
- Depression.
- Loss of appetite/ Difficulty eating.
- Raised temperature.
- Cough.
- Nasal discharge, often thick and yellow (purulent or pus like).
- Swollen lymph nodes (glands) around the throat.
- Drainage of pus from the lymph nodes around the jaw.
How do you get rid of strangles in a horse?
Tips for Avoiding Infection and Spread
- Do not allow new horses to come in contact with the others for at least two weeks. ...
- Take daily temperatures on new horses for two weeks.
- Reserve one or more stalls or paddocks for use only by new horses.
- Have a plan in case a horse gets strangles and you need to isolate him. ...
How long is horse with strangles contagious?
Horses who have had strangles may be contagious to other horses for a minimum of 3 weeks after all signs have resolved. Some horses are contagious for much longer (months). How many times can a horse get strangles? Can A Horse Get Strangles More Than Once? Yes, but this is uncommon.
Can humans catch the strangles from horses?
Transmission to Humans. In rare cases, humans have contracted infections from the bacteria that cause Strangles. To prevent human infection, people caring for horses with Strangles should avoid getting any nasal or abscess discharge from the horse on their eyes, nose, or mouth.
Can a horse get strangles more than once?
Yes, a horse can get strangles again after having it. However, it's not highly likely. About 75% of horses who recover from Strangles develop an immunity that lasts for 5 years or more. For what its worth, I caught chicken pox twice.
How do I know if my horse has strangles?
What are the clinical signs of strangles? The incubation period for strangles is 3 to 8 days, at which point clinical signs, including lethargy, anorexia, fever, nasal discharge, and swollen lymph nodes with abscess formation may appear.
How long does it take for a horse to show symptoms of strangles?
It normally takes 3-14 days after the horse has been in contact with the strangles bacteria for signs to develop (incubation period). However, there have been times when it has taken up to 28 days.
Can horse strangles go away on its own?
There is usually a thin watery nasal discharge that soon becomes thick and yellow. One or more abscesses form in the inflamed lymph nodes. These tend to rupture either to the outside or into the back of the throat and discharge thick yellow pus. Horses usually recover fully after natural rupture of the abscesses.
How do you detect strangles?
General Information. Diagnostic testing to detect shedding of the bacteria which causes Strangles in horses, Streptococcus equi, currently includes bacterial isolation by aerobic culture and subsequent biochemical identification, and bacterial DNA detection by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test.
How do you help a horse with strangles?
Infected horses must be isolated, please see the article 'Strangles Management' for more information on this. The treatment for carriers involves the removal of any chondroids (dried pus) from the guttural pouches via endoscopy and the use of topical antibiotics (usually penicillin) within the guttural pouches.
What disinfectant kills strangles?
If you are on site, thoroughly disinfect any equipment you have used there with a product that is known to kill strangles (eg: Safe-4, Virkon, Steri-7). Change outer clothing, disinfect boots and thoroughly wash and disinfect hands.
Do horses cough with strangles?
Strangles is NOT an airborne disease, though a horse can cough or snort infected material several feet. However, the disease can spread rapidly between horses, especially those that have not been exposed to the disease in the past.
Can a vaccinated horse get strangles?
We utilised a genome sequencing approach to confirm that two cases of strangles in previously healthy horses that had received the Pinnacle I. N. vaccine (Zoetis) were caused by the vaccine strain.
When is a horse with strangles contagious?
Horses who have had strangles may be contagious to other horses for a minimum of 3 weeks after all signs have resolved. Some horses are contagious for much longer (months).
What happens if your horse tests positive for strangles?
If the blood test is positive, your vet will advise isolation and a guttural pouch lavage. The guttural pouch is a cavity within the horse's head that can harbour and hide bacteria; this means that horses may carry strangles bacteria without showing disease signs.
