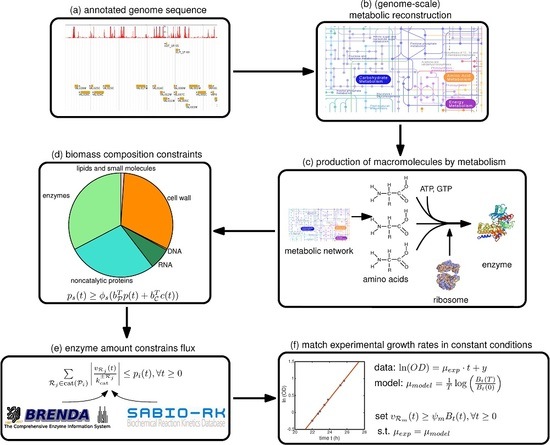
Role of Secondary Metabolites:
- (1) Some of them attract animals for pollination and seed dispersal.
- (2) They are used by the plants in their defence against herbivores and pathogens.
- (3) They act as agents of plant-plant competition.
- (4) They are used in making drugs, insecticides, flavours, pigments, scents, rubber, spices and other industrial...
What is the function of secondary metabolites in plants?
Secondary metabolites accumulate in plants and response as a defence mechanism of the plants. What is a secondary metabolite? Secondary metabolites or Phytochemicals (Plant chemicals) are the natural products or plants constituents which are responsible for the medicinal properties of plants.
What is the role of secondary metabolites in antibiotic action?
The major functions of the secondary metabolites including antibiotics are: competitive weapons against other livings such as animals, plants, insects, and microorganisms The other functions include interference in spore formation (not obligatory) and germination [ 5 ].
Where can I find secondary metabolites?
1 Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge 02139, USA. [email protected] Secondary metabolites, including antibiotics, are produced in nature and serve survival functions for the organisms producing them.
What are secondary metabolic compounds?
Secondary compounds are still involved and helping the lives of modern people. It has been extensively used as agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, food additives, and aromatics. Based on the structure of the compounds, the secondary metabolites are classified into five major classes:
What are five general functions of secondary metabolites?
The major functions of the secondary metabolites including antibiotics are:competitive weapons against other livings such as animals, plants, insects, and microorganisms.metal transporting agents.agents for symbiotic relation with other organisms.reproductive agent and.differentiation effectors.More items...•
What are the functions of primary and secondary metabolites in plants?
primary and secondary plant metabolites can be distinguished from each other (Figure 1). While primary metabolites (sugars, fats, amino acids, etc.) serve for primar- ily nutrition and as starting materials for further biosynthesis (e.g., starch, cellulose, etc.), secondary metabolites do not play a role for diet. ...
What are some functions of secondary metabolites Mcq?
Secondary metabolites are the chemical compounds that do not participate in plant metabolism....Examples of secondary metabolites used as drugs.Secondary metabolite (drug)UsedigoxinCardiotonicMorphineAnalgesicCodeineAnalgesicQuinineAnti-malarial5 more rows•Jan 12, 2021
What is the function of metabolites?
The various functions of metabolites include; fuel, structure, signalling, catalytic activity, defence and interactions with other organisms. The metabolites are produced by plants, humans and microbes.
What are the benefits of secondary metabolites in plants?
Secondary metabolites aid in growth, development, and immune function of plants, but are not required for survival. They generally serve roles in physiological processes that improve plant tolerance to environmental stresses.
Which are the secondary metabolites?
Secondary metabolites, also called specialised metabolites, toxins, secondary products, or natural products, are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of the organism.
Which of the following functions are attributed to different secondary metabolites in plants?
Important roles of secondary metabolites include (i) protection against harmful environmental conditions, (ii) protection against pathogens and herbivores, (iii) feeding deterrence and (iv) attraction of pollinators and seed dispersers.
What is the source for production of secondary metabolite?
The biosynthetic routes for production of secondary metabolites in plants are arise from the shikimate, polyketide and terpenoid routes. The shikimate pathway is highly conserved and reported to be the main source of phenylpropanoids and aromatic compounds [68].
Which of the following is not a secondary metabolites?
Amino acids and Glucose are primary metabolites but not secondary metabolites as they have some known functions.
What are the three functions of metabolism?
The three main purposes of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes.
What are secondary metabolites give examples?
Examples of secondary metabolites include antibiotics, pigments and scents. The opposite of secondary metabolites are primary metabolites, which are considered to be essential to the normal growth or development of an organism.
