
Routes of Medication Administration
- Routes of Medication Administration. In general, two categories of medication administration exist: parenteral and nonparenteral. ...
- Parenteral. This administration route involves medication that is injected in the body anywhere other than the mouth or alimentary canal (the entire passage along which food passes through the body ...
- Nonparenteral. ...
- Intravenous Route. ...
- Intramuscular Route. ...
- Subcutaneous Route. ...
- Rectal Route. ...
- Vaginal Route. ...
- Inhaled Route.
What are the different routes in administrating medications?
To get a better understanding, here are the 6 most common routes:
- Oral – Swallowed through the patients mouth as either a tablet, liquid, capsule, lozenge or chewable tablet.
- Rectal – This may be the next option for those who can’t swallow the medication. ...
- Inhalation – Medication is inhaled through the patients airway in the form of a powder, aerosol spray or mist. ...
What are the 10 routes of medication administration?
•Nasal – placed in the nostril •Inhalant – inhaled into the lungs •Transdermal – placed and affixed to the skin •Topical – applied to the skin or hair •Vaginal – inserted into the vagina •Rectal – inserted into the rectum •Subcutaneous – injected into the fat with a syringe Common Routes of Medication Administration
What are of the routes of administration for medications?
What are the different routes of medication administration?
- Oral: A majority of the drugs are administered orally as it is a convenient, safe and affordable route of administration. …
- Injection: …
- Sublingual and buccal routes: …
- Rectal route: …
- Vaginal route: …
- Ocular route: …
- Otic route: …
- Nasal route:
What are the 5 routes of Drug Administration?
- Oral administration. This is the most frequently used route of drug administration and is the most convenient and economic.
- Sublingual.
- Rectal administration.
- Topical administration.
- Parenteral administration.
- Intravenous injection.
What are the 8 route of drug administration?
The main routes of drug administration include:Oral route.Sublingual/ Buccal route.Rectal route.Topical route.Transdermal route.Inhalational route/ pulmonary route.Injection route.
How many routes of medication administration are there?
The 6 routes of medication administration To get a better understanding, here are the 6 most common routes: Oral – Swallowed through the patients mouth as either a tablet, liquid, capsule, lozenge or chewable tablet. Rectal – This may be the next option for those who can't swallow the medication.
What are the 3 major categories of medication administration routes?
Major routes are oral, parenteral and topical.
What are the 6 routes of medication safety?
These 6 rights include the right patient, medication, dose, time, route and documentation. Futhermore, nurses are also urged to do the three checks; checking the MAR, checking while drawing up medication and checking again at bedside.
What is the most common route of medication administration?
Oral route Many drugs can be administered orally as liquids, capsules, tablets, or chewable tablets. Because the oral route is the most convenient and usually the safest and least expensive, it is the one most often used.
What are the 6 routes of injection?
Jennifer LeOral route.Injection routes.Sublingual and buccal routes.Rectal route.Vaginal route.Ocular route.Otic route.Nasal route.More items...
What is the best route of drug administration and why?
The route by which the medicines are directly introduced into the bloodstream through a vein is known as intravenous route of administration. The intravenous route is considered to be the fastest route of drug administration. The injections and the infusions are administered by this route have 100% bioavailability.
What are the 7 steps of medication administration?
7 Rights Of Medication AdministrationMedication administration. ... Right Individual. ... Right Medication. ... Right Dose. ... Right Time. ... Right Route. ... Right Documentation. ... Right Response.
What are the 17 routes of drug administration?
Techniques involved in each route of medication administration are different, and some of the important points are summarized as follows:Intravenous Route. ... Intramuscular Route. ... Subcutaneous Route. ... Rectal Route. ... Vaginal Route. ... Inhaled Route.
What are the 5 basic principles for administering medication?
One of the recommendations to reduce medication errors and harm is to use the “five rights”: the right patient, the right drug, the right dose, the right route, and the right time.
How do you administer medication?
3:526:27How to give Medication - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSitting at the bottom if another medication is needed flush the feeding tube with a recommendedMoreSitting at the bottom if another medication is needed flush the feeding tube with a recommended amount of cool boiled water and repeat the process of giving the medication.
What are the 17 routes of drug administration?
Techniques involved in each route of medication administration are different, and some of the important points are summarized as follows:Intravenous Route. ... Intramuscular Route. ... Subcutaneous Route. ... Rectal Route. ... Vaginal Route. ... Inhaled Route.
What are the 7 steps of medication administration?
7 Rights Of Medication AdministrationMedication administration. ... Right Individual. ... Right Medication. ... Right Dose. ... Right Time. ... Right Route. ... Right Documentation. ... Right Response.
What are 10 medication administration rights?