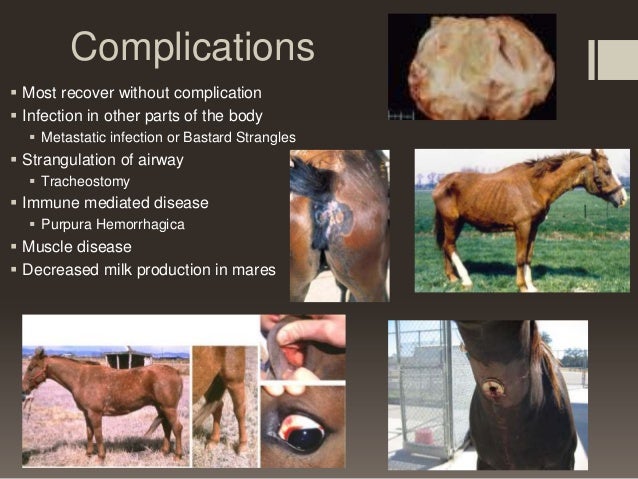
What are bastard strangles?
Metastatic strangles (sometimes called “bastard strangles”) is a condition in which lymph nodes in other parts of the body, such as the abdomen and chest, are affected. The diagnosis of strangles is confirmed by bacterial culture of secretions from abscesses or nasal swab samples.
Where is the guttural pouch in horse?
The guttural pouches are unique to a small number of animal species, including the horse. They are sacs of air that expand from the Eustachian tube, with one on each side of the horse's head. They are positioned beneath the ear and each guttural pouch cavity in an adult horse can hold as much as a coffee mug.
When is a horse contagious with strangles?
Horses who have had strangles may be contagious to other horses for a minimum of 3 weeks after all signs have resolved. Some horses are contagious for much longer (months).
How long should a horse with strangles be quarantined?
How long do horses with, or exposed to, strangles need to quarantined? At least 4 weeks after the disappearance of ALL clinical signs.
How long can a horse be a carrier of strangles?
Horses often remain infected, and infectious, for 4 to 6 weeks but 1 in 10 will continue to discharge infectious material for longer and may remain carriers for years acting as a source of further outbreaks. Horses with chondroids will remain carriers until the chondroids are removed.
Can strangles lay dormant?
Clinical signs Streptococcus equi can remain “dormant” in the upper respiratory tract of apparently unaffected horses with these individuals remaining a source of infection to other animals.
How to keep horses from strangling?
Thoroughly disinfect equipment, stables, fences, trailers, etc. Use a phenolic disinfectant. Change your clothes and wash your hands before coming in contact with healthy horses. Ideally, isolate new horses for two to three weeks. Check their temperatures regularly and watch for any signs of strangles. If signs occur, have a veterinarian take ...
What is strangles?
Strangles is a highly contagious bacterial infection of the upper airway in horses. Strangles can cause the lymph nodes to block the upper airway. Veterinarians can diagnose strangles by taking a swab.
What is a hot pack for horses?
Strangles is a highly contagious infection that causes fever, nasal discharge and abscesses near swollen lymph nodes. Hot packs can help the abscesses mature before opening and flushing them out. Horses that struggle to breathe may need antibiotics or hospital care. To prevent disease spread, isolate sick horses and refrain from sharing equipment ...
How to heal abscesses on horses?
This will help the abscesses mature so they can be safely opened. Once opened, flush the inside of the abscess with dilute povidone-iodine solutions until they heal. Horses usually recover fully after the abscesses open.
Why do horses refuse to eat?
These horses often refuse to eat due to pain. They may stand with their head and nose stretched out to help them breathe. Horses that are struggling to breathe need veterinary care right away. Some horses carry strangles but don’t show symptoms.
What to do if a horse has trouble breathing?
Horses that have trouble breathing need a more aggressive treatment. They’ll likely need anti-inflammatories and antibiotics. The horse may need hospital care to keep their airway open and keep them hydrated.
Can horses get strangles?
Horses that haven’t been exposed to the bacteria in recent years are more prone to strangles. Intramuscular and intranasal vaccines are available for horses. These vaccines decrease the severity of strangles symptoms but don’t completely prevent the disease.
What causes strangles in horses?
Strangles is caused by the Streptococcus equi and for a horse to become infected he needs to have been exposed to the bacteria which can happen when he comes into contact with an infected horse or a horse that is a carrier. The contact doesn’t need to be direct, it can also be indirect which is why it’s important to not share equipment with infected horses.
What are the first signs of strangles?
