
What are the main characteristics of Sporozoans? Sporozoans are organisms that are characterized by being one-celled, non-motile, parasitic, and spore-forming. Most of them have an alternation of sexual and asexual stages in their life cycle.
What is a sporozoan?
· Haplosporidian - Produce unicellular spores lacking polar filaments within the tissues of aquatic invertebrates · Paramyxean - Characterized by spore-within-spore arrangements As compared to a majority of other Protozoa, the complex life cycle that alternates between sexual and asexual stages are one of the defining characteristics of Sporozoans.
Do sporozoans have gliding motility?
Today, these trails are widely accepted as evidence of gliding motility among Sporozoa parasites. * Gliding of Sporozoans has also been associated with the capping phenomenon where the parasites aggregate on their surface and then release them to the posterior pole.
How do sporozoans reproduce sexually?
Here, sexual reproduction produces zygotes that develop to form sporozoites which in turn reproduce sexually or asexually. For Sporozoans, the sexual process of reproduction involves the formation of opposite sex gametes that may be structurally similar or different.
Why do sporozoans not have flagella?
Motility Unlike the adult/mature forms of some protozoa, sporozoans do not have flagella or cilia used for locomotion. For this reason, they depend on gliding, twisting, and bending to move. Whereas gliding allows for active zoite displacement, twisting and bending actions are primarily used for changing direction during motion.
What characteristics set the Apicomplexa apart from the other protozoan groups?
A defining characteristic of the apicomplexa is a group of organelles found at one end--called the apical end--of the organism. This 'apical complex' includes secretory organelles known as micronemes and rhoptries, polar rings composed of microtubules, and in some species a conoid which lies within the polar rings.
What are examples of Sporozoans?
Examples of sporozoan are Plasmodium and Eimeria.
How do Sporozoans differ from other types of protozoans?
Unlike the adult/mature forms of some protozoa, sporozoans do not have flagella or cilia used for locomotion. For this reason, they depend on gliding, twisting, and bending to move.
What do Sporozoans use for movement?
Unlike the crawling movement of amoebae and vertebrate fibroblasts, sporozoon protozoa are characterized by a 'gliding movement' in which no obvious changes occur in cell shape.
What is another name for Sporozoa?
Sporozoans Synonyms - WordHippo Thesaurus....What is another word for sporozoans?protozoaamebasparameciaplasmodiastentors3 more rows
What diseases are caused by Sporozoans?
Sporozoans are a group of non-flagellated, non-ciliated and non-amoeboid protists that are responsible for diseases such as malaria and toxoplasmosis.
Do Sporozoans have cell wall?
they lack cell wall.
What is Sporozoa in microbiology?
Sporozoans are organisms that belong to the phylum Sporozoa. It is characterized by single-celled, parasitic. Those are capable of reproducing asexually and sexually in alternative generations through spores.
Are Sporozoans heterotrophic or autotrophic?
heterotrophicSporozoa spôr˝əzō´ə [key], phylum of unicellular heterotrophic organisms of the kingdom Protista.
What is the structure of Sporozoa?
All Sporozoa have a cellular structure known as apical complex, which gave origin to the name of the Phylum, i.e., Apicomplexa. Sporozoa cellular organization consists of the apical complex, micropore, longitudinal microtubular cytoskeleton, and cortical alveoli.
What is the habitat of Sporozoans?
Some sporozoans, like the malarial organism, live primarily in the blood cells; others, like Coccidia, live in the epithelial cells lining the intestine. Still others live in muscles, kidneys, and other organs.
What causes Sporozoa?
Plasmodium Species (Blood Sporozoa) Transmission to humans is by the bloodsucking bite of female Anopheles mosquitoes. Four species of Plasmodium cause malaria in humans: Plasmodium vivax, P falciparum, P malariae, and P ovale.
Which parasite is Sporozoa?
Sporozoa – organisms whose adult stage is not motile e.g., Plasmodium, Cryptosporidium.
What is an example of a flagellate?
Trypanoso... bruceiDictyochal...BicosoecidaPedinellalesFlagellate/Representative species
What is an example of Sarcodina?
RhizopodaHeliozoaSarcodina/Lower classifications
Are all Sporozoans parasites?
Phylum Apicomplexa: Sporozoans They are capable of gliding movements. All sporozoans are parasites of animals and cause disease. They are also characterized by the presence of a unique cellular structure called an apical complex. The apical complex secretes enzymes which allow the sporozoan to enter a host cell.
What is a sporozoan?from thefreedictionary.com
n. Any of numerous parasitic protozoans that produce infective spores and often have complex life cycles involving both sexual and a sexual reproduction....
