How does fiscal policy affect the economy?
Fiscal policy is an important tool for managing the economy because of its ability to affect the total amount of output produced—that is, gross domestic product. The first impact of a fiscal expansion is to raise the demand for goods and services. This greater demand leads to increases in both output and prices.
How does fiscal policy impact the budget deficit?
How does fiscal policy impact the budget deficit? Updated at 2018/07/12. A: Fiscal policy refers to any uses of the government budget to affect the economy. This includes government spending and levied taxes. Policy is said to be expansionary when spending increases or when taxes are lower. Conversely, policy is contractionary when spending ...
What are the 3 tools of fiscal policy?
The three main types of fiscal policy are:
- Fiscal Neutral Policy
- Expansionary Fiscal Policy
- Contractionary Fiscal Policy
How do fiscal and monetary policies affect aggregate demand?
Fiscal policy affects aggregate demand through changes in government spending and taxation. Those factors influence employment and household income, which then impact consumer spending and investment. Monetary policy impacts the money supply in an economy, which influences interest rates and the inflation rate.
What are the possible effects of a contractionary fiscal policy on the economy?
How does contractionary fiscal policy affect economic growth? Contractionary fiscal policies typically slow economic growth. Reducing government spending slows an economy, as does increasing tax revenue. However, contractionary fiscal policy is typically used to slow an economy that is growing quickly.
What is the cause and effect of contractionary fiscal policy?
Contractionary Policy as Fiscal Policy Governments engage in contractionary fiscal policy by raising taxes or reducing government spending. In their crudest form, these policies siphon money from the private economy, with hopes of slowing down unsustainable production or lowering asset prices.
How does contractionary fiscal policy affect interest rates?
Contractionary fiscal policy decreases the national deficit. The demand for loanable funds decreases (or the supply increases), and the interest rate decreases. Monetary policy has the opposite effect on interest rates as fiscal policy.
Does contractionary fiscal increase unemployment?
contractionary fiscal policy the use of fiscal policy to contract the economy by decreasing aggregate demand, which will lead to lower output, higher unemployment, and a lower price level.
What does contractionary monetary policy cause?
Contractionary monetary policy can lead to increased unemployment and decreased borrowing and spending by consumers and businesses, which can eventually lead to an economic recession if too aggressively applied.
How does contractionary fiscal policy affect inflation?
This is called contractionary fiscal policy. To reduce the total level of spending, the government could increase tax rates. As more income is collected in taxes, less is available for spending, reducing inflationary pressures.
What are examples of contractionary fiscal policy?
When the government uses fiscal policy to decrease the amount of money available to the populace, this is called contractionary fiscal policy. Examples of this include increasing taxes and lowering government spending.
What is the effect of expansionary fiscal policy on the money supply?
Expansionary monetary policy works by expanding the money supply faster than usual or lowering short-term interest rates. It is enacted by central banks and comes about through open market operations, reserve requirements, and setting interest rates.
What is an example of contractionary fiscal policy?
An example of contractionary fiscal policy could be when the government decides to decrease government spending. Meaning, that government programs,...
What are the effects of contractionary fiscal policy?
Contractionary fiscal policy will slow down the economy. If the government decides to cut taxes and decrease government spending, then the effect w...
What is a contractionary policy?
A contractionary policy is the government fiscal policy attempting to slow down the economy. The government increases taxes, lowers transfer paymen...
What are the two contractionary fiscal policies?
The two contractionary fiscal policies are expansionary and contractionary. Expansionary aims to grow the economy while contractionary aims to shri...
What is contractionary fiscal policy?
Understanding Contractionary Fiscal Policy. Fiscal policy refers to a government's spending and taxing habits. There are two kinds of fiscal policy direction: contractionary and expansionary. Think of contractionary policy as anything that directly reduces government deficits or increases surpluses. Expansionary policy involves activity that ...
What could expansionary fiscal policy cause?
According to general equilibrium models in contemporary macroeconomics, expansionary fiscal policy could cause crowding out of private activity in the credit market. This argument also flows the other way: Contractionary policy could allow for increased private activity in the credit market. This phenomenon is sometimes referred to in ...
What happens if the government's fiscal policy leads to surplus?
If the government's contractionary fiscal policy leads to surplus, the government can act as a creditor rather than a debtor. The effects of this are no more certain than the effects from deficit spending, but all economists agree it will have some impact.
Why is spending cut contractionary?
