Types of Lipoproteins
- HDL – The high-density lipoprotein, it is also called good cholesterol and the density is due to high lipid and the protein ratio. ...
- VLDL- Very low-density lipoproteins. These lipoproteins are derived from the liver for the export of triacylglycerols.
- IDL- The Intermediate-density lipoproteins. ...
What are the two types of lipoproteins and their functions?
Lipoprotein. Two types of lipoprotein are involved in this function: low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) and high-density lipoproteins (HDLs). LDLs transport cholesterol from its site of synthesis in the liver to the body’s cells, where the cholesterol is separated from the LDL and is then used by the cells for various purposes.
What are the types of lipoproteins in a lipid panel?
The main types of lipoproteins that are analyzed in a lipid panel include: Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL). These lipoproteins consist of mainly triglycerides, some cholesterol molecules, and less protein. Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDL). LDL consists of more cholesterol than triglycerides and protein.
What are very low-density lipoproteins?
Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL). These lipoproteins consist of mainly triglycerides, some cholesterol molecules, and less protein. The more fat a lipoprotein contains, the less density it has.
How are lipoproteins classified based on density?
Classifying lipoproteins based on density. High-Density Lipoproteins (HDL) HDL has a density range between 1.063 and 1.121 g/mL and size between 5 and 12 nm. In a healthy individual, it is composed of approximately 33% protein, 29% phospholipid, and 8% triacylglycerol.
What are the types of lipoprotein?
There are four major classes of circulating lipoproteins, each with its own characteristic protein and lipid composition. They are chylomicrons, very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL).
What are the types and functions of lipoproteins?
Two types of lipoprotein are involved in this function: low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) and high-density lipoproteins (HDLs). LDLs transport cholesterol from its site of synthesis in the liver to the body's cells, where the cholesterol is separated from the LDL and is then used by the cells for various purposes.
How many types of lipoproteins are present in blood?
Plasma lipoproteins can be divided into seven classes based on size, lipid composition, and apolipoproteins (chylomicrons, chylomicron remnants, VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL, and Lp (a)). Chylomicron remnants, VLDL, IDL, LDL, and Lp (a) are all pro-atherogenic while HDL is anti-atherogenic.
What are the two types of lipoproteins?
LDL and HDL Cholesterol: "Bad" and "Good" CholesterolLDL (low-density lipoprotein), sometimes called “bad” cholesterol, makes up most of your body's cholesterol. ... HDL (high-density lipoprotein), or “good” cholesterol, absorbs cholesterol and carries it back to the liver.
What means lipoprotein?
Lipoproteins are particles made of protein and fats (lipids). They carry cholesterol through your bloodstream to your cells. The two main groups of lipoproteins are called HDL (high-density lipoprotein) or "good" cholesterol and LDL (low-density lipoprotein) or "bad" cholesterol.
What is lipoprotein with example?
Lipoproteins are protein molecules that transport fat in the body. They contain cholesterol and triglycerides. Examples include high-density lipoproteins (HDL), known as “good” cholesterol, and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) or “bad” cholesterol.
What is the largest lipoprotein?
ChylomicronsChylomicrons are the largest lipoproteins present in the circulation, with their size dependent on the fed/fasted state, the rate of absorption of fat, and the type and amount of fat absorbed.
What are lipoproteins used for?
Lipoproteins are parcels made of fat and protein. Their job is to carry fats (also called lipids) around the body in the blood. LDL cholesterol (or 'bad cholesterol') is also a lipoprotein.
Is cholesterol A lipoprotein?
Facts about cholesterol Cholesterol and other fats are carried in your bloodstream as spherical particles called lipoproteins. The two most commonly known lipoproteins are low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL).
Why HDL is called good cholesterol?
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol is known as the "good" cholesterol because it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. Higher levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
What's a good HDL number?
HDL cholesterol levels greater than 60 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) are high. That's good. HDL cholesterol levels less than 40 mg/dL are low.
What is lipoprotein made of?
Lipoproteins are round particles made of fat (lipids) and proteins that travel in the bloodstream to cells throughout your body. Cholesterol and triglycerides are two types of lipids found in lipoproteins. Your body makes different types of lipoproteins.
What are HDL and LDL and their functions?
HDL cholesterol can be thought of as the “good” cholesterol because a healthy level may protect against heart attack and stroke. HDL carries LDL (bad) cholesterol away from the arteries and back to the liver, where the LDL is broken down and passed from the body.
What are the functions of LDL?
Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDL) LDL is responsible for carrying cholesterol to cells that need it. Elevated LDL levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
What is the functional difference between LDL and HDL?
