Key facts about the nervous systemTable quiz
| Definition | A network of neurons that sends, receive ... |
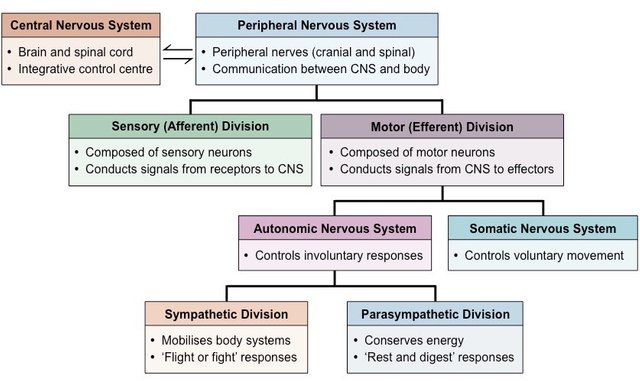
| Divisions | Central nervous system Peripheral nervou ... |
| Central nervous system | Brain and spinal cord |
| Peripheral nervous system | Spinal and cranial nerves. Functional di ... |
Full Answer
What are the categories of the nervous system?
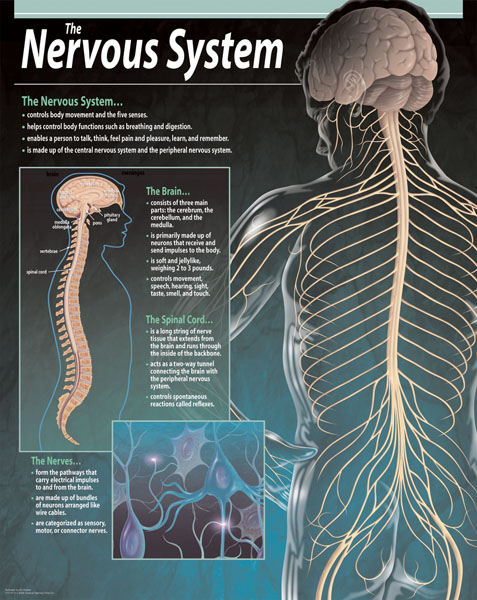
Jan 01, 2020 · The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and extend to all …
What are the four types of nervous systems?
Jun 08, 2021 · Classification of Nervous System Autonomous Nervous System. The autonomic nervous system comprises nerves that connect the central nervous system to the... Peripheral …
What are the four characteristics of the nervous system?
Nov 20, 2021 · According to the topographic principle, the human nervous system is conditionally divided into central and peripheral. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the spinal cord …
What are the different divisions of the nervous system?
Apr 02, 2022 · somatic system - voluntary visceral system - involuntary, including autonomic nervous system - sympathetic or parasympathetic directional subdivisions afferent = towards …

What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic nervous system becomes active during a state of relaxation. It helps the body to conserve and store energy. It slows the heartb...
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system gets the body to prepare for emergency action. It is involved in the fight-or-flight response, which is the sudden r...
What are Cranial Nerves?
Cranial nerves are 12 pairs that are attached to the surface under the brain.
What are Spinal Nerves?
Spinal Nerves are 31 pairs that are attached to the spinal cord.
What is the function of the somatic nervous system?
The somatic nervous system relays information from the skin, sensory organs, & muscles to the Central Nervous System (Brain and Spinal cord). It al...
How many divisions are there in the nervous system?
The nervous system (NS) is structurally broken down into two divisions;
What are the main structures of the nervous system?
Neurons, or nerve cell, are the main structural and functional units of the nervous system. Every neuron consists of a body (soma) and a number of processes (neurites). The nerve cell body contains the cellular organelles and is where neural impulses ( action potentials) are generated. The processes stem from the body, they connect neurons with each other and with other body cells, enabling the flow of neural impulses. There are two types of neural processes that differ in structure and function;
How many pairs of nerves are there in the peripheral nervous system?
Peripheral nervous system. The PNS consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves, 31 pairs of spinal nerves and a number of small neuronal clusters throughout the body called ganglia. Peripheral nerves can be sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) or mixed (both).
What is the PNS?
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) represents the conduit between the CNS and the body. It is further subdivided into the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS) .
Which neurons send neural impulses to the peripheral tissues?
