The main units of the geologic time scale, from largest (longest) to smallest, are: eon The geological time scale (GTS) is a system of chronological measurement that relates stratigraphy to time, and is used by geologists, paleontologists, and other Earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships between events that have occurred throughout Earth’s hist…Geologic time scale
What are the units of the geologic time scale?
The geologic time scale is a means of measuring time based on layers of rock that formed during specific times in Earth’s history and the fossils present in each layer. The main units of the geologic time scale, from largest (longest) to smallest, are: eon, era, period, epoch and age.
What are the 5 major divisions of geologic time?
Ans: 5 major divisions of geologic time are- eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages. Q.2. What are the 11 periods on the geologic time scale?
What are the 5 subgroups of time?
It is organised into 5 subgroups: – Eons, Eras, Periods, Epochs and Ages. Eons are the biggest which are divided into eras and eras further divided into periods, epochs and ages.
What is the difference between eras and periods in geology?
Periods- Periods in geological time scale refers to the unit which is smaller than eras but bigger than epochs. All the eras are divided into smaller units called periods.
What are the 5 different geologic time units?
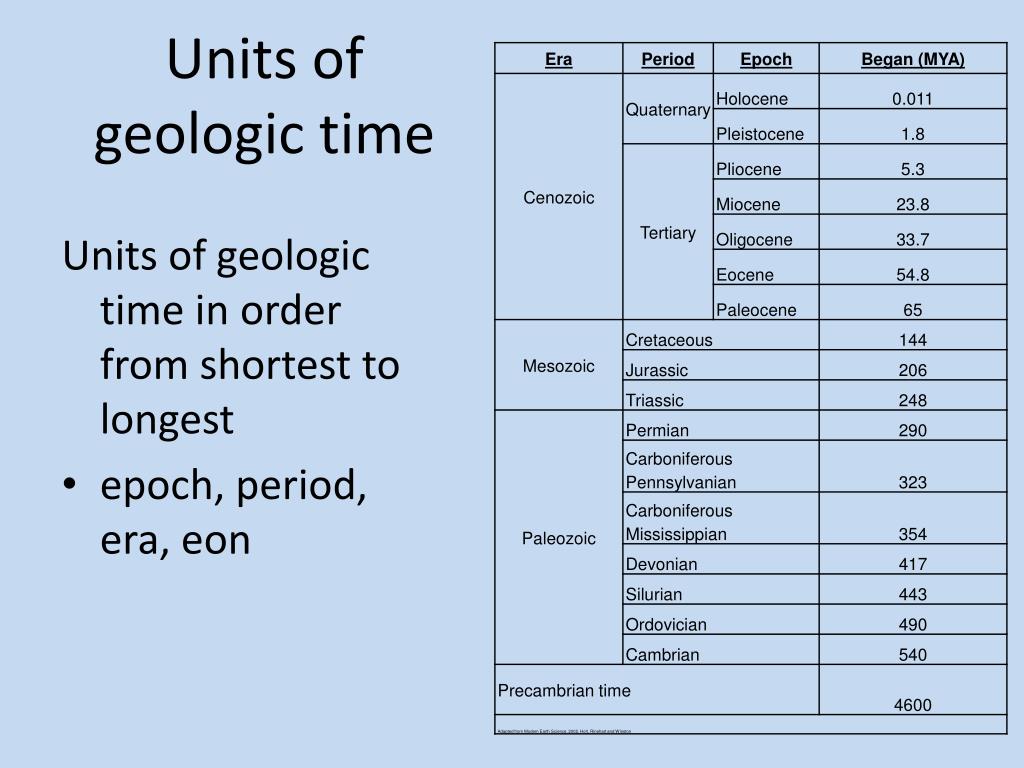
Geologic time scale showing the geologic eons, eras, periods, epochs, and associated dates in millions of years ago (MYA).
What are the units of geologic time?
The geologic time scale is the “calendar” for events in Earth history. It subdivides all time into named units of abstract time called—in descending order of duration—eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
What are the four units of geologic time?
The geologic time scale is divided into (from longest to shortest): eons, eras, periods, epochs and ages.
What are the 5 sub groups that the geologic time scale is Organised into?
Geological Time Scale is organised into \(5\) subgroups: – Eons, Eras, Periods, Epochs and Ages. Eons is the largest in the GTS. Eons are divided into Eras which are further subdivided into Periods, Epochs and Ages. Earliest Eon is known as Hadean followed by the Archaean eon, Proterozoic eon and then Phanerozoic Eon.
What is the most commonly used unit of geologic time?
Eons are the largest intervals of geologic time and are hundreds of millions of years in duration. In the time scale above you can see the Phanerozoic Eon is the most recent eon and began more than 500 million years ago.
