Precautions
Estradiol. Estradiol is an Estrogen. The mechanism of action of estradiol is as an Estrogen Receptor Agonist. The chemical classification of estradiol is Estradiol Congeners. Therapeutic Estradiol is a steroid sex hormone vital to the maintenance of fertility and secondary sexual characteristics in females.
What is the chemical classification of estradiol?
Difference Between Estradiol and Estrogen. However, there are another two main types of estrogens; estrone and estriol. Estriol is the least effective hormone and found mostly in pregnant females, whereas estrone is the most abundant estrogen hormone in menopause. Estradiol is further described below.
What is the difference between estrone and estriol?
Estradiol. Estradiol is the 17-beta-isomer of estradiol, an aromatized C18 steroid with hydroxyl group at 3-beta- and 17-beta-position. Estradiol-17-beta is the most potent form of mammalian estrogenic steroids. Estradiol is an Estrogen. The mechanism of action of estradiol is as an Estrogen Receptor Agonist.
What is the mechanism of action of estradiol?
Estradiol is the most active type of estrogen that involves in hundreds of activities in the body. It is one of the hormones that have a great effect on the symptom relief for insomnia, headaches, mental fogginess, and fatigue.
What is the most active type of estrogen?
What are the compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in target tissues?
Which isomeric form of estrogen is the most active?
What is estradiol 17?
How much estradiol is excreted in a day?
What is the maximum amount of estradiol in untreated animals?
How does estradiol release to the environment?
How long does estradiol last?
See 4 more
About this website
Estradiol: Uses, Dosage & Side Effects - Drugs.com
Estradiol is used to treat symptoms of menopause such as hot flashes, and vaginal dryness, burning and irritation. Includes estradiol side effects, interactions and indications.
Estradiol - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
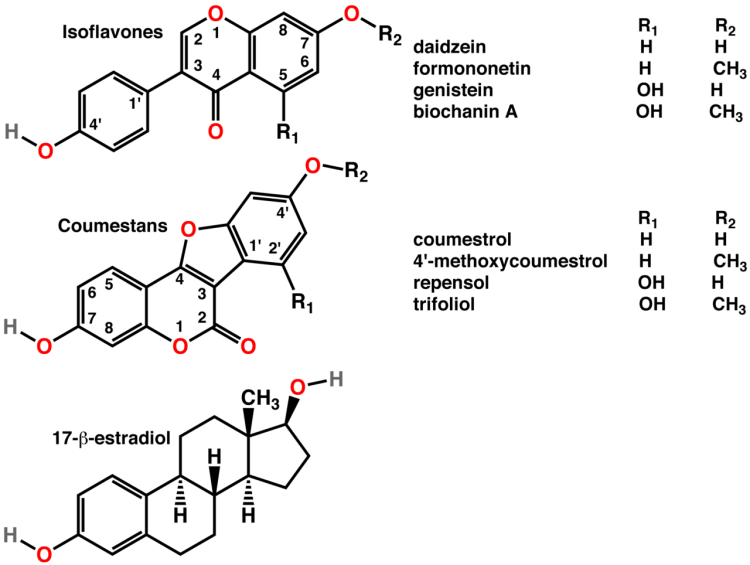
Estradiol (Fig. 20.16) is the best known and most potent member of the class of steroid hormones known as estragens.Estradiol controls development and maintenance of female sex characteristics and is often referred to as the “female hormone” [54].Actually, estradiol is the central member of a triad of structurally similar estragens.
Oestradiol | You and Your Hormones from the Society for Endocrinology
Alternative names for oestradiol. E2; estradiol; 17-beta (o)estradiol. What is oestradiol? Oestradiol (E2) is a steroid hormone made from cholesterol and is the strongest of the three naturally occurring oestrogens (oestrone E1, oestradiol E2, oestriol E3). It is the main oestrogen found in women and has many functions, although it mainly acts to mature and maintain the female reproductive system.
How is estradiol made?