Once a horse has been infected with strangles he may not display any symptoms immediately but within three to fourteen days there’ll be obvious signs that he has strangles. While not every horse will display every symptom the common signs to look out for are:
How can I prevent my horse from getting strangles?
As the saying goes, prevention is better than cure and strangles is no different. While it can be vaccinated against this is only a short term preventative measure. Long term prevention is harder but if you’re careful you can drastically lower the risk.
How long does it take for a horse to recover from strangles?
Around 90% of horses will make a full recovery, and will no longer be infectious, within three to four weeks but this isn’t the case for 10% of horses. While those horses will have made a full recover they can still carry the infection and as a result of this can easily infect other horses.
Can a horse still remain infectious after they’ve recovered from strangles?
After most horses have fully recovered they’re no longer infectious but around 10% of horses are classed as ‘carriers’ this means that they are still infectious, even though they’ve fully recovered, and can still infect other horses.
Do I have to tell people my horse has strangles?
Every state/country is different and will have their own laws and regulations but strangles is highly contagious and as such is generally considered a notifiable disease. This means that you’ll need to report any cases or even suspected cases. A lot of authorities keep the information confidential unless the owner has agreed to the information being released.
What is strangles?
Strangles is a bacterial infection (caused by the bacteria known as Streptococcus equi) that affects the horse’s upper airway and lymph nodes. It causes the pharynx, larynx, and trachea to swell and can, if not treated, block the airways – the name strangles actually comes from the fact that, before modern treatments, horses were often suffocated, as if they’d been strangled.
How do horses get strangles?
The bacteria that cause strangles typically enter the horse through the mouth or nose. This most often occurs through close contact with an infected horse, but it can also occur through contact with contaminated ...
What is a strangle?
Strangles is a common and highly contagious respiratory disease of equids caused by the bacterium Streptococcus equi subspecies equi. For almost 1,000 years it has been making its rounds through horse populations worldwide.
How long does a horse's scab survive?
The bacteria can survive for around a month in the environment under ideal wet, humid, cold.
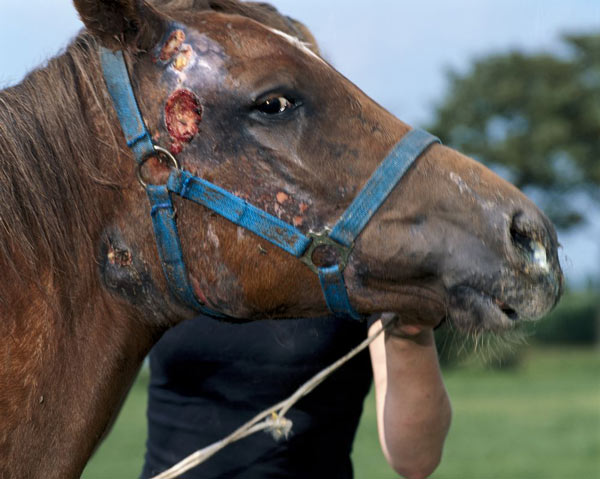
What are the signs of a horse having a strangle?
Any horse that shows suspicious signs of illness (high temperature, nasal discharge, difficulty in swallowing, swollen throat or glands) should be isolated until strangles is confirmed or ruled out by veterinary examinations and laboratory investigations. Any horse that has strangles should be immediately isolated from all other horses.
Why does my horse's nose poke forward?
This is followed by swelling of the lymph nodes (glands) under the jaw and in the throat and the horse may hold his head low with his nose poked forwards to relieve discomfort and to aid respiration. There is usually a thin watery nasal discharge that soon becomes thick and yellow.
Why do horses need to be euthanized?
Many horses loose weight and often require euthanasia on humane grounds with colic, respiratory distress or other complicating illnesses associated with peritonitis, pleuritis and/or multifocal organ damage. Occasionally a horse becomes a symptomless carrier and this has been discussed above.
Can a horse die from a strangle?
This is something else that should be discussed with your veterinarian. Strangles is rarely fatal but deaths can occur.
Can a horse become a carrier?
Occasionally a horse becomes a symptomless carrier and this has been discussed above. Often these carriers only spread the infection when they are stressed e.g., at the time of foaling or after transportation or handling for farriery or routine worming or vaccination. Unless they can be successfully treated by guttural pouch medication, it is difficult to know how these animals are best managed as they are a serious risk of infection to other horses. This is something else that should be discussed with your veterinarian.
