What is an elementary particle?
Elementary particles are particles with no measurable internal structure; that is, it is unknown whether they are composed of other particles. They are the fundamental objects of quantum field theory.
What is a fermion particle?
Fermions are one of the two fundamental classes of particles, the other being bosons. Fermion particles are described by Fermi–Dirac statistics and have quantum numbers described by the Pauli exclusion principle.
What is a boson particle?
Bosons are one of the two fundamental particles having integral spinclasses of particles, the other being fermions. Bosons are characterized by Bose–Einstein statistics and all have integer spins. Bosons may be either elementary, like photons and gluons, or composite, like mesons .
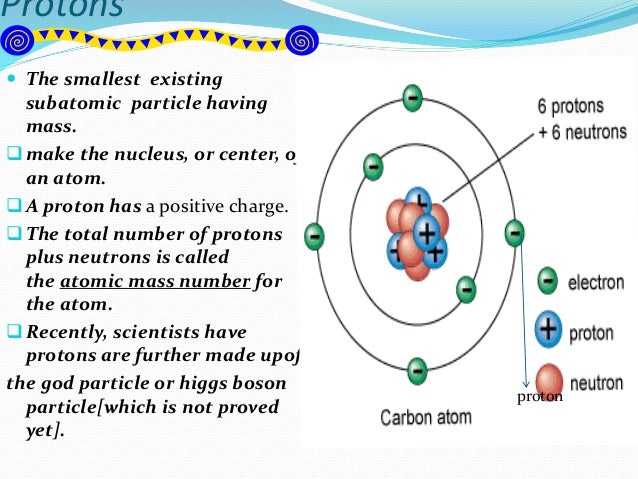
What is the smallest particle in an atom?
What is the fastest thing in the universe?
What is the smallest thing in existence?
Does neutron have mass?
Who discovered electron?
Why does a neutron have no charge?
What does the God particle prove?
See 2 more
Which particle has the largest size?
Conversely, the largest (in terms of mass) fundamental particle we know of is a particle called a top quark, measuring a whopping 172.5 billion electron volts, according to Lincoln.
Are electrons the largest particle?
An electron is one of the most important types of subatomic particles. Electrons combine with protons and (usually) neutrons to make atoms. Electrons are much smaller than neutrons and protons. The mass of a single neutron or proton is more than 1,800 times greater than the mass of an electron.
Is nucleus the largest part of the atom?
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus.
Are protons the biggest?
Protons are nearly the same size as neutrons and are much larger than electrons. A proton has a mass about 1,836 times greater than the mass of an electron, but the masses of protons and neutrons differ from each other by less than one percent.
Which is bigger electron or neutron?
Like protons, neutrons are bound into the atom's nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force. Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, but they are both much more massive than electrons (approximately 2,000 times as massive as an electron).
What are the 7 particles of an atom?
IntroductionParticleElectric Charge (C)Mass (g)Protons+1.6022 x 10-191.6726 x 10-24Neutrons01.6740 x 10-24Electrons-1.6022 x 10-199.1094 x 10-28Sep 10, 2022
What's the smallest part of an atom?
However, the atom itself is not the smallest known particle, but instead each atom is made up of three individual parts: electrons, protons and neutrons. Furthermore, protons and neutrons themselves are made up of even smaller parts called quarks.
What are the 3 main parts of an atom?
Given that these particles make up atoms, they are often referred to as subatomic particles. There are three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons.
Which is big proton or electron?
proton, stable subatomic particle that has a positive charge equal in magnitude to a unit of electron charge and a rest mass of 1.67262 × 10−27 kg, which is 1,836 times the mass of an electron.
Which particle is the smallest?
QuarksQuarks, the smallest particles in the universe, are far smaller and operate at much higher energy levels than the protons and neutrons in which they are found.
Are electrons smaller than protons?
Electrons are much smaller than protons or neutrons. Despite being so small, their charge is as strong as a proton, which means that one proton and one electron will balance each other out.
How big is an electron?
Using the best available values for the wave-length and the scattering by matter of hard X-rays and γ-rays, the radius of the electron is estimated as about 2 × 10−10 cm.
What is the heaviest subatomic particle?
The new findings were announced at the LHCP 2020 Conference. Top quarks are the heaviest known fundamental subatomic particles, according to a study published in 2019 in the journal Physical Review D. Each top quark is roughly as massive as an atom of tungsten.
What is the smallest particle of an element?
An atom is the smallest particle of an element, having the same chemical properties as the bulk element. The first accurate theory explaining the nature of matter was Dalton’s Atomic Theory: 1. All matter is composed of atoms, and atoms are indivisible and indestructible.
How many quarks are in a neutron?
A neutron contains two down quarks with charge −1⁄3 e and one up quark with charge +2⁄3 e. Like protons, the quarks of the neutron are held together by the strong force, mediated by gluons. The nuclear force results from secondary effects of the more fundamental strong force.
How many times more mass does a protons have than an electron?