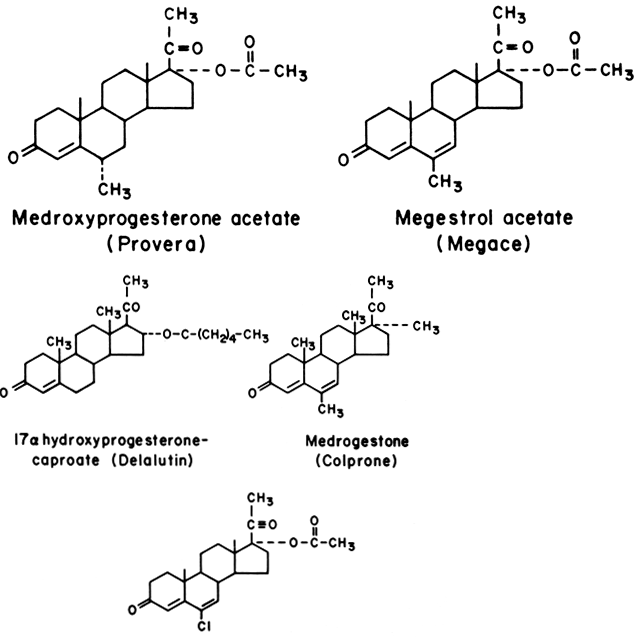
An alternative way of making estradiol is based on using androstenolon acetate (3-acetoxy-5-androsten-17-one) (28.1.18) . Reduction of the keto-group in this molecule by hydrogen using a Raney nickel catalyst and subsequent acylation of the resulting hydroxyl group with benzoyl chloride forms a diester (28.1.19). This undergoes a number of transformations, in particular reduction of the double bond at C 5 – C 6 with hydrogen over a platinum catalyst, and then mild alkaline hydrolysis in methanol of the acetyl protecting group at C 3, oxidation of the resulting hydroxyl group to a ketone using chromium (VI) oxide, and then the benzoyl protecting group of the hydroxyl at C 17 is hydrolyzed by an aqueous base, giving the keto-alcohol (28.1.20). This compound undergoes bromination with molecular bromine, just as in the method described for making estrone, which results in the formation of a dibromide (28.1.21). This product undergoes dehydrobromination when heated in collidine, giving a dienone (28.1.22). When heated in tetraline to a temperature about 325 °C, methane molecule cleaves off the position 10 followed by aromatization of the ring A, and the desired estradiol (28.1.17) is formed [ 25, 26 ]. Estradiol is also made in other ways [ 27, 28 ].
Which genes are involved in the estrogen pathway?
CYP450 involved in the estrogen pathway are considered as important candidate genes for the susceptibility to breast carcinoma.
What is the most commonly requested hormone test?
Although estradiol estimation is one of the most frequently requested hormone tests, its usefulness in the investigation of infertility in women is generally considered to be limited (see F urther R eading ). A progestogen challenge is more helpful in establishing estrogenization of the uterus. A single intramuscular injection of 100 mg progesterone results in uterine bleeding within the next 7 days in women who have sufficient estrogen to produce endometrial proliferation. It also demonstrates that the ovary is responding to LH and FSH secretion from the pituitary and that the endometrium is responsive to estrogen and progesterone.
Where are the methine and methylene signals?
We have two methine groups left to identify from the spins at sites 8 and 14. The 1 H signals from the methylene group at site 6 (2.76 & 2.78 ppm) share gHMBC cross peaks with only two aliphatic 13 C signals at 40.1 (a methine) and 28.2 ppm (a methylene). These two carbon signals must be from sites 8 and 7, respectively. Note that the lack of planarity in this portion of the molecule means that the methine group whose 13 C signal appears at 40.1 ppm is highly unlikely to be from C14 (we already know the shift of the signal from C9).
What is the role of estradiol in the implantation process?
During the normal cycle the role of estradiol is to induce the proliferation of the endometrium, which is then converted to a secretory structure ready to support the implantation by the increased concentrations of progesterone secreted by the corpus luteum after ovulation.
How is estradiol 17 produced?
FIGURE 3. The structure of Estradiol-17β. Estradiol is produced in large amounts by maturing follicles and assays are required to assess concentrations from the lows of menopausal levels (ca 10 pg/mL) through to high levels which exceed 5000 pg/mL in patients at risk of excessive responses.
What is the most important product of the ovary?