Today, 10 laws are emphasized to reduce the incidence of medication error: right patient, right drug, right dosage, right time, right route, right to refuse (patient and nurse), right knowledge, right questions or challenges, right advice, and right response or outcome [7] . ...
What are the 5 rights of administering medication?
One of the recommendations to reduce medication errors and harm is to use the “five rights”: the right patient, the right drug, the right dose, the right route, and the right time.
What is medication route?
A medication administration route is often classified by the location at which the drug is administered, such as oral or intravenous. The choice of routes in which the medication is given depends not only on the convenience and compliance but also on the drug’s pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic profile. Therefore it is crucial to understand the characteristics of the various routes and techniques associated with them. Many interprofessional healthcare team members are involved in the administration of medications to patients.
What is medication administration route?
A medication administration route is often classified by the location at which the drug is applied, such as oral or intravenous. The choice of routes in which the medications are applied depends not only on the convenience but also on the drug’s properties and pharmacokinetics. This activity describes medication administration routes ...
How is inhaled medication delivered?
An inhaled medication is delivered rapidly across the large surface area of the respiratory tract epithelium. Drugs absorbed into the pulmonary circulation enter directly into the systemic circulation via the pulmonary vein, bypassing the first-pass metabolism. The particle size of the inhaled medication is usually 1 to 10 µm for effective delivery. The efficacy of drug delivery to the lungs depends not only on the drug particle size and morphology but also on the patient’s respiratory physiology, such as tidal volume and tracheal inspiration velocity. [4]
Where to administer intravenous medication?
Intravenous injection is the most common parental route of medication administration and has the benefit of bypassing the first-pass metabolism by the liver. Given their superficial location on the skin, peripheral veins provide easy access to the circulatory system and are often utilized in the parenteral administration of medications. The upper extremity is usually the preferred site for intravenous medication as it has a lower incidence of thrombophlebitis and thrombosis than the lower limbs. The median basilic or cephalic veins of the arm or the metacarpal veins on the hand's dorsum are commonly used. In the lower extremity, the dorsal venous plexus of the foot can be used.
Why is nitroglycerin sublingual?
For instance, nitroglycerin is cleared more than 90% during a single pass through the liver; therefore, it is given as a sublingual form. The sublingual and buccal routes also have advantages of rapid absorption, convenience, and low infection incidence.
How to use lubricant for vaginal mucosa?
A lubricant can be used to reduce friction against the vaginal mucosa as the medication is administered. Gently separate labial folds with the non-dominant gloved hand while with the dominant gloved index finger, insert the lubricated suppository to about 8-10 cm along the posterior vaginal wall. Inhaled Route.
Why do you need a tourniquet when injecting intravenous medication?
A tourniquet may be used over the site intended for the intravenous medication to make the vein more visible and easier to access. However, when used, the tourniquet must be removed before injecting the medication to prevent extravasation. In central lines or peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) lines for the medication administration, ultrasound guidance is often used. [10]
What training is required for administration of medication?
Training in administration of medication is essential for staff working in the health and social care sector. All of our staff who work with medication administration are fully trained in this field and receive regular refreshers and updates.
Why do we need to treat patients with medication?
There are many reasons for treating patients with medication, with the main three being: Diagnosis – This is to investigate the cause of the illness or examine the nature of the symptoms. Treatment – After the diagnosis, the medication is used to reduce symptoms and fight the illness. Prevention – Medication to stop the illness or disease being ...
Why is professional training required for medication administration?
Professional training is required for medication administration as even though its purpose is to improve our health, if done incorrectly, it can be highly dangerous. Our nurse case managers receive regular expert training and are frequently checked against our high-level competencies for this reason.
What is rescue medicine?
Rescue medication can be used to treat a wide range of illnesses , ranging from mild severity to serious conditions. Here are the most common conditions that rescue medicine is used for: Seizures – Some patient’s seizures may usually last the same amount of time and stop by themselves without the use of medication.
How to check if a prescription is correct?
Right Medication – The prescription is thoroughly checked by reading the type of medicine it is and the expiry date to make sure this is correct.
Can you swallow oral meds?
Oral – Swallowed through the patients mouth as either a tablet, liquid, capsule, lozenge or chewable tablet. Rectal – This may be the next option for those who can’t swallow the medication. The drug is administered rectally as a suppository.
Can you swallow medicine?
When you think of taking medicine, you probably imagine swallowing a pill or receiving an injection. However, there are many ways to administer medication. The route we take for our patients depends on varying factors, such as the illness itself, the severity of the illness, the needs of the patient and their condition.
What is the most commonly used route for drug administration?