Protons have a mass that is 1,836 times that of the electron, at 1.6726×10-27 kg, while neutrons are the most massive of the three, at 1.6929×10-27 kg (1,839 times the mass of the electron). The total number of protons and neutrons in an atoms’ nucleus (called “nucleons”) is called the mass number.
Which subatomic particles are attracted to each other?
The two subatomic particles that are attracted to each other are protons and electrons.
How big is a proton?
The diameter of the proton is about as much as a millimetre divided by a thousand billion (10^-15m). Physicists can not yet compare what`s larger: a quark, Higgs boson or an electron. … “So we can say that an electron is lighter than a quark, but we can not say that it is smaller than quark” – concludes Prof. Wrochna.
How big is a quark?
As of 2014, experimental evidence indicates they are no bigger than 10−4 times the size of a proton, i.e. less than 10−19 metres.
What is the smallest particle in matter?
Atoms are the smallest neutral particles into which matter can be divided by chemical reactions. An atom consists of a small, heavy nucleus surrounded by a relatively large, light cloud of electrons. Each type of atom corresponds to a specific chemical element. To date, 118 elements have been discovered or created.
What are the two fundamental classes of particles?
Fermions are one of the two fundamental classes of particles, the other being bosons. Fermion particles are described by Fermi–Dirac statistics and have quantum numbers described by the Pauli exclusion principle. They include the quarks and leptons, as well as any composite particles consisting of an odd number of these, such as all baryons and many atoms and nuclei.
Which particle has half integer spin?
Elementary particles are classified according to their spin. Fermions have half-integer spin while bosons have integer spin. All the particles of the Standard Model have been experimentally observed, recently including the Higgs boson in 2012.
What is the first elementary scalar particle discovered in nature?
Since then, the particle has been shown to behave, interact, and decay in many of the ways predicted for Higgs particles by the Standard Model, as well as having even parity and zero spin, two fundamental attribut es of a Higgs boson. This also means it is the first elementary scalar particle discovered in nature.
Which particles carry fractional charge?
Quarks are the only known carriers of fractional charge, but because they combine in groups of three (baryons) or in pairs of one quark and one antiquark (mesons), only integer charge is observed in nature. Their respective antiparticles are the antiquarks, which are identical except that they carry the opposite electric charge ...
What is a quasi particle?
Quasiparticles are effective particles that exist in many particle systems. The field equations of condensed matter physics are remarkably similar to those of high energy particle physics. As a result, much of the theory of particle physics applies to condensed matter physics as well; in particular, there are a selection of field excitations, called quasi-particles, that can be created and explored. These include:
What is the smallest particle into which a substance can be divided while maintaining the chemical properties of the substance?
Molecules are the smallest particles into which a substance can be divided while maintaining the chemical properties of the substance. Each type of molecule corresponds to a specific chemical substance. A molecule is a composite of two or more atoms. See list of compounds for a list of molecules.
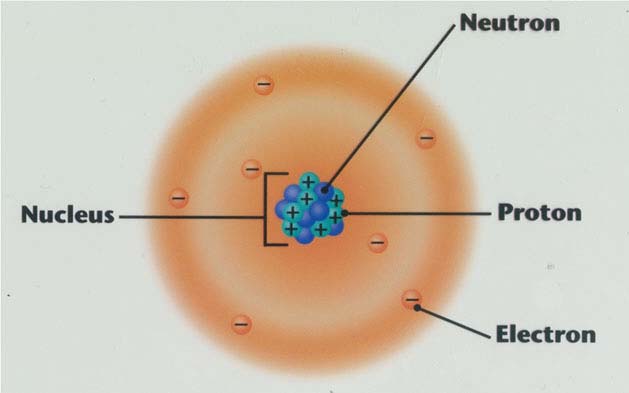
Which particle is the largest particle in an atom?
Electrons are the largest particle in an atom.
What is the core of an atom made of?
the core of the atom, made up of protons and neutrons
What does the atomic number tell you?
The atomic number tells you the number of electrons in the nucleus.
What is the smallest particle in an atom?
Electrons are the smallest of the three particles that make up atoms. Electrons are found in shells or orbitals that surround the nucleus of an atom. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus.
What is the fastest thing in the universe?
Laser beams travel at the speed of light, more than 670 million miles per hour, making them the fastest thing in the universe.
What is the smallest thing in existence?
Protons and neutrons can be further broken down: they’re both made up of things called “quarks.” As far as we can tell, quarks can’t be broken down into smaller components, making them the smallest things we know of.
Does neutron have mass?
neutron: A subatomic particle forming part of the nucleus of an atom. It has no charge. It is equal in mass to a proton or it weighs 1 amu.
Who discovered electron?
Their work culminated in the discovery by English physicist J.J. Thomson of the electron in 1897.
Why does a neutron have no charge?
Like all hadrons, neutrons are made of quarks. A neutron is made of two down quarks and one up quark. One up quark has a charge of +2/3, and the two down quarks each have a charge of -1/3. The fact that these charges cancel out is why neutrons have a neutral (0) charge.
What does the God particle prove?
This particle helps give mass to all elementary particles that have mass, such as electrons and protons.