HDL helps rid your body of excess cholesterol so it's less likely to end up in your arteries. LDL is called “bad cholesterol” because it takes cholesterol to your arteries, where it can collect in your artery walls. Too much cholesterol in your arteries may lead to a buildup of plaque known as atherosclerosis.
Which is a type of lipoprotein quizlet?
on Lipids, you have already encountered two types of lipoproteins— Chylomicrons and VLDL (very low density lipoproteins). Chylomicrons are packaged in the small intestine from dietary sources of lipids. VLDL is packaged in the liver from endogenous sources, either newly synthesized or recycled lipids.
What are the different types of lipoproteins?
Based on their density, lipoproteins can be classified into chylomicrons, very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL), low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). Lipoproteins are complex particles that consist of a central core of cholesterol esters and triacylglycerols ...
What is the classification of lipoproteins?
Classification of lipoproteins by electrophoretic mobility. Lipoproteins are also classified by their electrophoretic mobility pattern into alpha (α), beta (β), pre-β, and broad-β lipoproteins. Those lipoproteins with minimum protein content move faster whereas the lipoproteins with higher protein content move slower.
What is the brain of the lipoprotein system?
Known as the brain of the lipoprotein system, apolipoproteins regulate many processes of remodeling and uptake. Apolipoproteins bind to the surface of the lipoproteins complex. With the help of specific enzymes or proteins that the complex binds to on the cell membrane, the lipoproteins are directed to the metabolic site.
What is the truncated form of apolipoprotein B?
Chylomicrons consists of a truncated form of apolipoprotein B that is apoB-48. Apolipoprotein C occurs in HDL, VLDL and chylomicrons and apolipoprotein E occurs in all classes of lipoproteins.
Which lipoprotein has the highest protein content?
The movement of lipoproteins is based on the nature of the apoprotein associated with the lipoprotein. α lipoproteins have the highest protein content. HDL are α lipoproteins, VDL are pre-β lipoproteins, LDL are β lipoproteins, and IDL are broad-β lipoproteins.
How are lipoproteins separated?
This allows lipoproteins of different sizes to be separated and identified through processes such as electrophoresis and ultracentrifugation. Upon centrifugation, lipoproteins with high protein content sediment easily due to their high density whereas lipoproteins with high lipid content have low density and will float on the surface.
What is the lipoprotein that transports triglycerides?
In a healthy individual, it is composed of approximately 50% triacylglycerol, 18% phospholipid, and 10% protein. This lipoprotein is responsible for the transportation of synthesized triglyceride from the liver to the adipose tissue for storage.
How many different types of lipoproteins are there?
There are five different types of lipoproteins in the blood, and they are commonly classified according to their density. The main types of lipoproteins that are analyzed in a lipid panel include very low-density lipoproteins (VLDS), low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL).
What is the protein component of a lipoprotein?
When triglycerides and cholesterol are removed from this lipoprotein complex, and you have the protein alone, the protein component is referred to as an apolipoprotein. Different types of apolipoproteins are associated with different lipoproteins. 1
Why is LDL higher than VLDL?
LDL consists of more cholesterol than triglycerides and protein. Because it contains less lipid and more protein in comparison to VLDL, its density is greater. LDL is responsible for carrying cholesterol to cells that need it. Elevated LDL levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Why is VLDL less dense than lipoproteins?
In this case, VLDL is less dense than most lipoproteins because of its high lipid composition. VLDL is made in the liver and is responsible for delivering triglycerides to cells in the body, which is needed for cellular processes. As triglycerides get delivered to cells, VLDL is made up less of fat and more of protein, ...
What is a very low density lipoprotein?
Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL) These lipoproteins consist of mainly triglycerides, some cholesterol molecules, and less protein. 1 The more fat a lipoprotein contains, the less density it has. In this case, VLDL is less dense than most lipoproteins because of its high lipid composition.
What is the name of the protein that transports cholesterol and triglycerides?
This lipid and protein complex is referred to as a lipoprotein. When triglycerides and cholesterol are removed from this lipoprotein complex, and you have the protein alone, ...
What are the different types of cholesterol?
If you've had your cholesterol checked before, you have probably noticed a lot of different types of cholesterol listed on your lab result. LDL, VLDL, HDL —what do they all mean? All of these types of cholesterol may be made up of similar parts, but their functions in the body are different.
What are lipoproteins made of?
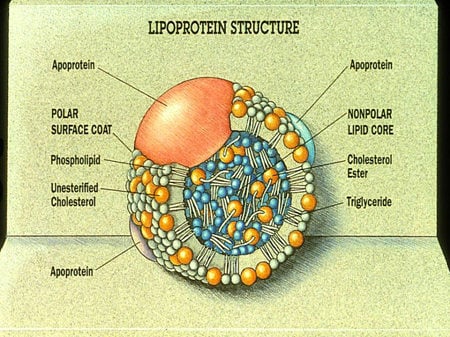
What are Lipoproteins? Lipoproteins are special particles made up of droplets of fats surrounded by a single layer of phospholipid molecules. Phospholipids are molecules of fats which are attached to a phosphorus-containing group. They are distinctive in being amphipathic, which means they have both polar and non-polar ends.
