What are the indications of PAPI?
When using a Papi What indication would signal the pilot is slightly high on the glidepath?
What does the Precision Approach Path Indicator consist of?
Which PAPI light indication would make you believe you are on glideslope?
Is PAPI required for ILS?
What is precision approach in aviation?
What is the difference between PAPI and Apapi?
What is precision approach lighting system?
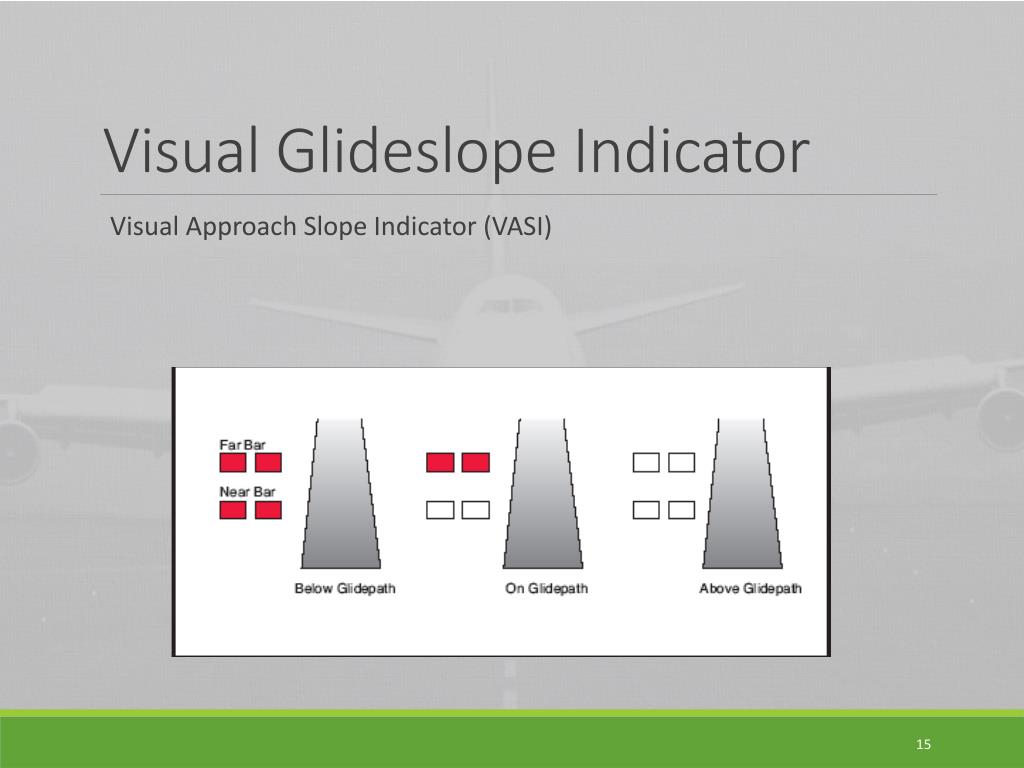
The precision approach path indicator (PAPI) uses light units similar to the VASI but are installed in a single row of either two or four light units. These lights are visible from about 5 miles during the day and up to 20 miles at night.
What is the difference between PAPI and VASI?
What is TCH on approach plate?
Which substitution is appropriate during an ILS approach?
What is the most used visual approach slope indicator systems?
How do PAPI lights work?
The lower segment of the beam is red, and the upper part is white. The transition between the two colours must take place over an angle not greater than three minutes of arc. This characteristic makes the color change very conspicuous, a key feature of the PAPI signal. To form the PAPI guidance signal, the color transition boundaries of the four units are fixed at different angles. The lowest angle is used for the unit furthest from the runway, the highest for the unit nearest to the runway. The designated glideslope is midway between the second and third light unit settings. Depending on the position of the aircraft relative to the specified angle of approach, the lights will appear either red or white to the pilot. The pilot will have reached the normal glidepath (usually 3 degrees) when there is an equal number of red and white lights. If an aircraft is beneath the glidepath, red lights will outnumber white; if an aircraft is above the glidepath, more white lights are visible.
What is PAPI in aviation?