Estradiol-17β (known as E2) is arguably the most important product of the human ovary. It is produced by the maturing follicle under the drive of both FSH and LH under the 2-cell, 2-gonadotropin mechanism for estradiol biosynthesis. The primary precursor is cholesterol (with 27 carbon atoms), which is metabolized by side-chain cleavage to the C21 product pregnenolone, which is freely transformed to progesterone in the granulosa cells. There is no further route of metabolism of these products within the granulosa cells, but the theca cells, under the drive of LH, metabolize pregnenolone to the C19 androgens, mainly androstenedione. The androgens then return to the granulosa cells to be converted to estradiol and estrone back in the granulosa cell compartment by the aromatase enzyme.
What is ethyl estradiol?
Ethinyl Estradiol is a semisynthetic estrogen. Ethinyl estradiol binds to the estrogen receptor complex and enters the nucleus, activating DNA transcription of genes involved in estrogenic cellular responses. This agent also inhibits 5-alpha reductase in epididymal tissue, which lowers testosterone levels and may delay progression ...
Where are estrogen receptors found?
Estrogen receptors are found in the female reproductive tract, breast, pituitary, hypothalamus, bone, liver and other tissues. The receptor interacts with a specialized nucleotide sequence, resulting in either an increase or decrease in the transcription of hormone regulated genes.
What is the role of estrogen in breast cancer?
The estrogen-binding protein complex (ie, cytosol-binding protein and estrogen) distributes into the cell nucleus where it stimulates DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis. The presence of these receptor proteins is responsible for the palliative response to estrogen therapy in women with metastatic carcinoma of the breast.
When was ethylestradiol first synthesized?
(NCI04) NCI Thesaurus (NCIt) Ethinylestradiol was first synthesized in 1938 by Hans Herloff Inhoffen and Walter Hohlweg at Schering.
Is ethylestradiol a contraceptive?
Ethinylestradiol is combined with other drugs for use as a contraceptive, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, moderate acne, moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms of menopause, prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. FDA Label. Female contraception. Evra is intended for women of fertile age.
Does estradiol break DNA in hamsters?
Induced DNA breaks in hamster kidneys, but not in livers, following 2 weeks of treatment with a single estradiol implant. Tumors of kidney, bone, testis, uterus and breast, were induced in animals exposed to estrogens. Mutagenicity: Estradiol induced DNA breaks in hamster renal cells, but not in hepatocytes.
Is ethyl estradiol a semisynthetic?
Patients should be counselled regarding the risks of thrombotic events. Ethinyl Estradiol is a semisynthetic estrogen. Ethinyl estradiol binds to the estrogen receptor complex and enters the nucleus, activating DNA transcription of genes involved in estrogenic cellular responses.
Abstract
Aptamers, short synthetic ssDNA or RNA molecules with a specific three-dimensional structure, are promising recognition elements in biosensor technology.
1. Introduction
The release of steroid hormones such as estrogens and androgens into the environment has become an issue of great concern, given their interference with the endocrine system of humans and wildlife [1], [2]. A strong demand for efficient monitoring methods has led to the exploration of several new strategies.
2. Materials and methods
DNA was purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT, Leuven, Belgium). E2 Sepharose ® 6B affinity chromatography beads, Dexamethasone Sepharose ® 6B Novel Immobilized Steroid Beads and Nortestosterone Sepharose ® 6B Novel Immobilized Steroid Beads (Fig. S1) were supplied by Polysciences Inc. (Eppelheim, Germany).
3. Results
Following SELEX A, 19 clones were sequenced after 5 selection cycles. All clones showed a unique sequence, whereas 9 of them expressed a similar motif of 8 nucleotides (CTCTGCAT). Following SELEX B, 24 clones were sequenced after 10 selection cycles. Results revealed a strong enrichment of 2 G-rich sequences in 18 and 5 clones, respectively.
4. Discussion
In order to select aptamers which target different functional groups of E2, two independent SELEX procedures were performed using E2 as target molecule during positive selection steps and dexamethasone or nortestosterone during counterselection steps.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Hasselt University, the Limburg Sterk Merk (LSM) tUL impulsfinanciering phase II to J.V. and the European union through EFRO, the Flemish government and the Province of Limburg (NanoSensEu grant number IVA-VLANED 1.44).