Can penicillin kill strangles?
The bacteria that cause strangles can be killed by certain antibiotics including penicillin but there is considerable disagreement as to, if or when antibiotic treatment should be given.
Can horses recover from abscesses?
Horses usually recover fully after natural rupture of the abscesses. You should seek veterinary help without delay. The veterinarian will help confirm the diagnosis by clinical examination and the collection of swab samples for laboratory investigation and will help you with appropriate treatment and management.
How long does it take for a horse to get a strangle?
The incubation period of strangles is 3–14 days, and the first sign of infection is fever (103°–106°F [39.4°–41.1°C]). Within 24–48 hr of the initial fever spike, the horse will exhibit signs typical of strangles, including mucoid to mucopurulent nasal discharge, depression, and submandibular lymphadenopathy.
What is a strangle?
Tables (0) Videos (0) Strangles is an infectious, contagious disease of Equidae characterized by abscessation of the lymphoid tissue of the upper respiratory tract. The causative organism, Streptococcus equi equi, is highly host-adapted and produces clinical disease only in horses, donkeys, and mules.
What is post exposure immunity in horses?
Postexposure immunity is prolonged after natural disease in most horses, and protection is associated with local (nasal mucosa) production of antibody against the antiphagocytic M protein. The clinical attack rate of strangles is reduced by 50% in horses vaccinated with IM products that do not induce mucosal immunity. Local (mucosal) production of antibody requires mucosal antigen stimulation. An intranasal vaccine containing a live attenuated strain of S equi equi was designed to elicit a mucosal immunologic response. This attenuated strain is not temperature sensitive (inactivated by core body temperature) like the intranasal influenza vaccine. Reported complications include S equi equi abscesses at subsequent IM injection sites (live bacteria on hands of administrator), submandibular lymphadenopathy, serous nasal discharge, and purpura hemorrhagica (see Type III Reactions : Other Type III Reactions ).
What is a metastatic strangle?
Metastatic strangles (“bastard strangles”) is characterized by abscessation in other lymph nodes of the body, particularly the lymph nodes in the abdomen and, less frequently, the thorax. S equi is the most common cause of brain abscess in horses, albeit rare.
How often should you disinfect horses exposed to strangles?
The rectal temperature of all horses exposed to strangles should be obtained twice daily, and horses developing fever should be isolated (and potentially treated with penicillin). Contaminated equipment should be cleaned with detergent and disinfected using chlorhexidine gluconate or glutaraldehyde.
Can NSAIDs be used on horses?
NSAIDs can be administered judiciously to reduce pain and fever and to improve appetite in horses with fulminant clinical disease. Tracheotomy may be required in horses with retropharyngeal abscessation and pharyngeal compression.

What Is Strangles?
Signs of Illness
- Early signs 1. Fever, temperature above 102 F 2. Depression 3. Nasal discharge which starts clear and becomes thick and yellow A few days after onset, the horse will develop painful swelling of the lymph nodes. This swelling produces abscesses that will rupture and discharge pus. More serious cases arise when horses have lymph node swelling in the ...
Treatment
- Veterinarians usually recommend applying hot packs to the lower jaw. This will help the abscesses mature so they can be safely opened. Once opened, flush the inside of the abscess with dilute povidone-iodine solutions until they heal. Horses usually recover fully after the abscesses open. Many veterinarians refrain from using antibiotics for uncomplicated cases. Ant…
Preventing Disease Spread
- How strangles spreads
1. Horse-to-horse contact 2. Contact with contaminated people, tack, drinking troughs, etc. - What to do if strangles occurs
1. Isolate all the horses with symptoms to one area. 2. Use separate tools and grooming equipment in the isolation area. 3. Completely clean all feed, manure and bedding from contaminated areas. Keep these materials away from healthy horses. 4. Thoroughly disinfect eq…
Vaccines
- Horses that haven’t been exposed to the bacteria in recent years are more prone to strangles. Intramuscular and intranasal vaccines are available for horses. These vaccines decrease the severity of strangles symptoms but don’t completely prevent the disease.