What is the difference between primary and secondary metabolites in plants?
The immediate end products produced by a living organism as a result of growth are called primary metabolites. The metabolites that help in carrying out other bodily functions which are not involved in the growth and maintenance of cellular activities are called secondary metabolites.
What are primary metabolism in plants?
Central carbon metabolism, also known as primary metabolism, contributes to the synthesis of intermediate compounds that act as precursors for plant secondary metabolism. Specific and specialized metabolic pathways that evolved from primary metabolism play a key role in the plant's interaction with its environment.
What are the 4 primary metabolites?
The decomposition products and the polymeric products formed during the process, such as polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, and esters, are called primary metabolites. The common primary metabolites are amino acids, nucleosides, and the enzyme or coenzyme.
What distinguishes primary metabolites from secondary metabolites?
The main difference between primary metabolites and secondary metabolites is that primary metabolites are directly involved in primary growth development and reproduction whereas secondary metabolites are indirectly involved in metabolisms while playing important ecological functions in the body.
What are secondary metabolites?
Secondary metabolites, including antibiotics, are produced in nature and serve survival functions for the organisms producing them. The antibiotics are a heterogeneous group, the functions of some being related to and others being unrelated to their antimicrobial activities.
Do antibiotics stimulate spore formation?
Although antibiotics are not obligatory for sporulation, some secondary metabolites (including antibiotics) stimulate spore formation and inhibit or stimulate germination. Formation of secondary metabolites and spores are regulated by similar factors.
What is a secondary metabolite?
Secondary metabolites or Phytochemicals (Plant chemicals) are the natural products or plants constituents which are responsible for the medicinal properties of plants. There are thousands of secondary metabolites . some plants are classified on the basis of secondary metabolites found in them.
What are the three major groups of secondary metabolites?
Secondary metabolites can be divided into three major groups. Flavonoids. Alkaloids. Terpenoids. 1. Flavonoids. Flavonoid: General structure. These are polyphenolic compounds comprise of 15 carbons with two aromatic rings connected by a three-carbon bridge. Subtypes of flavonoids are.
What is the most diverse group of secondary metabolites found in plants?
Terpenoid: General Structure. Terpenoids are the volatile substance which gives plants and flowers its unique fragrance, this is the largest and most diverse group of secondary metabolites found in plants.
What are the two types of metabolites in plants?
Types of metabolites in plants. Plants have basically two types of metabolites namely Primary metabolites and Secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites are mainly used for photosynthesis, growth, development and respiration of plants. Secondary metabolites accumulate in plants and response as a defence mechanism of the plants.
What are alkaloids known for?
Alkaloids are well known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective activities.
What are the functions of alkaloids in plants?
The major function of alkaloids in plants. Defence mechanism against bacteria and other microorganisms. Helps in plant metabolisms and catabolisms. Storage and reservoir of nitrogen. As growth regulators in plants. It also helps as a growth stimulator and inhibitors.
Which alkaloids are simple in structure?
They are simple in structure examples are hordenine, mescaline and yohimbine.
Why are secondary metabolites important?
These plant secondary metabolites are important candidates for human nutrition. A number of plant secondary metabolites possess antioxidant properties that act as the first line of defense against oxidative damage induced by different environmental (including high temperature) constraints.
What are the most important secondary metabolites?
The most important secondary metabolites have been the anti-infective drugs and, among these, the β-lactams are the most important class. Other important classes include the aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides, lipopeptides, polyenes, and the echinocandins. Successful microbial secondary metabolites include many used to combat cancer, ...
What are the effects of SMs on plants?
Plant SMs are important compounds that add color, taste, and odor to plants and also mediate plant responses to adverse environmental conditions ( Verma and Shukla, 2015 ). A number of factors cause significant perturbations in the production of SM in plants. The endogenous levels of different SMs vary among different plant species and also within the same plant species ( Barton, 2007 ). A number of cellular and biochemical factors influence the storage and transportation of SM. Developmental factors influence the initiation and subsequent differentiation of particular cellular structures involved in the biosynthesis and storage of SM ( Broun et al., 2006 ). Furthermore, the endogenous levels of SM are also influenced by a number of environmental stresses such as nutrient deficiencies, wounding, metal ions, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, light, circadian rhythm, seasonality, salinity, drought, and temperature ( Gouvea et al., 2012; Verma and Shukla, 2015 ). Apart from this, the endogenous concentration of SM is associated with the metabolic pathway of the particular SM and growth conditions ( Akula and Ravishankar, 2011 ). The concentration of SM is also affected by biotic factors (pathogen attack) and thereby mediates plant defense mechanism. For instance, there exists a significant variation in the levels of phenolics in plants in response to environmental stresses such as light intensity and nutrient availability ( Verma and Shukla, 2015 ).