Oral Route. The drug is administered to or by way of the mouth. 1 A drug given via this route is absorbed into the systemic circulation from the gastrointestinal tract. The oral route is the most frequently used route for drug administration.
Where is buccal route administered?
The buccal route is administered by placing the buccal dosage form between the gum and the inner cheek. The drug is rapidly absorbed from the buccal mucosa and enters the systemic circulation, thus avoiding first-pass metabolism. In addition, this route can also be used for a local effect (e.g. hydrocortisone muco-adhesive buccal tablet for the treatment of aphthous ulceration of the mouth).
What are the advantages of intravenous route?
Advantages of the Intravenous Route. Immediate effect (suitable for emergencies) Can be given to unconscious patients. Avoids first-pass metabolism. Achieves predictable and precise control over drug plasma levels compared to other routes.
What is IV drug?
A drug administered by the intravenous (IV) route is given directly into a vein as direct injection or infusion.
What is variable drug absorption dependent upon?
Variable drug absorption dependent upon the muscle group used and the blood flow to the muscle
How is a drug destroyed?
The drug may be destroyed by digestive enzymes and/or stomach acid
What are the factors that affect drug absorption?
Drug absorption may vary. Examples of factors affecting drug absorption are gastrointestinal motility, gastric emptying rate and the presence of food in the gastrointestinal tract. The drug may be destroyed by digestive enzymes and/or stomach acid.
What are the different routes of medication administration?
There are various routes of medication administration. The major routes of medication administration are oral, parenteral, and topical.
Which route of medication administration is the most common?
The oral route of medication administration is simple, convenient and the most common route.
What is intraosseous route?
The intraosseous route involves the administration of medications directly into the bone marrow. This is usually used when there is poor or no access to an intravenous space. It is often done in emergency situations.
What is parenteral route?
The parenteral route of medication administration is considered to be any route other than the gastrointestinal tract. However, it is used to indicate medication given by injection into tissues of the body.
What is the peritoneal space used for mediation?
This route of mediation administration uses the peritoneal space of the abdominal cavity. This route allows medications to be absorbed into the circulation.
Where are medications applied?
With the topical route of administration, medications are applied to the skin or the mucus membrane.
Can sublingual medications be swallowed?
Sublingual medications should not be swallowed immediately but allowed to dissolve.
What are the 10 routes of drug administration?
Oral administration. This is the most frequently used route of drug administration and is the most convenient and economic. …
What are the common injectable routes of administration?
Administration by injection (parenteral administration) includes the following routes:
What is difference between enteral and parenteral routes of administration?
What do Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Refer To? Enteral nutrition generally refers to any method of feeding that uses the gastrointestinal (GI) tract to deliver part or all of a person’s caloric requirements. … Parenteral nutrition refers to the delivery of calories and nutrients into a vein.
What is the slowest route of medication administration?
Swallowing a drug is a relatively slow method of taking a drug. After the drug is swallowed, it is dissolved in the stomach and then absorbed into the bloodstream from the linings of the stomach and later, the small intestine.
What are the 7 Medication rights?
To ensure safe medication preparation and administration, nurses are trained to practice the “7 rights” of medication administration: right patient, right drug, right dose, right time, right route, right reason and right documentation [12, 13].
What is the fastest route of absorption for a drug?
The fastest route of absorption is inhalation, and not as mistakenly considered the intravenous administration. Absorption is a primary focus in drug development and medicinal chemistry, since a drug must be absorbed before any medicinal effects can take place.
Can IV drugs be taken orally?
IV administration can also be a controlled way to give drugs over time. Certain drugs may be given by IV administration because if you took them orally (by mouth), enzymes in your stomach or liver would break them down.
What is the most commonly used route for drug administration?
1. Oral route . This is the most frequently used route for drug administration. When possible, it is the first choice for the administration of drugs, since it is both convenient and economical. Drugs administered orally are placed in the mouth and swallowed.
What is the route of drug administration?
The route of drug administration is simply defined as the path by which a drug is taken into the body for diagnosis, prevention, cure or treatment of various diseases and disorders. For a drug to produce its desired therapeutic effect, it must come in contact with the tissues of organs and cells of tissues by one way or the other;
What is parenteral route?
Parenteral route, on the other hand, refers to any routes of administration that do not involve drug absorption via the gastrointestinal tract (par = around, enteral = gastrointestinal), including injection routes (e.g., intravenous route, intramuscular route, subcutaneous route etc.), inhalational and transdermal routes. 1.1 1.
What is the local route?
The local route is the simplest mode of administration of a drug at the site where the desired action is required. When the systemic absorption of a drug is desired, medications are usually administered by two main routes: the enteral route and the parenteral route. Classification of various routes of drug administration.
How do drugs enter the bloodstream?