What is the largest unit of geologic time?
EonEon: Two or more eras compose an Eon. This is the largest division of time, lasting hundreds of millions of years.
Which unit of geologic time is the oldest Brainly?
The eon is the broadest category of geological time. Earth's history is characterized by four eons; in order from oldest to youngest, these are the Hadeon, Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic.
How many geological periods are there?
A period is a major rank below an era and above an epoch. It is the geochronologic equivalent of a chronostratigraphic system. As of April 2022 there are currently 22 defined periods/systems.
Which of the following is the correct order of geologic time?
So, the correct option is 'Precambrian, Palaeozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic'.
How is geologic time scale divided into periods?
To make geologic time easier to comprehend, geologists divided the 4.6 billion years of Earth's history into units of time called eons. Then they further divided the eons into two or more eras, eras into two or more periods, periods into two or more epochs, and epochs into two or more ages.
How is the geologic time scale organized?
From largest to smallest, this hierarchy includes eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
How do you calculate geologic time?
The rate at which the isotopes decay is in effect our "geological clock". By measuring the amount of the parent and daughter isotopes in a crystal, and then applying the decay rate, the actual age in years since the rock crystallized can be calculated.
Which is a unit of geologic time consisting of two or more periods?
Two or more geological periods comprise an era, which is hundreds of millions of years in duration. The period is the basic unit of geological time in which a single type of rock system is formed, lasting tens of millions of years.
What is an example of geologic time scale?
Some examples of events listed on the geologic time scale include the first appearance of plant life on Earth, the first appearance of animals on Earth, the formation of Earth's mountains, and the extinction of the dinosaurs.
What is the calendar of geology?
For the purposes of geology, the “calendar” is the geologic time scale. One way to distinguish and define each segment of time is by the occurrence of major geologic events and the appearance (and disappearance) of significant life-forms, starting with the formation of Earth’s crust followed by the appearance of ever-changing forms of life on Earth.
Will geologists change the geologic time scale?
As technology of dating methods improves, geologists probably will make small but significant changes to the geologic time scale for years to come. Moreover, as geologists discover more complete sections of rock, which preserve evidence of significant portions of geologic time, and as the International Commission on Stratigraphy evaluates ...
What is the largest unit of geologic time?
A geologic period is divided further into epochs. Eons are the largest unit of geologic time. Epochs are the smallest unit of geologic time. A geologic epoch is divided further into eras.
What is geologic time scale?
The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth's history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until the present. It divides Earth's long history into units of time.
What are the three units of time that divide the Precambrian and present?
Geologists divide the time between Precambrian and the present into three long units called eras ( Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic ).
What Is The Geologic Time Scale?
The geologic time scale is a means of measuring time based on layers of rock that formed during specific times in Earth’s history and the fossils present in each layer. The main units of the geologic time scale, from largest (longest) to smallest, are: eon, era, period, epoch and age. Each corresponds to the time in which a particular layer of rock was formed.
How Was The Geologic Time Scale Invented?
The geologic time scale was not invented by any one person. Instead, it is the result of centuries of research and experimentation.
How Do We Know The Ages Of The Ancient Rocks?
Although following the patterns of fossil distribution in rock layers enabled early geologists to state that one stratum was older than another, there was no way for them to know the exact ages of the rocks.
Why do scientists know how old a fossil is?
Because the geologic time scale is used worldwide, if a scientist from America says he found a fossil in a Cretaceous rock formation, then scientists in other countries will know (roughly) how old the fossil is.
What is the term for the Mesozoic era?
Scientists often use terms such as “Mesozoic Era” and “Jurassic Period” when referring to certain times in Earth’s history. Both the Mesozoic Era and the Jurassic Period are stages in the geologic time scale. The geologic time scale links particular times in Earth’s history with the layers of rock in the Earth’s crust that were formed ...
What is the Jurassic Period?
A well-known period of the geologic time scale is the Jurassic Period, made famous by the film Jurassic Park. The Jurassic Period began around 201 million years ago (Mya), and ended around 145 My a. During this time, a particular layer of limestone was formed in the Jura Mountains of France and Switzerland. The Jurassic Period gets its name ...
Why did the geologic time scale cause confusion?
Confusion arose because similar rock layers were given different names in different parts of the world. The creation of the geologic time scale gave scientists a globally recognized standard for measuring and comparing the ages of rocks and fossils.
How many epochs are there in the Cenozoic era?
4. Epochs- Periods are further divided into epochs like the Quaternary period of Cenozoic era is divided into 3 epochs, i.e., Holocene, Pleistocene and Pliocene.
What is the term for the unit that is smaller than eras but bigger than epochs?
