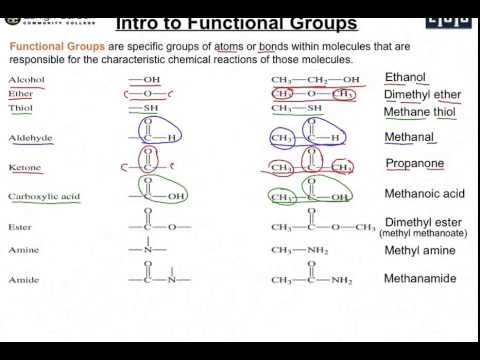
Functional groups are groups of one or more atoms with distinctive chemical properties regardless of what is attached to them. The atoms of functional groups are bound by covalent bonds with one another and with the rest of the molecule. Functional groups in a coordination complex which bind to a central atom are called ligands.
What are the properties of a functional group?
Properties of Functional Groups. A functional group can participate in specific chemical reactions. Some of the important functional groups in biological molecules include: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl groups. These groups play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins ...
What is the most common functional group?
The names of the six most important functional groups are:
- Hydroxyl.
- Carbonyl.
- Carboxyl.
- Amino.
- Sulfhydryl.
- Phosphate.
What are the 4 functional groups in biology?
- Hydroxyl functional group. Hydroxyl functional group is the group of alcohols. ...
- Carbonyl functional group. Carbonyl functional groups of aldehydes and ketones generally also increase polarity and reactivity of biological molecules.
- Carboxyl functional group. ...
- Amino functional group. ...
- Phosphate functional group. ...
- Sulfhydryl functional group. ...
What is an example of a functional group?
What are some examples of functional groups?
- Hydroxyl Functional Group.
- Aldehyde Functional Group.
- Ketone Functional Group.
- Amine Functional Group.
- Amino Functional Group.
- Amide Functional Group.
- Ether Functional Group.
- Ester Functional Group.

What are the classifications of the functional groups?
In fact, a traditional approach to the subject of organic chemistry involves the classification of compounds according to their functional groups. Thus the structural features C=C, C≡C, C=O, OH, NH2, and C≡N are the functional groups of alkenes, alkynes, carbonyl compounds, alcohols, amines, and nitriles, respectively.
What are the characteristic functional groups that forms proteins?
Properties of Functional Groups Some of the important functional groups in biological molecules include: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl groups. These groups play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
What are the characteristic functional groups in carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates usually contain a carbonyl (=O) and hydroxyl (−OH) functional group. The carbonyl group bonds with a carbon atom to form a ring structure that is often found in polysaccharides that usually form hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl groups.
What describes a functional group?
A functional group is defined as an atom or group of atoms within a molecule that has similar chemical properties whenever it appears in various compounds. Even if other parts of the molecule are quite different, certain functional groups tend to react in certain ways.
What is the importance of functional groups?
Functional groups are important in chemistry because they are the portion of a molecule that is capable of characteristic reactions. They, therefore, determine the properties and chemistry of many organic compounds. An organic compound is any compound that contains carbon and another element.
What are the four functional groups?
Each of the four types of macromolecules—proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids—has its own characteristic set of functional groups that contributes greatly to its differing chemical properties and its function in living organisms.
What are functional groups examples?
A functional group in organic chemistry is a collection of atoms within molecules which bind together to react in predictable ways. Examples of functional groups include the group hydroxyl, ketone, amine, and ether.
What are functional groups explain with suitable examples?
Functional groups are group of atoms or bonds that define the function of the hydrocarbon that they get attached to. Examples: Alcohol, Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic acid, Halogens, Double & Triple covalent bonds.
How many functional groups are there?
For these three functional groups, it is important to remember that the “W” part has to be considered together with the C=O, since overall they define the functional group. For example, the COOR is ester; it can not be recognized as a “ketone” plus an “ether”.
What is the major functional group?
The 7 major functional groups are: hydroxyl (such as alcohols, ROH), methyl (carbon-carbon bonds), carbonyl (carbon-oxygen double bonds), carboxyl (a combination of a carbonyl and hydroxyl group), amino (carbon-nitrogen bonds), phosphate (carbon, phosphate bonds), and sulfhydryl (carbon-sulfur bonds).
Are all functional groups polar?
Functional groups can sometimes be classified as having polar or non-polar properties depending on their atomic composition and organization.
What is meant by a functional group in an organic compound?
Definition: A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that is bonded to a carbon chain. It defines the chemical property of the organic compound. (i) Ethanol: -OH functional group.
Which of the following are characteristics of proteins?
What Are Some Characteristics of Protein?Amino Acids. ... Size. ... Structure. ... Denaturing. ... Strength. ... Stored Energy. ... Biological Processes.
What are the 4 types of protein structure?
The complete structure of a protein can be described at four different levels of complexity: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure.
What are the groups of proteins?