The PAPI is a light array positioned beside the runway. It normally consists of four equi-spaced light units color-coded to provide a visual indication of an aircraft's position relative to the designated glideslope for the runway. An abbreviated system (APAPI) consisting of two light units can be used for some categories of aircraft operations. The international standard for PAPI is published by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) in Aerodromes, Annex 14 to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, Volume 1, Chapter 5. National regulations generally adopt the standards and recommended practices published by ICAO. An earlier glideslope indicator system, the visual approach slope indicator (VASI) is now obsolete and was deleted from Annex 14 in 1995. The VASI only provided guidance down to heights of 60 metres (200 ft) whereas PAPI provides guidance down to flare initiation (typically 15 metres, or 50 ft).
What is PAPI in airports?
The PAPI system is co-opted for use by the Final Approach Runway Occupancy Signal (FAROS) system being introduced by several major airports in the United States for the purpose of allowing pilots to resolve a runway incursion without requiring a priori notice of an occupied runway from the control tower. In FAROS, automated line-of-sight runway sensors detect if a vehicle has committed a runway incursion, and if so, will flash the PAPI lights to alert the pilot of an aircraft on final approach that the runway is currently occupied. The pilot then becomes responsible for resolving the conflict by notifying the air traffic controller and executing a go-around. Once the tower has ascertained that the runway has been cleared, the ground controller resets the PAPI so that landing operations may resume normally.
How high is the VASI?
The VASI only provided guidance down to heights of 60 metres (200 ft) whereas PAPI provides guidance down to flare initiation (typically 15 metres, or 50 ft). The PAPI is usually located on the left-hand side of the runway at right angles to the runway center line.
What is the APAPI system?
An abbreviated system (APAPI) consisting of two light units can be used for some categories of aircraft operations. The international standard for PAPI is published by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) in Aerodromes, Annex 14 to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, Volume 1, Chapter 5.
How many lights does a 747 have?
With the 747, because the cockpit is approximately 20 feet behind the nose and much higher than other aircraft, the flight crew in a 747 will typically see one red and three white lights when they are on the glide slope. The aircrew of Concorde would see four white lights as the Concorde's approach angle was higher than traditional aircraft.
How to tell the ratio of white to red lights?
The ratio of white to red lights seen is dependent on the angle of approach to the runway. Above the designated glide slope a pilot will observe more white lights than red; at approaches below the ideal angle more red lights than white will be seen. For the optimum approach angle the ratio of white to red lights will remain equal throughout, for most aircraft, the exceptions being the Boeing 747 and now retired Concorde. With the 747, because the cockpit is approximately 20 feet behind the nose and much higher than other aircraft, the flight crew in a 747 will typically see one red and three white lights when they are on the glide slope. The aircrew of Concorde would see four white lights as the Concorde's approach angle was higher than traditional aircraft.
What is a PAPI 2 box?
The two-box PAPI system uses only two LHAs and provides simplified glide slope information. The PAPI can be configured to read white/green/red for use on heliports.
How far out can a PAPI be seen?
Flight Light PAPIs have the most reliable photometrics in the industry. On a normal day a 2-lamp PAPI unit is visible from over 10 miles out. Light distribution curves far exceed FAA requirements.
What is interlock relay?
The interlock relay option operates PAPI in conjunction with runway lights.
How far is the PAPI beam effective?
The PAPI projects a distortion free beam of uniform intensity over ten degrees of azimuth and is effective to within 1000 ft. of touchdown.
What is PAPI in aviation?
The precision approach path indicator (PAPI) provides the pilot with a safe and accurate glide slope on final approach to the runway. A row of PAPI light housing assemblies (LHAs) placed perpendicular to the approach path are seen by the pilot in combinations of red and white to indicate a path that is too high, too low or correctly on slope.
What is a style B?
Style B is current powered and operates on 6.6 amp series circuits from an L828 constant current regulator. Lamp brightness is controlled by the output setting on the regulator.
Is interconnect wiring good?
However, in the case of problems, the following pointers will help you locate and correct the problems. It is assumed that all interconnect wiring is good.
What is the frequency of a VHF radio?
In general aviation, the most common types of radios are VHF. A VHF radio operates on frequencies between 118.0 and 136.975 and is classified as 720 or 760 depending on the number of channels it can accommodate. The 720 and 760 uses .025 spacing (118.025, 118.050) with the 720 having a frequency range up to 135.975 and the 760 going up to 136.975. VHF radios are limited to line of sight transmissions; therefore, aircraft at higher altitudes are able to transmit and receive at greater distances.
What are in runway lights?