Similarly, a spending cut is contractionary because it reduces expenditures. According to standard measurements of gross domestic product (GDP), contractionary fiscal policy seemingly reduces total output. Taxes tend to reduce private consumption just as spending cuts reduce government consumption.
What would happen if the government decreased its borrowing?
In a similar fashion, a decrease in government borrowing could leave more money for private investments. Less pressure on interest rates means more room for small borrowers. In the long run, less government spending often means fewer taxes, further increasing the pool of available funds for private markets. If the government's contractionary fiscal ...
How does the federal government borrow money?
The federal government borrows money by issuing U.S. Treasuries. In this case, the government issues $100 billion worth of Treasuries. That directly absorbs $100 billion from the credit market, money that might otherwise have been spent on other investments or consumer goods. Public issues take place by crowding out potential private issues.
How does government debt affect interest rates?
If private individuals are induced to increase their savings to purchase government debt, the real interest rate tends to rise . When real interest rates rise, it is more difficult for individuals and small companies to obtain loans.
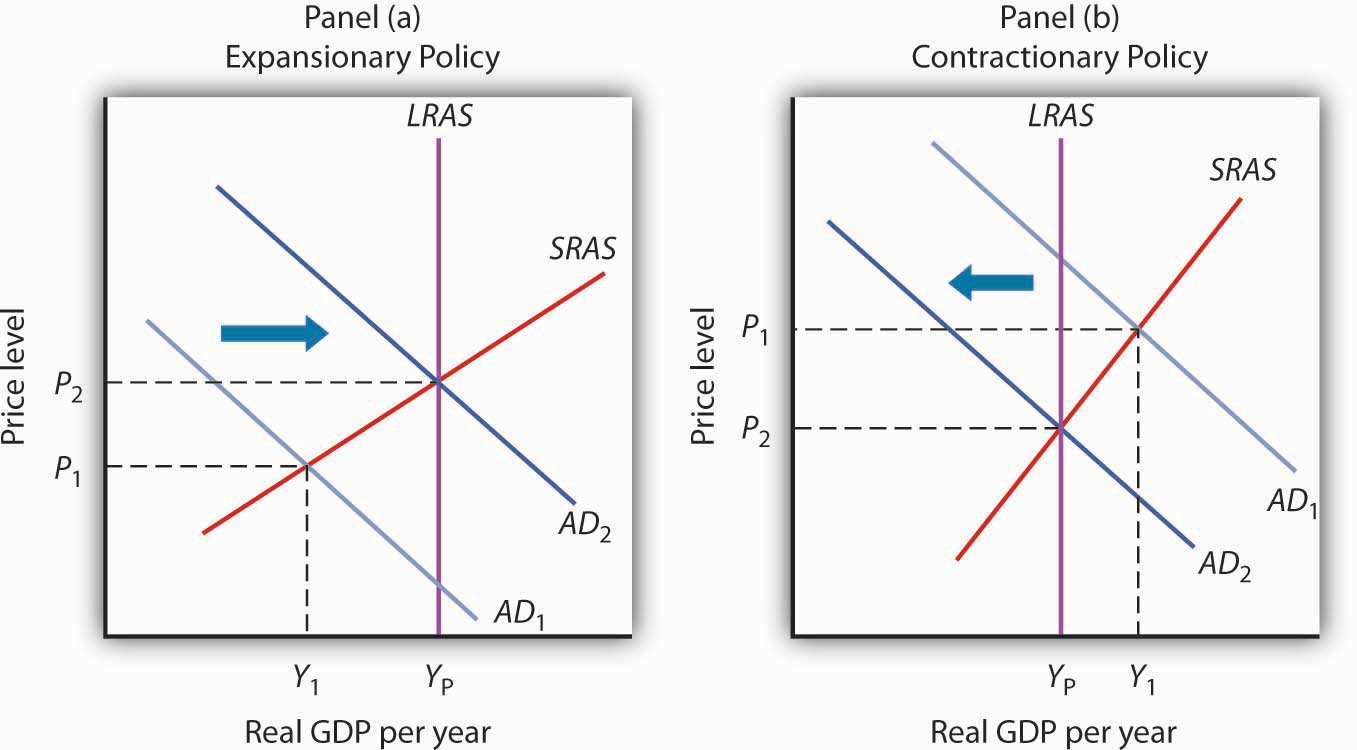
How does expansionary fiscal policy work?