Efferent neurons (motor or descending) send neural impulses from the CNS to the peripheral tissues, instructing them how to function. Afferent neurons (sensory or ascending) conduct impulses from the peripheral tissues to the CNS. These impulses contain sensory information, describing the tissue's environment.
What are the functions of the nervous system?
This property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions ( heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements. Ultimately, the nervous system structures preside over everything that makes us human; our consciousness, cognition, behaviour and memories.
Which two types of neural processes are long and conduct impulses away from the neuronal body?
There are two types of neural processes that differ in structure and function; Axons are long and conduct impulses away from the neuronal body. Dendrites are short and act to receive impulses from other neurons, conducting the electrical signal towards the nerve cell body.
What is the classification of nerves?
Nerves can be categorized as afferent, efferent, and mixed based on the direction of signal transmission within the nervous system. Nerves can be further categorized as spinal nerves or cranial nerves based on where they connect to the central nervous system.
How are nerves classified?
Nerves are primarily classified based on their direction of travel to or from the CNS, but they are also subclassified by other nerve characteristics.
Which nerves carry impulses from sensory receptors or sense organs toward the central nervous system?
Afferent nerve: Carries nerve impulses from sensory receptors or sense organs toward the central nervous system. Schwann cell: The principal glia of the peripheral nervous system. efferent nerve: Nerves that conduct signals from the central nervous system along motor neurons to their target muscles and glands.
Which nerves conduct signals away from the central nervous system to target muscles and glands?
Efferent nerv es conduct signals away from the central nervous system to target muscles and glands. Mixed nerves contain both afferent and efferent axons, and thus conduct both incoming sensory information and outgoing muscle commands in the same nerve bundle. Afferent and efferent nerve transmission: Schematic of efferent ...
How many groups are there in the nervous system?
Nerves are categorized into three, primary groups based on the direction of signal transmission within the nervous system.
Which nerves connect to the spinal cord?
Spinal nerves innervate much of the body and connect through the spinal column to the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are assigned letter-number designations according to the vertebra where they connect to the spinal column. Cranial nerves innervate parts of the head and connect directly to the brain.
What is the role of A-gamma fibers in motor neurons?
A-gamma fibers are typically motor neurons that control the intrinsic activation of the muscle spindle. Fibers of the B group are myelinated with a small diameter and have a low conduction velocity. The primary role of B fibers is to transmit autonomic information.
What is the nervous system?
Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology. The nervous system is the master controlling and communicating system of the body. Every thought, action, and emotion reflects its activity. Its signaling device, or means of communicating with body cells, is electrical impulses, which are rapid and specific and cause almost immediate responses.
What are the functions of the nervous system?
Functions of the Nervous System. To carry out its normal role, the nervous system has three overlapping functions. Monitoring changes. Much like a sentry, it uses its millions of sensory receptors to monitor changes occurring both inside and outside the body; these changes are called stimuli, and the gathered information is called sensory input.
Which division of the nervous system carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the muscles and gland
Motor division. The motor, or efferent division carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the muscles and glands; the motor division has two subdivisions: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. Somatic nervous system.
What is the division of the sensory system?
The sensory, or afferent division, consists of nerves (composed of nerve fibers) that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. Somatic sensory fibers.
What is the CNS?
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, which occupy the dorsal body cavity and act as the integrating and command centers of the nervous system. Peripheral nervous system (PNS). The PNS, the part of the nervous system outside the CNS, consists mainly of the nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord.
How long is the spinal cord?
The cylindrical spinal cord is a glistening white continuation of the brain stem. Length. The spinal cord is approximately 17 inches (42 cm) long. Major function. The spinal cord provides a two-way conduction pathway to and from the brain, and it is a major reflex center (spinal reflexes are completed at this level).
Why do we divide the nervous system?
We only have one nervous system, but, because of its complexity, it is difficult to consider all of its parts at the same time; so, to simplify its study, we divide it in terms of its structures (structural classification) or in terms of its activities (functional classification).
What are the structural divisions of the nervous system?
The picture you have in your mind of the nervous system probably includes the brain, the nervous tissue contained within the cranium, and the spinal cord, the extension of nervous tissue within the vertebral column. That suggests it is made of two organs—and you may not even think ...