Drugs may be inhaled as gases (e.g., nitrous oxide) and enter the bloodstream by diffusing across the alveolar membrane. This is the method of administration of volatile anesthetics such as ether, halothene, and methoxyflurane.
What are the three injection routes?
There are three commonly used injection routes: subcutaneous (SC), intramuscular (IM), and intravenous (IV). Other routes such as intra-arterial (IA), intrathecal (IT), intraperitoneal (IP), intravitreal etc., are used less frequently.
How does the route of administration affect the drug?
The route of administration of a medication directly affects the drug bioavailability, which determines both the onset and the duration of the pharmacological effect. The choice of route of administration may be influenced by many factors among which include:
How are drugs administered?
There are several different ways drugs can be administered. You’re probably familiar with injections and pills that you swallow, but medications can be given in many other ways as well.
What is the administration of medication?
Administration of medication requires thorough understanding the drug, including: how it moves through your body. when it needs to be administered. possible side effects and dangerous reactions. proper storage, handling, and disposal. Healthcare providers are trained in all of these issues.
How to take a drug correctly?
Talk with your doctor. Be sure to take your medications correctly to get the most out them and to reduce your risk of side effects and other problems. Anyone giving you the drug should follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Make sure that you understand everything about taking your medication.
What is prescribing a drug?
prescribing a drug. entering the drug or dosage information into a computer system. a drug is being prepared or dispensed. a drug is taken by or given to someone. The “rights” are a starting point in helping to make sure that medications are given correctly and safely.
What are the 5 rights of a patient?
the right drug. the right time. the right dose. the right route. Medication errors happen all too often in the United States, even when drugs are given by professionals. The Food and Drug Administration receives more than 100,000 reports ...
How is a medication dosage determined?
For some medications, dosage must be determined by trial and error. In these cases, your healthcare provider would need to monitor you when you first start treatment.
Why do we take medications?
We take medications to diagnose, treat, or prevent illness. They come in lots of different forms and we take them in many different ways. You may take a drug yourself, or a healthcare provider may give it to you. Drugs can be dangerous, though, even when they’re meant to improve our health.
What is the name of the route a nurse administers medications?
Medications can be administered through various routes, and it’s important the nurse is familiar with each route. It’s also important the nurse if familiar with the “lingo” or abbreviations used to describe each routes. For example, the term P.O. is used a lot in nursing to describe medications that are taken via the mouth, or IM, subQ, and IV are terms used to describe routes nurses administer medications by injection.
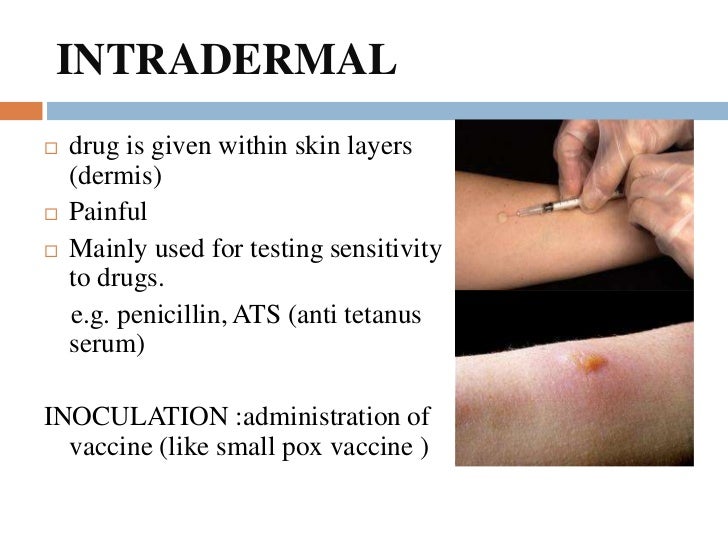
Where is medication injected?
Medication is injected in the dermis which is found in between the epidermis and hypodermis. A “wheal” is created on the skin. Used in allergy test or Mantoux TB skin test that checks for tuberculosis. Medication is injected in the subcutaneous fat/hypodermis.
What is the name of the medication that nurses administer?
This is the most common route nurses administer medications like capsules, tablet, and liquids. Nitroglycerin is a drug given this route that treats chest pain. Includes certain opioid pain meds, smoking cessation products etc.
What is the name of the drug that is given to chest pain?
Nitroglycerin is a drug given this route that treats chest pain.
How many IV lines are hung?
Two IV lines are hung and connect into some type of IV access.
Do nurses use abbreviations?
However, it’s important that when using abbreviations with documenting or taking orders, that the nurse uses approved abbreviations set by the employer. Most employers will have a list or set of guidelines on what abbreviations are allowed vs. not allowed.