Expansionary fiscal policy increases the level of aggregate demand, through either increases in government spending or reductions in taxes. Expansionary policy can do this by: 1 increasing consumption by raising disposable income through cuts in personal income taxes or payroll taxes; 2 increasing investments by raising after-tax profits through cuts in business taxes; and 3 increasing government purchases through increased spending by the federal government on final goods and services and raising federal grants to state and local governments to increase their expenditures on final goods and services.
How does fiscal policy help the economy?
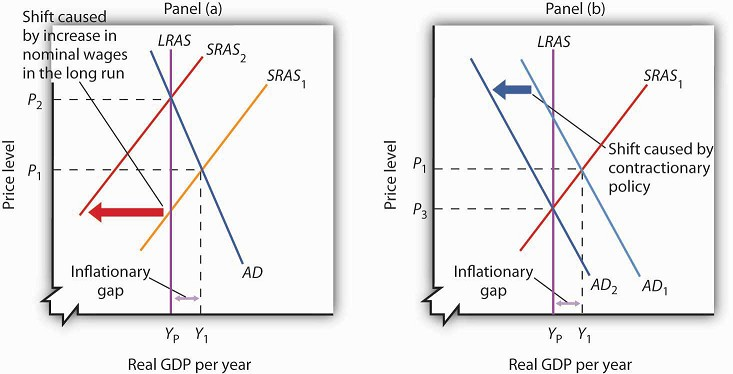
Fiscal policy can also be used to slow down an overheating economy. Suppose the macro equilibrium occurs at a level of GDP above potential, as shown in Figure 3. The intersection of aggregate demand (AD 0) and aggregate supply (AS 0) occurs at equilibrium E 0. In this situation, contractionary fiscal policy involving federal spending cuts or tax increases can help to reduce the upward pressure on the price level by shifting aggregate demand to the left, to AD 1, and causing the new equilibrium E 1 to be at potential GDP.
What is a healthy, growing economy?
In this well-functioning economy, each year aggregate supply and aggregate demand shift to the right so that the economy proceeds from equilibrium E 0 to E 1 to E 2. Each year, the economy produces at potential GDP with only a small inflationary increase in the price level. But if aggregate demand does not smoothly shift to the right and match increases in aggregate supply, growth with deflation can develop.
What is discretionary fiscal policy?
On the other hand, discretionary fiscal policy is an active fiscal policy that uses expansionary or contractionary measures to speed the economy up or slow the economy down. Expansionary fiscal policy occurs when the Congress acts to cut tax rates or increase government spending, shifting the aggregate demand curve to the right.
How does expansionary fiscal policy affect aggregate demand?
Expansionary fiscal policy increases the level of aggregate demand, through either increases in government spending or reductions in taxes. Expansionary policy can do this by: increasing consumption by raising disposable income through cuts in personal income taxes or payroll taxes; increasing investments by raising after-tax profits ...
Why does aggregate demand not grow?
This could be caused by a number of possible reasons: households become hesitant about consuming; firms decide against investing as much; or perhaps the demand from other countries for exports diminishes. For example, investment by private firms in physical capital in the U.S. economy boomed during the late 1990s, rising from 14.1% of GDP in 1993 to 17.2% in 2000, before falling back to 15.2% by 2002. Conversely, increases in aggregate demand could run ahead of increases in aggregate supply, causing inflationary increases in the price level. Business cycles of recession and boom are the consequence of shifts in aggregate supply and aggregate demand. As these occur, the government may choose to use fiscal policy to address the difference.
What is fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy is the use of government spending and tax policy to influence the path of the economy over time. Automatic stabilizers, which we learned about in the last section, are a passive type of fiscal policy, since once the system is set up, Congress need not take any further action. On the other hand, discretionary fiscal policy is an active ...
What are the effects of fiscal policy?
Another of the effects of fiscal policy is in the composition of aggregate demand. GDP consists of government spending, business spending, individual consumption, and net exports. A fiscal policy of increased spending may result in government expenditures being a larger percentage of GDP. Targeted tax policy changes will result in a change in the proportion of output attributed to business or individual spending.
How can fiscal policy be tuned?
Fiscal policy can be very finely tuned by targeting specific companies, individuals, or behaviors. For example, to stimulate the housing market the government may choose to give large tax deductions to people who purchase a house. To increase investment in agriculture, implementing low tax rates on farmers and agricultural businesses will have a positive effect. Conversely, governments can tax an undesired behavior, such as higher tax rates on certain business or goods, like cigarettes or alcohol.
How does lowering taxes affect aggregate demand?