What are the two types of estrogen?
However, there are another two main types of estrogens; estrone and estriol. Estriol is the least effective hormone and found mostly in pregnant females, whereas estrone is the most abundant estrogen hormone in menopause. Estradiol is further described below. The incorporation of three types of estrogen called tri-estrogen, ...
Where is estradiol synthesized?
The estradiol is synthesized in the ovarian granulose cells and is then converted into estriol, the most abundant form of estrogen that is excreted with urine.
What receptors do estrogen bind to?
When mediating the actions of estrogen, it first binds to the receptors called estrogen receptor (ER). There are two main subtypes of ER, namely; ERα and ERβ. Each of this receptor type is specific for tissue and organ type.
What hormones help with insomnia?
Estradiol. Estradiol is the most active type of estrogen that involves in hundreds of activities in the body. It is one of the hormones that have a great effect on the symptom relief for insomnia, headaches, mental fogginess, and fatigue.
Does estrogen affect the cardiovascular system?
Additionally, estrogen deficiency may have certain effects on the tissues such as bone, cardiovascular system, and central nervous system. However, the exact mechanisms of action associated with these types of tissues are yet to be understood.
What are the compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in target tissues?
Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. (See all compounds classified as Estrogens .)
Which isomeric form of estrogen is the most active?
It occurs in two isomeric forms, alpha and beta. Beta-estradiol has the greatest physiological activity of any naturally occurring estrogen. The alpha-form is relatively inactive.
What is estradiol 17?
Estradiol-17beta is produced commercially by the reduction of estrone using, for example, complex metal hydrides, such as sodium borohydride and lithium aluminum hydride.
How much estradiol is excreted in a day?
Human excretion of estradiol may be as high as 5 mg/day. A nonpregnant and pregnant diary cow excretes approximately 0.8-1.2 mg/day and up to 11.4 mg/day of 17alpha-estradiol, respectively. As high as 6 mg estrogenicity as 17beta-estradiol equivalent (EEQ)/per kg dry weight has been found in swine manure (1).
What is the maximum amount of estradiol in untreated animals?
No residues of estradiol, resulting from the use of estradiol or any of the related esters, are permitted in excess of the following increments above the concentrations of estradiol naturally present in untreated animals: (a) In uncooked edible tissues of heifers, steers, and calves: (1) 120 parts per trillion for muscle. (2) 480 parts per trillion for fat. (3) 360 parts per trillion for kidney. (4) 240 parts per trillion for liver. (b) In uncooked edible tissues of lambs: (1) 120 parts per trillion for muscle. (2) 600 parts per trillion for fat, kidney, and liver.
How does estradiol release to the environment?
Estradiol's production and use as an estrogen may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. Estradiol is a natural steroidal estrogen hormone released by mammals. If released to air, an estimated vapor pressure of 6.4X10-9 mm Hg at 25 °C indicates estradiol will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere. Particulate-phase estradiol will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Estradiol irradiated with a xenon arc lamp exhibited a photodegradation half-life of 2 hours in river water and 41.7 hours in air-saturated purified water, and therefore estradiol may be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, estradiol is expected to have no mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 30,000. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 3.6X10-11 atm-cu m/mole. A 6% mineralized of estradiol in 5 days after application to a agricultural soil microcosm suggests biodegradation is not an important environmental fate process. If released into water, estradiol is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 200 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is high, provided the compound is not metabolized by the organism. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions. Occupational exposure to estradiol may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where estradiol is produced or used. Exposure to estradiol via ingestion will occur when administered drugs containing this compound. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to estradiol at well below the therapeutic dose via ingestion of drinking water and dermal contact with contaminated sediments. (SRC)
How long does estradiol last?
The terminal half-lives for various estrogen products post oral or intravenous administration has been reported to range from 1-12 hours. One pharmacokinetic study of oral estradiol valerate administration in postmenopausal women revealed a terminal elimination half-life of 16.9 ± 6.0 h. A pharmacokinetic study of intravenous estradiol administration in postmenopausal women showed an elimination half-life of 27.45 ± 5.65 minutes. The half-life of estradiol appears to vary by route of administration.