How are lipoproteins differentiated?
Different lipoproteins are differentiated based on specific proteins attached to the phospholipid outer layer, called the apolipoprotein. This also helps to make the fatty molecule more stable, and also binds to cell surface receptors in some cases, to enable the cell to take up the lipoprotein by receptor-mediated endocytosis.
What are the correlations between lipoproteins and cardiovascular risk?
Lipoproteins show varying patterns that correlate with the risk of having a fatal cardiovascular event. High LDL, VLDL and triglyceride levels are associated with a high risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. High HDL is correlated with reduced cholesterol levels, and a lower cardiovascular risk. Thus a high measurement of apo-A-1 correlates with a low atherosclerosis risk. HDL levels drop with cigarette smoking, and rise with regular exercise, alcohol use, estrogen levels and weight loss.
What is VLDL cholesterol?
VLDL, very low density lipoprotein – this is composed of protein, fats and cholesterol synthesized in the liver. It is associated with 5 different apoproteins, namely , B-100, C-I, C-II, C-III and E. It is converted to IDL and LDL by removal of the apoproteins, except for one called apoprotein B100, along with esterification of the cholesterol. They are second only to chylomicrons in the percentage triglyceride content.
Why do lipoproteins have polar ends?
In a lipoprotein, the polar ends of all the phospholipid molecules face outwards, so as to interact with water, itself a polar molecule. This enables the lipoprotein to be carried in the blood rather than rising to the top, like cream on milk. The non-polar fat balled up inside the phospholipid layer, at the center of the lipoprotein, is thus transported to the place where it must be stored or metabolized, through the bloodstream, despite being insoluble in blood. Thus lipoproteins are molecular level trucks to carry fats wherever they are required or stored.
What is the lipid profile?
The lipid profile. An important part of the health evaluation is the lipid profile. This consists of measuring the total plasma cholesterol, the LDL, VLDL and HDL levels, as well as the triglyceride level.
Which lipoprotein has the highest triglyceride content?
Chylomicrons – these are the largest and least dense of the lipoproteins, with the highest triglyceride content. They consist of a protein component synthesized in the liver, which wraps around diet-derived cholesterol and fats.
What are the two types of lipoproteins?
Two types of lipoprotein are involved in this function: low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) and high-density lipoproteins (HDLs). LDLs transport cholesterol from its site of synthesis in the liver to the body’s cells, where the cholesterol is separated from the LDL and is then used by the cells for various purposes.
What is the name of the genetic disorder that involves excessive concentrations of lipoproteins in the blood?
Several hereditary genetic disorders, called hyperlipoproteinemias, involve excessive concentrations of lipoproteins in the blood. Other such diseases, called hypolipoproteinemias, involve abnormally reduced lipoprotein levels in the blood.
Why are lipoproteins important in blood?
Lipoproteins in blood plasma have been intensively studied because they are the mode of transport for cholesterol through the bloodstream and lymphatic fluid. Cholesterol is insoluble in the blood, and so it must be bound to lipoproteins in order to be transported.
What are the different types of lipids?
However, they are hydrophobic and can't freely circulate in your blood. Lipoproteins are lipids that have been coated with phospholipids and protein to help them become soluble. There are four forms of lipoproteins based on their composition. Chylomicrons have the most lipid and lowest protein content. VLDL, LDL, and HDL have increasingly more protein and are named for their relative density. Doctors use the ratio of HDL to LDL as a measure of cardiovascular health.
How do fatty acids form lipoproteins?
Triglyceride molecules clump together and then are coated with phospholipids and a few proteins, which altogether form a chylomicron, the first type of lipoprotein. Chylomicrons also contain a fat-soluble, steroid molecule called cholesterol. Your body needs cholesterol in order to make steroid hormones and cell membranes.
Why do lipids floated on top of water?
Compared to water, lipids have a low density. Remember that vinaigrette analogy from above? The oil (i.e. lipids) floated on top because lipids are less dense than water. The more lipid a lipoprotein has, the less dense it will be. The more protein a lipoprotein has, the denser it will be. We classify lipoproteins based on their density. For instance, a high density lipoprotein or HDL has a high percentage of protein compared to lipid. The table below lists the major lipoprotein forms and the relative percentage of phospholipid, triglyceride, protein and cholesterol.
How many types of molecules are there in living things?