If the government lowers taxes while keeping spending constant, there will be a shift in either aggregate demand or supply, depending on which type of taxes have been lowered. If payroll taxes and individual income tax rates are lowered, consumers will have more income to spend on all types of goods and services, boosting aggregate demand. If corporate tax rates are lowered, businesses are likely to expand and hire more workers, expanding aggregate supply as more goods are produced. As these workers increase their own consumption of goods and services, aggregate demand also increases, resulting in both higher levels of GDP and prices.
What happens when the government increases spending without changing tax policy?
When the government increases spending without changing tax policy, aggregate demand shifts upward. This is an expansionary policy, leading to higher gross domestic product ( GDP) and higher levels of employment and output in the sectors of the economy where the government is spending. Generally, the key recipients are the defense industry and related suppliers. There are additional trickle-down effects of fiscal policy as the workers in these industries spend more, boosting sales and hiring in all areas of the economy.
What can dictate the actions of a company?
A country's fiscal policy can dictate the actions of a companies.
Can expansionary policies cause a deficit?
Expansionary policies may result in a government budget deficit, though not always . If the economy is fairly healthy when spending increases, any budget surplus will be reduced, but not necessarily eliminated. A contractionary policy stance can result in budget surpluses, especially if the budget is already balanced. The effect on the budget deficit in either case, however, depends on the original budget as well as the magnitude and direction of the change in fiscal policy.
What is contractionary fiscal policy?
Contractionary Fiscal Policy. It is a policy that helps decrease money supply in the economy. It is generally adopted during high economic growth phases. Decision to implement it can come from the nation’s finance ministry or the central bank. It leads to increased imports. It decreases expenditure of the government.
What are expansionary and contractionary fiscal policies?
Expansionary and contractionary fiscal policies raise and lower money supply, respectively, into the economy. In this Buzzle article, you will come across the pros and cons of using expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy.
What is fiscal policy?
A fiscal policy defines the relationship between taxation and expenditure. It uses a variety of tools for this purpose, in turn, having a profound effect on factors like unemployment, inflation, aggregate demand, and investments. It is mainly divided into 2 types: expansionary and contractionary. However, a third stance called ‘neutral’ has been ...
How does slowing down production affect economic growth?
Once production slows down, it takes a long time to gear up again. It stabilizes prices and increases consumer confidence. Reduced price fluctuation leads to non-erratic expenditure. It reduces economic growth since there is reduced supply of money. Reduced prices, less demand, etc., leads to stunted economic growth.
Why is it important to reduce taxes?
It increases the expenditure of the government, thereby leading to reduced taxation. A reduction in taxes would lead to an increase in the deficit of the government’s budget. This would lead to high borrowing and rising government debt. It helps fuel the economic growth of the nation, especially during a recession.
How does reduced demand affect economic growth?
Reduced prices, less demand, etc., leads to stunted economic growth. It slows down the inflation. This is also achieved through reduced government spending. Interest rates can be raised, and this leads to reduced demand and prices to match the low money supply. It leads to increased unemployment.
Why is there a slowing down of production?
This can be used to pay off excess debts or accumulate surplus. Since there is reduced money supply , there is a slowing down of production. Companies have restriction on borrowing, and this leads to reduced operations and manufacturing. Once production slows down, it takes a long time to gear up again.
Answer
Arrange the steps to show the effects of contractionary fiscal policy.
New questions in Business
Taxton United has total owners equity if $21,526. the firm has current assets of $7,314, current liabilities if $4,580 and goal assets of $45,369. wha …
Understanding Contractionary Fiscal Policy
- Fiscal policy refers to a government's spending and taxing habits. There are two kinds of fiscal policy direction: contractionary and expansionary. Think of contractionary policy as anything that directly reduces government deficits or increases surpluses. Expansionary policyinvolves activity that directly increases deficits or reduces surpluses. A...
Understanding Crowding Out and Crowding in
- Suppose the federal government increases its fiscal expenditures by $100 billion in a given year. If taxes are politically unpopular, the government normally finances extra spending through borrowing. The federal government borrows money by issuing U.S. Treasuries. In this case, the government issues $100 billion worth of Treasuries. That directly absorbs $100 billion from the …
Two Types of Crowding in
- Some economists have argued that, under the right circumstances, an expansionary government policy might produce crowding in instead of crowding out. If, as Keynesian economists propose, an increase in aggregate demand creates economic expansion, then businesses find it profitable to add to capacity. This boost to the markets, called induced investment, might be stronger tha…