3. Periods- Periods in geological time scale refers to the unit which is smaller than eras but bigger than epochs. All the eras are divided into smaller units called periods. The Palaeozoic era is divided into periods- Permian, Carboniferous, Devonian, Silurian, Cambrian, Ordovician. All the other periods are given in the table below.
What is geological time scale?
Geological Time Scale is the tabulated form showing the sequence and duration of the eras and the periods with their dominant form of life since the beginning of life on the earth. (MODERN’S a b c + of Biology)
How many subgroups are there in the Geological Time Scale?
The Geological Time Scale has been reworked many times to reflect the latest knowledge of Earth’s history. It is organised into 5 subgroups: – Eons, Eras, Periods, Epochs and Ages.
When did life start on Earth?
Life on earth started about 4 billion years ago and humans were one of the last organisms to evolve. We wrack our brains just trying to imagine what would have happened a few hundred years ago. To help us comprehend the full expense of time, scientists have turned to the rocks. Geologists are now able to describe crucial events in life’s history- from its origin to disastrous extinction events. There was no idea what happened in what order. To know when and how life originated, how it looked, Geological Time Scale was made by geologists.
Who wrote the first law of stratigraphy?
Scientist Nicolas Steno published the first law of stratigraphy in 1669 .He argued that the layers closer to the surface must be younger than the layers below them. So, he thought, the farther we dig, the older the fossils that we get.
Who was the first to name the layers of rock?
Based on Steno’s ideas, Italian geologist Giovanni Arduino in the 1760 s went a step further and began naming the layers of rock. But as rock layers do not appear in this same order all over the world, there was no way for geologists to compare rocks from one location to another.
What Is The Geologic Time Scale?
An Example of The Geologic Time Scale in Use
- A well-known period of the geologic time scale is the Jurassic Period, made famous by the film Jurassic Park. The Jurassic Period began around 201 million years ago (Mya), and ended around 145 Mya. During this time, a particular layer of limestone was formed in the Jura Mountains of France and Switzerland. The Jurassic Period gets its name from these mountains. 1. You can fin…
What Period of The Geologic Time Scale Are We Currently Living in?
- We are currently living in the Meghalayan Age of the Holocene Epoch of the Quaternary Period of the Cenozoic Era of the Phanerozoic Eon.
Geologic Time Scale Divisions
- The main divisions of the geologic time scale, from largest to smallest, are: 1. Eon 2. Era 3. Period 4. Epoch 5. Age Unlike units of time such as seconds, hours and days, the units of the geologic time scale are not equal. Earth’s entire history is divided into four eons; the Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic and Phanerozoic. The first three eons are referred to as Precambrian; the Phaneroz…
Why Is The Geologic Time Scale Useful?
- The geologic history of the Earth dates all the way back to the time that the Earth was formed, some 4.6 billion years ago. Since it is difficult to work with such vast timespans, geologists and other scientists divided the Earth’s geologic history into smaller, more manageable units of time, together known as the geologic time scale. This scale acts like a ‘calendar’ of the geologic event…
How Was The Geologic Time Scale invented?
- The geologic time scale was not invented by any one person. Instead, it is the result of centuries of research and experimentation. One of the first people to realise that rocks formed in layers was Nicolaus Steno, a Danish scientist and part-time fossil collector. In the 1660s, Steno published a paper in which he stated that layers of sedimentary rock are laid down horizontally in successio…
How Are Fossils Important in The Geologic Time Scale?
- Fossils are very important in the geologic time scale. Long before scientists had the technology to date ancient rocks, they used fossils to understand events that had happened in the Earth’s history and when they happened. The fact that particular rock strata could be recognized by the fossils they contained allows geologists to match layers of rocks between different parts of a co…
The Geologic Time Scale and Evolution
- Investigation of the fossilized remains of organisms in rock layers gives scientists clues about how living creatures have evolved. The oldest, lowest strata contain the fossils of simple, soft-bodied animals, while higher layers contain animals that are more complex and specialized. The fossil record, written in Earth’s rocks through the eons, shows how some species have evolved, …
How Do We Know The Ages of The Ancient Rocks?
- Although following the patterns of fossil distribution in rock layers enabled early geologists to state that one stratum was older than another, there was no way for them to know the exact ages of the rocks. Today, radiometric dating is used to assign actual ages to the rocks of the Earth’s crust. The layers of igneous rock between the sedimentary, fossil-bearing layers can be dated us…
Who Uses The Geologic Time Scale?
- Knowledge of the geologic timescale is vital for miners who are searching for particular types or ages of rocks to mine for important minerals. Farmers may wish to know the age and origin of the sediments on their lands so that they can plant suitable crops and find water sources. Geologists use the geologic time scale to determine the ages of surface rocks all over the world. This help…