All living things are made up of four main types of molecules:
Is lipoprotein cholesterol the same as LDL cholesterol?
All lipoproteins have basically the same function - they help transport lipids in the blood. However, some lipoproteins are healthier for us than others. Doctors typically compare the amount of HDL to LDL. In general, the higher the HDL/LDL ratio the better since HDL is delivering excess cholesterol to your liver for disposal. In contrast, a low HDL/LDL ratio is unhealthy because LDLs have the highest percentage of cholesterol. If there are too many LDLs in your blood they will start depositing cholesterol in your arteries. This causes plaques to form, increases in your blood pressure, and could lead to a heart attack.
Content
The lipoproteins They are complex particles that function in the transport and absorption of lipids through the blood, to and from different tissues. They are made up mainly of nonpolar lipids such as cholesterol and triglycerides, in addition to some phospholipids and proteins.
Structure
Plasma lipoproteins are particles with an almost spherical structural morphology, since they are, in reality, complex micelles of lipids and proteins, in which the hydrophobic or apolar regions of the lipids face each other in the center, while the hydrophilic or poles are exposed towards the surface, in contact with the aqueous medium.
Composition of lipoproteins
As explained, lipoproteins are particles that basically consist of a mixture of lipids and proteins that perform transport functions.
Features
Lipoproteins actively participate in the transport and intestinal absorption of fatty acids that are obtained from food, in addition, these particles also contribute in the transport of lipids from the liver to peripheral tissues and in reverse transport, that is, , from the peripheral tissues to the liver and intestine.
Types (classification)
Lipoproteins are classified according to their density, a characteristic directly related to the relationship between the proportion of lipids and proteins that compose them, and which is very useful when they are separated by ultracentrifugation processes.
Chylomicrons
Chylomicrons (CM, from English Chylomicrons) are formed from fatty acids and lipids that enter the body with food, which, once absorbed by the cells of the intestinal epithelium, mix and recombine with each other and with some proteins.
Very low-density lipoproteins
Very low-density lipoproteins or VLDL (of English Very Low Density Lipoprotein ), also known as “pre-β lipoproteins” are produced in the liver and fulfill the function of exporting triglycerides, which represent one of its main components.
How many classes of lipoproteins are there?
According to the density at which they float by ultracentrifugation, lipoproteins (the complexes to which apolipoproteins belong) are commonly grouped into 6 classes with different properties and functions, namely:
Which lipoproteins are taken up by cells?
Apolipoproteins B-100 and E mediate the interaction of LDL lipoproteins with apo B, E (LDL) receptors in hepatic and extrahepatic tissues, and with apoE receptors in the liver, so that these are “taken up” by cells , thus regulating its plasma levels.
What are apolipoproteins made of?
The apolipoproteins are the proteins that are part of lipoproteins, which are "pseudomycelar" macromolecular complexes composed of an apolar center or nucleus made up of triglycerides and cholesterol esters, surrounded by a layer of phospholipids and lipoproteins and that participate in lipid homeostasis.
What is the cofactor of lipid metabolism?
Apolipoproteins are also cofactors for lipid metabolism enzymes, for example lipoprotein lipase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides in chylomicrons, requires the presence of a class C apolipoprotein.
How do phospholipids interact with lipoproteins?
They maintain and stabilize the structure of lipoproteins by interacting with the micellar structure and phospholipids on the surface of lipoprotein particles, providing a hydrophilic surface for their contact with the aqueous medium that surrounds them.
How many apolipoproteins are in blood plasma?
The blood plasma of a human being has dozens of different apolipoproteins, classified into five main groups: apolipoproteins A, B, C, D and E. Some of these groups can be subdivided according to the presence of variants or isoforms and for this purpose adds a number in roman letters that designates the sub-rating.
Which lipoprotein is the least dense?
Chylomicrons are the largest lipoproteins, and therefore the least dense. They are synthesized in the intestines and are responsible for the transport of lipids and fats that come from the food we eat.

Classifying Lipoproteins Based on Density
Classification of Lipoproteins by Electrophoretic Mobility
- Lipoproteins are also classified by their electrophoretic mobility pattern into alpha (α), beta (β), pre-β, and broad-β lipoproteins. Those lipoproteins with minimum protein content move faster whereas the lipoproteins with higher protein content move slower. The movement of lipoproteins is based on the nature of the apoprotein associated with the ...
Classification of Lipoproteins by Apolipoprotein Content
- Lipoproteins are also classified by the nature of apolipoprotein content. Known as the brain of the lipoprotein system, apolipoproteins regulate many processes of remodeling and uptake. Apolipoproteins bind to the surface of the lipoproteins complex. With the help of specific enzymes or proteins that the complex binds to on the cell membrane, the lipoproteins are directed to the …
Further Reading