Types of Proteins. There is a total of seven different protein types under which all proteins fall. These include antibodies, contractile proteins, enzymes, hormonal proteins, structural proteins, storage proteins, and transport proteins.
Which functional group plays a key role in how proteins fold?
The α-helices, the most common secondary structure in proteins, the peptide –CO–NH–groups in the backbone form chains held together by NH ̄OC hydrogen bonds.”3 The α-helices form the backbone of proteins and help to aid in the folding process.
What are functional groups?
Functional groups. Large biological molecules are generally composed of a carbon skeleton (made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms) and some other atoms, including oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Often, these additional atoms appear in the context of functional groups. Functional groups are chemical motifs, or patterns of atoms, ...
Which group is hydrophilic?
One example of a strongly hydrophilic group is the carboxyl group (COOH), which can act as an acid and lose a proton to form a negatively-charged carboxylate ion (COO ). Carboxyl groups are commonly found in amino acids, fatty acids, and other biomolecules. An example of a less hydrophilic group is the carbonyl group (C=O), an uncharged but polar (contains partial positive and partial negative charges) functional group. Carbonyls are found in many different biological molecules, including proteins, peptides, and carbohydrates.
What are some examples of less hydrophilic groups?
An example of a less hydrophilic group is the carbonyl group (C=O), an uncharged but polar (contains partial positive and partial negative charges) functional group. Carbonyls are found in many different biological molecules, including proteins, peptides, and carbohydrates.
What are the two types of fuels that are made up of carbon and hydrogen?
Hydrocarbons, made up entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms, make wonderful combustion fuels (such fuels include propane, butane, and the bulk of commercial gasoline).
Why are alkanes less reactive than alkenes?
Alkanes are less reactive than alkenes. This is because alkenes have double bonds (C=C). It is easy to break just one of these bonds in the double bond and make a reaction happen, but breaking the C-C single bond in an alkane is difficult. Comment on Nahin Khan's post “Alkanes are less reactive...”.
Is a charged group positive or negative?
more. A charged group is either positive or negative (gains or loses an electron) and a polar group contains atoms that have a difference in electronegativity. Comment on Citrus's post “A charged group is either...”. Button opens signup modal.
Is a carboxyl group acidic?
Charged (forms R-COO) at the pH of most biological systems. Since carboxyl groups can release H into solution, they are considered acidic.
What are Functional Groups?
In organic chemistry, we encounter a number of special substituent groups which are attached to the hydrocarbon backbone. These groups impart certain characteristics to the molecule of which it is a part of and thus, become the highlight of that particular molecule.
Classes of Functional Groups
There are a number of functional groups in organic chemistry and functional groups can be defined as a group of atoms placed in a molecule. They possess their own characteristic properties, regardless of the other atoms of the same molecule. Common examples are carboxylic acids, alcohols, ketones, amines, etc.
What is the need for Functional Groups?
Compounds belonging to the same functional group will undergo same set of reactions and behave similarly. Hence, studying a set of compounds with similar behaviour is made easy by the concept of functional groups.
Characteristic Properties of different Functional Groups
The carbon directly attached to the functional group in an organic molecule is referred to as the alpha carbon; the carbon next to an alpha carbon is a beta carbon, the one next to that is gamma carbon and so on.
Context and Applications
This topic is a prerequisite for the completion of certain undergraduate and graduate courses, especially for Bachelors and Masters in Chemistry and Chemical Engineering courses.
Practice Questions
Q1. Out of alcohols, amines, acids and the other functional groups discussed above, which of them exhibits highest extent of hydrogen bonding?
How to create a sense of belonging and purpose for its individual members?
Create a sense of belonging and purpose for its individual members. Allow individuals to experience successes they may not have been able to do on their own. Help individuals see the bigger picture. Inspire individuals to perform at higher levels for the collective good.
What is team focus?
Focusing a group of individuals on a common goal, helping them to succeed, celebrating their successes, and, most importantly, connecting their performance to the bigger picture—this is what teams are all about.

What Is A Functional Group?
- A group of atoms forming a component of a molecule that accounts for a particular function or chemical behavior is called a functional group. These moieties or sections can be found in different molecules. In fact, a moiety can identify a compound and introduce it into a particular genre or classification of similar compounds. When we define a func...
Classification of Functional Groups
- Functional groups can be classified in the following ways. 1. Hydrocarbons This type of functional group contains only hydrogen and carbon as constituent elements. They are commonly represented with ‘R’. They are also called hydrocarbyl groups. The bonding between the carbon atoms can be single, double, or triple. The carbon and hydrogen bonds are always single. These …
List of Functional Groups
- Now that we have defined what a functional group in chemistry is, let us find out the types with proper examples. 1. Alcohol (-OH) The suffix of this functional group is -ol and the organic compound formed is called an alcohol. Example - Methyl alcohol or methanol. 1. Aldehyde (-CHO) In this functional group, a hydrogen and an oxygen atom are bonded with a carbon atom leaving …