressants 3 Carbamazepine, an anti-seizure medication 4 Underactive thyroid or adrenal glands 5 Decreased function of the kidneys, liver or heart 6 Certain cancers, including lung cancer 7 Certain illnesses, such as pneumonia or urinary tract infections, that can cause dehydration
Why is hyponatremia more common in older adults?
Hyponatremia is more common in older adults because they're more likely to take medications or have medical conditions that put them at risk of the disorder. These risk factors include: Drugs that make you urinate more (diuretics) Some types of antidepressants. Carbamazepine, an anti-seizure medication.
How to treat hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia treatments may include changing a medication that affects your sodium level, treating the underlying disease, changing the amount of water you drink or changing the amount of salt in your diet.
Why is hyponatremia a problem?
What causes hyponatremia? In general, too much water in your body is usually the main problem and this dilutes the sodium levels. Much less frequently, hyponatremia is due to significant sodium loss from your body. Too much water in your body causes your blood to become “watered down.”.
How to treat hyponatremia?
If you have mild symptoms, your doctor makes small adjustments to your therapy to correct the problem. This usually involves restricting water intake, adjusting medications and removing or treating the causes.
What is hyponatremia in labs?
What is hyponatremia? Hyponatremia is usually discovered on laboratory tests as a lower than normal sodium level in the blood. It will appear as sodium or Na+ in your lab results. Actually, the main problem in the vast number of situations is too much water that dilutes the Na+ value rather than too much sodium.
What happens if you have hyponatremia?
In many cases, hyponatremia causes extra water to move out of the bloodstream and into body cells, including brain cells. Severe hyponatremia causes this to occur quickly, resulting in swollen brain tissue. If left untreated, complications can include: 1 Mental status changes 2 Seizures 3 Coma 4 Death
Why is water watered down?
Too much water in your body causes your blood to become “watered down.”. A good example is people who run in long races or run on hot days. They lose both salt and water in their sweat and often replace these losses with mostly water. This combination can be deadly because it dilutes the remaining sodium in the body.
What is the best medication for hyponatremia?
Certain newer medications, like tolvaptan (Samsca®), may be used to correct blood sodium levels. Treatment to correct any underlying medical problems – like congestive heart failure (when poor heart function causes fluid to build up in the body) – is also used to improve hyponatremia.
Can you lose too much sodium?
It’s also possible to lose too much sodium from your body. Medications, like diuretics, can cause your kidneys to increase the amount of sodium excreted in urine. Medical problems like diarrhea may cause excessive sodium loss if left untreated. Chronic or binge alcohol consumption can cause people to lose too much sodium through increased urination and vomiting. You can have hyponatremia without feeling dehydrated or volume depleted. This is most often the case in hospitalized patients.
What causes low sodium levels in the blood?
Conditions that cause low sodium levels in the blood usually also cause decreased levels of chloride, per the U.S. National Library of Medicine. In addition, hypochloremia can result from metabolic alkalosis or chronic respiratory acidosis, conditions that affect the acidity level of the blood, Dr. Weiner says.
What are the health conditions that can cause hyponatremia?
Download the MyPlate app to do the job, so you can stay focused and achieve your goals! A range of health conditions can cause hyponatremia, according to the Mayo Clinic, including: Heart, kidney and liver problems. Hormonal problems like Addison's disease or thyroid problems.
How to measure sodium and chloride levels?
Sodium and chloride levels can be measured through a blood test. According to the U.S. National Library of Medicine, normal blood sodium levels are between 135 to 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). When levels fall lower than that, it is called hyponatremia. Advertisement.
What causes water to be in urine?
Hormonal problems like Addison's disease or thyroid problems. Syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH), a condition in which elevated levels of this hormone cause your body to retain water instead of excreting it normally in your urine.
What are the symptoms of hyponatremia?
The Mayo Clinic recommends you seek emergency medical attention right away if you experience any of the severe symptoms of hyponatremia, such as: 1 Nausea 2 Vomiting 3 Confusion 4 Seizures or loss of consciousness
Can you get hyponatremia from losing sodium?
Less commonly, hyponatremia can occur if you lose a large amount of sodium from your body. "People who are at risk of hyponatremia are people who, for whatever reason, are either taking in a whole lot of water or people who can't get rid of water," explains Daniel Weiner, MD, FASN, an associate professor at Tufts University School ...
Can burns cause hyponatremia?
People with burns across a large area of the body may also develop hyponatremia as well, notes the U.S. National Library of Medicine. Advertisement. Certain medications can also lead to low blood sodium levels, including some antidepressants, MDMA (Ecstasy), pain medications and thiazide diuretics, which are commonly used to treat high blood ...

Overview
- Hyponatremia occurs when the concentration of sodium in your blood is abnormally low. Sodium is an electrolyte, and it helps regulate the amount of water that's in and around your cells. In hyponatremia, one or more factors — ranging from an underlying medical condition to drinking too much water — cause the sodium in your body to become diluted. W...
Symptoms
- Hyponatremia signs and symptoms may include: 1. Nausea and vomiting 2. Headache 3. Confusion 4. Loss of energy, drowsiness and fatigue 5. Restlessness and irritability 6. Muscle weakness, spasms or cramps 7. Seizures 8. Coma
Causes
- Sodium plays a key role in your body. It helps maintain normal blood pressure, supports the work of your nerves and muscles, and regulates your body's fluid balance. A normal blood sodium level is between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). Hyponatremia occurs when the sodium in your blood falls below 135 mEq/L. Many possible conditions and lifestyle factors can lead to h…
Risk Factors
- The following factors may increase your risk of hyponatremia: 1. Age.Older adults may have more contributing factors for hyponatremia, including age-related changes, taking certain medications and a greater likelihood of developing a chronic disease that alters the body's sodium balance. 2. Certain drugs.Medications that increase your risk of hyponatremia include thiazide diuretics as …
Complications
- In chronic hyponatremia, sodium levels drop gradually over 48 hours or longer — and symptoms and complications are typically more moderate. In acute hyponatremia, sodium levels drop rapidly — resulting in potentially dangerous effects, such as rapid brain swelling, which can result in a coma and death. Premenopausal women appear to be at the greatest risk of hyponatremia-relat…
Prevention
- The following measures may help you prevent hyponatremia: 1. Treat associated conditions.Getting treatment for conditions that contribute to hyponatremia, such as adrenal gland insufficiency, can help prevent low blood sodium. 2. Educate yourself.If you have a medical condition that increases your risk of hyponatremia or you take diuretic medications, be aware of …