What is the classification of sporozoa?from microscopemaster.com
Classification of Sporozoa. · Kingdom: Protozoa - Single-celled eukaryotes that either exist as parasites or as free-living organisms. Sexual and asexual reproduction has been observed in some of the species. · Subphylum: Sporozoa - A group that exclusively consists of parasitic protozoa.
What are the four groups of sporozoites?from microscopemaster.com
Sporozoans have also been grouped based on general spore-morphology. The four groups of Sporozoa based on general spore morphology include: · Apicomplexan - Form unique oocysts that contain the sporozoites (infective forms of the parasites) · Microsporan - Form unicellular spores that contain coiled polar tubes.
How do sporozoites reproduce?from microscopemaster.com
Within the host cells, the sporozoites (which are known as trophozoites at this stage) can continue reproducing asexually through a process known as schizogony. This involves division of the nucleus to form a multinuclear schizont that undergoes segmentation to form individuals known as merozoites. Some of these individuals penetrate new cells where asexual reproduction continues while others develop to form gamonts involved in sexual reproduction.
How do zygotes form?from microscopemaster.com
To form the zygote, the microgamete penetrates the macrogamete for fertilization. The zygote formed through fertilization of the female gamete goes through sporogony to form sporozoites within the oocysts. This may involve a simple division of the zygote or multiple divisions depending on the organism.
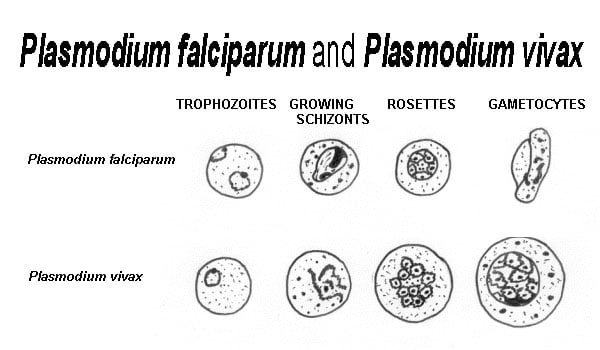
What is the surface protein of Plasmodium falciparum?from microscopemaster.com
Based on molecular studies, the surface proteins (located in the surface coat of the organisms) have been shown to be GPI-anchored. In such parasites as Plasmodium falciparum, this complex (a biomolecule consisting of carbohydrates, lipids, and phosphates) is attached to the C-terminus of surface proteins where it acts as a posttranslational modification biomolecule of the cell surface.
What are the diseases caused by sporozoans?from thefreedictionary.com
Sporozoans cause diseases such as malaria and cryptosporidiosis. Most sporozoans, which were formerly placed in the class Sporozoa, are now classified as apicomplexans.
What phylum is a sporozoan?
Sporozoans do not have flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia. They are capable of gliding movements. All sporozoans are parasites of animals and cause disease.
How do sporozoans reproduce?
Most sporozoans have a complex life-cycle, involving both asexual and sexual reproduction. Typically, a host is infected by ingesting cysts, which divide to produce sporozoites that enter the host's cells. Eventually, the cells burst, releasing merozoites which infect new host cells.
What is the role of protozoa in the ocean?from cliffsnotes.com
Protozoa play an important role as zooplankton, the free-floating aquatic organisms of the oceans. Here, they are found at the bases of many food chains, and they participate in many food webs. Size and shape. Protozoa vary substantially in size and shape.
How do protozoa get food?from cliffsnotes.com
Protozoa are heterotrophic microorganisms, and most species obtain large food particles by phagocytosis. The food particle is ingested into a food vacuole. Lysosomal enzymes then digest the nutrients in the particle, and the products of digestion are distributed throughout the cell.
What is the name of the trophozoite in protozoa?from cliffsnotes.com
Many protozoa alternate between a free-living vegetative form known as a trophozoite and a resting form called a cyst. The protozoal cyst is somewhat analogous to the bacterial spore, since it resists harsh conditions in the environment. Many protozoal parasites are taken into the body in the cyst form.
What are the three organelles that move the protozoa?from cliffsnotes.com
Many protozoal species move independently by one of three types of locomotor organelles: flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia. Flagella and cilia are structurally similar, having a “9-plus-2” system of microtubules, the same type of structure found in the tail of animal sperm cells and certain cells of unicellular algae.
Why are protozoa considered eukaryotic?from cliffsnotes.com
Protozoa are eukaryotic microorganisms. Although they are often studied in zoology courses, they are considered part of the microbial world because they are unicellular and microscopic. Protozoa are notable for their ability to move independently, a characteristic found in the majority of species. They usually lack the capability ...
Do protozoa reproduce sexually?from cliffsnotes.com
Although most protozoa reproduce by asexual methods, sexual reproduction has been observed in several species. Most protozoal species are aerobic, but some anaerobic species have been found in the human intestine and animal rumen. Protozoa are located in most moist habitats.