What is the process of producing metabolites?
The network of metabolites, working with enzyme reactions during the entire process of metabolism, is called the metabolome [10]. The metabolome involves/implicates all the series of combinations of cascading reactions between enzymes and substrates in the steps of metabolism, and ending in the production of the primary and secondary metabolites.
What are the antitumor agents from plants that have been very useful?
Antitumor agents from plants that have been very useful are taxol and camptothecin. If modern medicine is to continue in its present form, novel families of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites must continue to be discovered and enter the marketplace at regular intervals. View chapter Purchase book.
What is a microbiological secondary metabolite?
Abstract. Microbial secondary metabolites are low-molecular-mass products of secondary metabolism, usually produced during the late growth phase (idiophase) of microorganisms. They have unusual structures and their production arises from intracellular intermediates (amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, etc.), which are condensed into more complex ...
What are some examples of nutrients that are produced in adequate amounts to sustain cell growth?
Produced in adequate amount to sustain cell growth, for example, vitamins, amino acids, nucleosides, and so on. Examples, are ethanol, citric acid, acetic acid, lactic acid, vitamins, and amino acids . Not necessary for growth, development, and reproduction—their production is influenced by environmental factors.
Abstract
Secondary metabolites, including antibiotics, are produced in nature and serve survival functions for the organisms producing them. The antibiotics are a heterogeneous group, the functions of some being related to and others being unrelated to their antimicrobial activities.
About this chapter
Demain A.L., Fang A. (2000) The Natural Functions of Secondary Metabolites. In: Fiechter A. (eds) History of Modern Biotechnology I. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, vol 69. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44964-7_1
What are secondary metabolites used for?
Predominantly, the secondary metabolites are used for variety of biological activities like antimicrobial and antiparasitic agents, enzyme inhibitors and antitumor agent, immunosuppressive agents, etc. [ 7 ].
Why are secondary metabolites important?
The battle against any disease is a vibrant symmetry between advances in chemotherapy and natural selection on infectious or invasive agents. If the scientific community is to put constant importance in this never ending effort, then new sources of bioactive secondary metabolites with novel activities must be found. Secondary metabolites are one of their essential means of growth and defense , and these metabolites are readily available for discovery. Secondary metabolites with noteworthy biological activity are considered as an alternative to most of the synthetic drugs and other commercially valuable compounds.
How many secondary metabolites are there?
Over 2,140,000 secondary metabolites are known and are commonly classified according to their vast diversity in structure, function, and biosynthesis. There are five main classes of secondary metabolites such as terpenoids and steroids, fatty acid-derived substances and polyketides, alkaloids, nonribosomal polypeptides, and enzyme cofactors [ 6 ].
What is the difference between primary and secondary metabolites?
The difference between primary and secondary metabolite is ambiguous since many of the intermediates in primary metabolism is overlapping with the intermediates of secondary metabolites [ 2 ]. Amino acids though considered a product of primary metabolite are definitely secondary metabolite too. Contrary to the observation that sterols are secondary metabolites that are indispensable part of many structural framework of a cell. The mosaic nature of an intermediate indicates common biochemical pathway being shared by primary and secondary metabolism [ 3 ]. The secondary metabolites serve as a buffering zone into which excess C and N can be shunted into to form inactive part of primary metabolism. The stored C and N can revert back to primary metabolite by the metabolic disintegration of secondary metabolite when on demand. There is dynamism and a delicate balance between the activities of the primary and secondary metabolism ( Figure 1) being influenced by growth, tissue differentiation and development of the cell or body, and also external pressures [ 4 ].
What is the sum of all the biochemical reactions carried out by an organism?
Introduction. The metabolism can be defined as the sum of all the biochemical reactions carried out by an organism. Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism and are usually restricted to small molecules.
What are alkaloids used for?
Many alkaloids are used in medicine, usually in the form of salts. Some examples include vinblastine which has antitumor properties [ 11 ]; quinine which has antipyretics and antimalarial properties [ 12 ]; and reserpine which can be used to treat high blood pressure. Alkaloids are regarded as reserve materials for protein synthesis, as protective substances discouraging animal or insect attacks, and as plant stimulants or regulators or simply as detoxification products. Alkaloids currently in clinical use include the analgesics morphine and codeine, the anticancer agent vinblastine, the gout suppressant colchicine, the muscle relaxant tubocurarine, the antiarrhythmic ajmalicine, the antibiotic sanguinarine, and the sedative scopolamine.