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
The two divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. The sympathetic system is associated with the fight-or-flight response, and parasympathetic activity is referred to by the epithet of rest and digest. Homeostasis is the balance between the two systems.
What are the functions of the nervous system?
The nervous system can be functionally divided into 3 actions: sensation, integration, and response. The nervous system is involved in receiving information about the environment around us (sensation) and generating responses to that information (motor responses). The nervous system can be divided into regions that are responsible for sensation (sensory functions) and for the response (motor functions). But there is a third function that needs to be included. Sensory input needs to be integrated with other sensations, as well as with memories, emotional state, or learning (cognition). Some regions of the nervous system are termed integration or association areas. The process of integration combines sensory perceptions and higher cognitive functions such as memories, learning, and emotion to produce a response.
What is the balance between the two systems?
Homeostasis is the balance between the two systems. At each target effector, dual innervation determines activity. For example, the heart receives connections from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. One causes heart rate to increase, whereas the other causes heart rate to decrease.
What is the process of combining sensory perceptions and higher cognitive functions such as memories, learning, and emotion?
Some regions of the nervous system are termed integration or association areas. The process of integration combines sensory perceptions and higher cognitive functions such as memories, learning, and emotion to produce a response. Sensation.
Which system regulates the internal organs?
The autonomic nervous system regulates many of the internal organs through a balance of two aspects, or divisions. In addition to the endocrine system, the autonomic nervous system is instrumental in homeostatic mechanisms in the body.
Which system is responsible for voluntary motor responses?
There are two main subdivisions of the motor division: the somatic nervous system (SNS) which is responsible for voluntary motor responses and the autonomic nervous system (ANS) which is responsible for involuntary motor responses. The voluntary motor response of the somatic nervous system (SNS) involves the contraction of skeletal muscle, ...
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and extend to all parts of the body. The nervous system transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, including internal organs. In this way, the nervous system’s activity ...
What is the basic unit of the nervous system?
The basic unit of the nervous system is a nerve cell, or neuron. The human brain contains about 100 billion neurons. A neuron has a cell body, which includes the cell nucleus, and special extensions called axons (pronounced AK-sonz) and dendrites (pronounced DEN-drahytz ). Bundles of axons, called nerves, are found throughout the body.
What are the different types of neurons?
Different types of neurons control or perform different activities. For instance, motor neuron s transmit messages from the brain to the muscles to generate movement. Sensory neurons detect light, sound, odor, taste, pressure, and heat and send messages about those things to the brain. Other parts of the nervous system control involuntary processes.
What are the parts of the brain that communicate?
The brain is made up of many networks of communicating neurons and glia. These networks allow different parts of the brain to “talk” to each other and work together to control body functions, emotions, thinking, behavior, and other activities. 1, 2, 3.
What is the name of the cell that sends electrical signals to neighboring neurons?
The nervous system also includes non-neuron cells, called glia (pronounced GLEE-uh ). Glia perform many important functions that keep the nervous system working properly.
What are the three major groups of neurons?
Three major groups arise from this classification: multipolar, bipolar, and unipolarneurons.
What are the structures of the neuron system?
Neurons have four specialized structures that allow for the sending and receiving of information: the cell body (soma), dendrites, axon and axon terminals ( see lowest figure). Cell body or soma: The cell body is the portion of the cell that surrounds ...
What is a multipolar neuron?
Multipolar neurons are defined as having three or more processes that extend out from the cell body. They comprise of more than 99% of the neurons in humans, and are the major neuron type found in the CNS and the efferent division of the PNS.
Where are unipolar neurons found?
Although rare, these are found in the retina of the eye and the olfactory system . Unipolar neurons have a single, short process that extends from the cell body and then branches into two more processes that extend in opposite directions.
Which neuron transmits information from sensory receptors in the skin, or the internal organs toward the CNS for
Sensory neurons, or afferent neurons transmit information from sensory receptors in the skin, or the internal organs toward the CNS for processing. Almost all sensory neurons are unipolar.
What is the cell body?
Cell body or soma: The cell body is the portion of the cell that surrounds the nucleus and plays a major role in synthesizing proteins.
Which process extends toward the CNS?
The process that extends toward the CNS is the central process . Unipolar neurons are found primarily in the afferent division of the PNS. Functional Classification of Neurons.