The in-runway lights consists of the Centerline Lighting, Touchdown Zone, Taxiway Lead-off and the Land and Hold Short light systems. The runway centerline and edge light change color when approaching the end of the runway as an indication for pilots.
What is a REIL?
REIL (Runway End Identifier Lights) are a pair of synchronized flashing lights positively indicating the approach end of the runway. They can be omni or uni-directional and are used in circumstances of reduced visibility.
What color is above the glide path?
Like the tricolor system but then pulsating red for below glide path and pulsating white for above glide path. Steady red is slightly below and steady white is on glide path.
How do airplanes use taxiways?
Airplanes use taxiways to transition from parking areas to the runway. Taxiways are identified by a con-tinuous yellow centerline stripe. A taxiway may include edge markings to define the edge of the taxi-way. This is usually done when the taxiway edge does not correspond with the edge of the pavement. If an edge marking is a continuous line, the paved shoulder is not intended to be used by an airplane. If it is a dashed marking, an airplane may use that portion of the pavement. Where a taxiway approaches a runway, there may be a holding position marker. These consist of four yellow lines (two solid and two dashed). The solid lines are where the airplane is to hold. At some controlled airports, holding position markings may be found on a runway. They are used when there are intersecting runways, and air traffic control issues instructions such as “cleared to land—hold short of runway 30.”
What is a VOR receiver checkpoint?
A VOR receiver checkpoint marking consists of a painted circle with an arrow in the middle. The arrow is aligned in the direction of the checkpoint azimuth.
What is equipment in a manual?
equipment. The equipment is designed and intended only for the purpose described in the manual. Uses not described in the
Who reserves the right to examine goods upon which a claim is made?
ADB SAFEGATE reserves the right to examine goods upon which a claim is made. Said goods must be presented in the same
How long does LED circuitry last?
LED specific circuitry for a period of 4 years from date of installation, per FAA EB67 (applicable edition).
What does CE certification mean?
The equipment listed as CE certified means that the product complies with the essential requirements concerning safety and
Does ADB have liability for defective goods?
ADB SAFEGATE's liability under no circumstances will exceed the contract price of goods claimed to be defective. Any returns
When is a syringe stored?
stored prior to installation, properly installed and properly operated after installation, and provided further that Buyer gives
Can manuals be reproduced?
This manual or parts thereof may not be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means,
What is PAPI system?
The PAPI system allows the pilot to have the necessary visual information to place the aircraft on the ideal approach slope and can be used by day or night. The system can be used by all aircraft as soon as it is set up since it does not require any airborne instrumentation.
Does the PU3L have a heat resistor?
In Order to operate in very low temperature or in high humidity conditions without loss of performance, the PU3L unit can be equipped with additional "Heating Resistor".

Overview
A precision approach path indicator (PAPI) is a visual aid that provides guidance information to help a pilot to acquire and maintain the correct approach (in the vertical plane) to an airport or an aerodrome. It is generally located on the left-hand side of the runway approximately 300 meters beyond the landing threshold of the runway.
Development
The precision approach path indicator system was first devised in 1974 by Tony Smith and David Johnson at the Royal Aircraft Establishment in Bedford, England. It took them a further two years to fully develop the technology. Smith and Johnson's work was honoured by a commendation from the RAE, a Fellowship from the Aeronautical Society, an award from the American Flight Safety Foundation, and a Gold Medal from the British Guild of Air Pilots. Engineering firm Resear…
Meaning
The ratio of white to red lights seen is dependent on the angle of approach to the runway. Above the designated glide slopea pilot will observe more white lights than red; at approaches below the ideal angle more red lights than white will be seen. For the optimum approach angle the ratio of white to red lights will remain equal throughout, for most aircraft, the exceptions being the Boeing 74…
Background
The greater number of red lights visible compared with the number of white lights visible in the picture means that the aircraft is flying below the glide slope. To use the guidance information provided by the aid to follow the correct glide slope a pilot would manoeuvre the aircraft to obtain an equal number of red and white lights.
Design
A typical engineering design specification for a PAPI light unit is shown below:
Optical construction:
• Preadjusted 2-lamp optical assembly.
• Anodized aluminium reflectors.
• Red color filters.
See also
• Approach lighting system (ALS)
• Pilot controlled lighting (PCL)
• Visual approach slope indicator (VASI)
• Instrument landing system (ILS)