Which metabolic pathway branch out from primary metabolism?
Secondary metabolites branch out from the pathways of primary metabolism. Commercially, important secondary and primary metabolic pathways are given in Table 4.
What are secondary metabolites used for?
Role of Secondary Metabolites: (1) Some of them attract animals for pollination and seed dispersal. (2) They are used by the plants in their defence against her bivores and pathogens. (3) They act as agents of plant-plant competition. (4) They are used in making drugs, insecticides, flavours, pigments, scents, rubber, ...
Which organisms are not involved in primary metabolism?
Many plants, fungi and microbes of certain genera and families synthesize a number of organic compounds which are not involved in primary metabolism (photosynthesis, respiration, and protein and lipid metabolism) and seem to have no direct function in growth and development of plants.
What are the chemicals that plants produce?
Plants produce thousands types of chemicals. Some of the organic compounds like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, nucleic acids, chlorophylls, hemes are required for their basic metabolic processes and found throughout the plant kingdom. These organic compounds are called primary metabolites or biomolecules. These are produced in large quantities and can easily be extracted from the plants.
Do metabolites accumulate in small quantities?
They accumulate in small quantities only in specific parts of plants. These are derivatives of primary metabolites. By the cultivation of plant cells in culture media, secondary metabolites can be produced on large scale. ADVERTISEMENTS:
Why are secondary metabolites considered end products of primary metabolites?
Secondary metabolites are considered to be the end products of primary metabolites because they are derived by the pathways in which the primary metabolites involve. For eg., antibiotics, toxins, pheromones, enzyme inhibitors, etc. Streptomycetes and related actinomycetes are the sources ...
Where are secondary metabolites formed?
Secondary metabolites are formed near the stationary phase of growth and are not involved in growth, reproduction and development.
What are Metabolites?
Metabolites are the intermediate products produced during metabolism, catalyzed by various enzymes that occur naturally within cells. Eg., antibiotics, and pigments. The term metabolites are usually used for small molecules. The various functions of metabolites include; fuel, structure, signalling, catalytic activity, defence and interactions with other organisms.
What are the sources of novel secondary metabolites?
For eg., antibiotics, toxins, pheromones, enzyme inhibitors, etc. Streptomycetes and related actinomycetes are the sources of novel secondary metabolites .
What are the two types of metabolites?
Plant metabolites are of two types: 1 Primary Metabolites 2 Secondary Metabolites
What are the intermediate products of anabolic metabolism?
They are the intermediate products of anabolic metabolism, which are used by the cells for the formation of essential macromolecules. Amino acids, vitamins, organic acids, are some of the primary metabolites produced industrially. Alcohol is the major primary metabolite produced on a large scale, industrially.
What are the primary metabolites?
Primary Metabolites. These are the chemical compounds produced during the growth and development, processes. They are also involved in the primary metabolic processes of respiration and photosynthesis. The primary metabolites are formed in the growth phase. They maintain the physiological functions of the body and are known as central metabolites.

Introduction
Types of Metabolites in Plants
What Is A Secondary Metabolite?
- Secondary metabolites have a wide range of functions in plants, ranging from involving in responses to environmental challenges, defending plants against pathogens and pest attacks, and attracting animals for pollination. Here’re some well-studied roles of secondary metabolites in plants. Scientists suggest that the expansion in secondary metabolit...
Types of Secondary Metabolites and Their Medicinal Properties
- We are studying a lot about flavonoids and alkaloids in food and their health benefits in day-to-day blogs. Today with the concept of superfoods is getting more and more prominent so are the secondary metabolites present in them. Secondary metabolites are the main important components behind each health benefits and medicinal properties of the plants.
Flavonoids
- Plants have basically two types of metabolites namely Primary metabolites and Secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites are mainly used for photosynthesis, growth, development, and respiration of plants. Secondary metabolites accumulate in plants and respond as a defense mechanism of the plants.
Alkaloids
- Secondary metabolites or Phytochemicals (Plant chemicals) are the natural products or plants constituents which are responsible for the medicinal properties of plants. There are thousands of secondary metabolites. some plants are classified on the basis of secondary metabolites found in them (1).
Terpenoids
- Three major groups of secondary metabolites
1. Flavonoids 2. Alkaloids 3. Terpenoids