Do protozoal cells have cell walls?from cliffsnotes.com
Smaller species may be the size of fungal cells; larger species may be visible to the unaided eye. Protozoal cells have no cell walls and therefore can assume an infinite variety of shapes. Some genera have cells surrounded by hard shells, while the cells of other genera are enclosed only in a cell membrane.
Protozoans
Protozoa are heterotrophic, eukaryotic, unicellular creatures. Either they live freely or they are parasites. Protozoan species are divided into approximately 65000 distinct categories. Their cell wall is absent. Numerous different cell organelles carry out the diverse functions carried out by various organs in higher animals.
Characteristics
Protozoa would be present in aquatic environments, which is their habitat. They are marine or freshwater creatures. Some are parasitic on plants and animals, while others live freely. Although they are mostly aerobic, some of them can also be found in the human intestine or rumen.
Classification
A phylum known as protozoa contains monocellular heterotrophs. It belongs to the kingdom of protozoa. Based on their anatomy and the parts of their bodies that are engaged in motility, protozoa are categorized into four main groups:
How big is a protozoa?
The shell of unicellular foraminifera can have a diameter of 20 cm. They lack the rigid cell wall, so they are flexible and found in various shapes.
What is Protozoa?
Protozoa are unicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms. They are either free-living or parasites. There are around 65000 species of protozoans categorised in different groups. They lack a cell wall. There are many different cell organelles, that perform various tasks performed by different organs in higher animals, e.g. mouth, anus, intestinal tract, etc.
What are the diseases that protozoa cause?
There are many protozoa, that cause various diseases in animals and humans, e.g. Plasmodium (malarial parasite), Trypanosoma (sleeping sickness), Trichomonas (trichomoniasis), etc. The protozoa have many stages in their life cycle. Some of the stages of the life cycle are infectious.
How many groups are there in protozoa?
Protozoa are divided into four major groups based on the structure and the part involved in the locomotion:
Which organelle is transparent?
The cytoplasm is differentiated into outer ectoplasm and inner endoplasm, ectoplasm is transparent and endoplasm contains cell organelles. Some of the protozoa have cytostome for ingesting food. Food vacuoles are present, where ingested food comes. Ciliates have gullet, a body cavity which opens outside.
How do asexuals reproduce?
Reproduction- Mostly they reproduce by asexual means. They multiply by binary fission, longitudinal fission, transverse fission or budding.
Which stage of the trophozoite stage is dormant and resistant to environmental stress?
The cyst stage is dormant and resistant to environmental stress, the trophozoite stage is reproductive and causes disease.
How big are protozoa?from biologywise.com
Protozoa vary in size and shape. Their sizes range from 10 to 55 micrometers, but they can be as large as 1 mm. The largest protozoa are called xenophyophores, which can measure up to 20 centimeters in diameter. Protozoa prefer living in moist and aquatic habitats.
Why are protozoa called protozoa?from biologywise.com
Protozoa also means ‘little animal’. They are named so because many species act like small animals. They search for and collect other microbes as food. Previously, protozoa were specified as unicellular protists possessing animal-like characteristics such as the capability to move in water.
How tall is an algal turf?from en.wikipedia.org
Algal turfs are thick, carpet-like beds of seaweed that retain sediment and compete with foundation species like corals and kelps, and they are usually less than 15 cm tall. Such a turf may consist of one or more species, and will generally cover an area in the order of a square metre or more. Some common characteristics are listed:
What are the two groups of protists that are parasites of animals?from biologywise.com
Ascetosporea: They are a group of protists that are parasites of animals, especially marine invertebrates. Two groups which come under this are the haplosporids and paramyxids . Haplosporid spores have a single nucleus and an opening at one end, covered with an internal diaphragm. After emerging, it develops within the cells of its host, usually a marine invertebrate. However, some infect other groups or freshwater species. Paramyxids grow within the digestive system of marine invertebrates, and produce multicellular spores.
What are the three organelles that move the protozoa?from cliffsnotes.com
Many protozoal species move independently by one of three types of locomotor organelles: flagella, cilia, and pseudopodia. Flagella and cilia are structurally similar, having a “9-plus-2” system of microtubules, the same type of structure found in the tail of animal sperm cells and certain cells of unicellular algae.
Why are protozoa considered eukaryotic?from cliffsnotes.com
Protozoa are eukaryotic microorganisms. Although they are often studied in zoology courses, they are considered part of the microbial world because they are unicellular and microscopic. Protozoa are notable for their ability to move independently, a characteristic found in the majority of species. They usually lack the capability ...
How do protozoa get food?from biologywise.com
The mode of nutrition of protozoa is heterotrophic, and most species obtain food by phagocytosis. Phagocytosis is the process where the cell changes shape by sending out pseudopodia to make contact with food particles.
