Following are the limitations of Beer-Lambert law:
- A diluted solution is used
- There shouldn’t be a scattering of the light beam
- Monochromatic electromagnetic radiation should be used
How is chemical limitations of beer's law?
Limitations to Beer's Law
- Fundamental Limitations to Beer's Law. Beer's law is a limiting law that is valid only for low concentrations of analyte. ...
- Chemical Limitations to Beer's Law. A chemical deviation from Beer's law may occur if the analyte is involved in an equilibrium reaction.
- Instrumental Limitations to Beer's Law
What are Lambert's laws?
Beer-Lambert Law Statement
- A is the amount of light absorbed for a particular wavelength by the sample
- ε is the molar extinction coefficient
- L is the distance covered by the light through the solution
- c is the concentration of the absorbing species
What is Beer's law and Lambert's law?
Generally, beers law relates only to concentration while Beer-Lambert law relates absorbance to both concentration and thickness of a sample. Beer Lamberts Law states a relationship between the attenuation of light through a substance and the properties of that substance.
What is modified Beer Lambert's law?
The modified Beer-Lambert law (MBLL) is the basis of continuous-wave near-infrared tissue spectroscopy (cwNIRS). The differential form of MBLL (dMBLL) states that the change in light attenuation is proportional to the changes in the concentrations of tissue chromophores, mainly oxy- and deoxyhaemoglobin.

What are the factors involved in the limitations to Beer's Law?
Limitations of Beer-Lambert law deviations in absorptivity coefficients at high concentrations (>0.01M) due to electrostatic interactions between molecules in close proximity. scattering of light due to particulates in the sample. fluoresecence or phosphorescence of the sample.
Which of the following is not a limitation of Beer-Lambert law?
Which of the following is not a limitation of Beer Lambert's law, which gives the relation between absorption, thickness, and concentration? Explanation: The law is derived assuming that the radiation is monochromatic. So, if bandwidth increases it will create deviation.
How can the limitation of Beer-Lambert law be overcome?
Beer-Lambert law is most efficient when the radiation source being passed through it is monochromatic, however, in practice this is not possible. These limitations are overcome by using polychromatic radiation in conjunction with a filter known as a monochromator to create a monochromatic beam.
What are some common mistakes that occur during a Beer's Law experiment?
Beyond this range, measurements and calculations using Beer's Law will be erroneous. Other common sources of error include the use of dirty cuvettes, poorly mixed solutions, poor pipetting techniques, and incorrect light source or wavelength.
Which of the following is a limitation of the Lambert Beer's law Mcq?
Following are the limitations of Beer-Lambert law: A diluted solution is used. There shouldn't be a scattering of the light beam. Monochromatic electromagnetic radiation should be used.
What does absorbance not depend on?
According to the Beer-Lambert Law, on which of the following does absorbance not depend? Colour of the solution.
What are possible causes of deviation from Beer-Lambert's law?
These deviations are due to: (1) chemical reasons arising when the absorbing compound, dissociates, associates, or reacts with a solvent to produce a product having a different absorption spectrum, (2) the presence of stray radiation, and (3) the polychromatic radiation.
Why is Beer's law only useful at low concentrations?
At low concentrations, lower than 0.04 the measured has to much error, this leads to important precision of the absorbance measurement. Lambert Beer law at high concentrations cannot give good correlations because when the absorbance is higher than 1, it is absorbed all light.
What are the applications of Beer-Lambert's law?
Beer's law is important in the field of physics, chemistry and meteorology. The law is used in chemistry to measure the concentration of chemical solutions, analyse oxidation, and measure polymer degradation. The law also explains the attenuation of radiation through the Earth's atmosphere.
What are the limitations of spectrophotometry?
Spectrophotometry is a conventional and inexpensive technique. However, it also has several limitations, including low sensitivity and selectivity. Spectrophotometric determination of iodate in seawater involved the reaction of with excess I− under acid conditions to form I2.
What is one common source of error in spectroscopy?
In practice there are other sources of error, such as environmental effects on photometer and sample, temperature, line voltage fluctuations, vibrations, contamination, or heating of the sample by the photometer. All these factors may impair the measured result, and ways and means are known to test and eliminate them.
Does temperature affect absorbance?
The absorption of aqueous glucose decreases with the increasing of temperature, also the absorbance decreases.
Why absorbance has no unit?
Absorbance doesn’t have any unit because it is the ratio of the amount of light that passes through a solution compared to the amount of light that...
What are the limitations of Beer-Lambert law?
Following are the limitations of Beer-Lambert law: A diluted solution is used There shouldn’t be a scattering of the light beam Monochromatic elect...
Why does Beer-Lambert law fails at higher concentrations?
Beer-Lambert law fails at higher concentrations because the linearity of the law is limited to chemical and instrumental factors. When the solution...
What is Beer-Lambert’s law for absorption spectroscopy?
Beer-Lambert’s law for absorption spectroscopy is a linear relationship between the absorbance and the concentration of an absorbing species. The s...
State the situations when Beer’s law is not obeyed.
Following are the situations when Beer’s law is not obeyed: When different types of molecules are in equilibrium with each other. An association co...
What is Beer-Lambert Law?
The Beer-Lambert law, also known as the Beer-Lambert–Bouguer law, or the Beer's law, states that the absorbance of a solution is proportional to its concentration, absorption coefficient, molar, and optical coefficient.
Derivation and Mathematical Expression
ε denotes molar extinction coefficient or molar absorptivity (or absorption coefficient),
Applications of Beer-Lambert Law
The law finds application in analytical chemistry. Analytical chemistry is concerned with the separation, measurement, and identification of matter by the use of spectrophotometry. To obtain the results, no extensive pre-processing of the material is required.
Limitation of Beer-Lambert law
When the concentration is low, i.e. 10mM, it is simple to analyze the absorptivity coefficient of the sample using this rule, but as the concentration rises, i.e. >10mM, there is a deviation due to the increase of the electrostatic interactions.
Things to Remember
The Beer-Lambert law states that the absorbance of a solution is proportional to its concentration, absorption coefficient, molar, and optical coefficient.
Sample Questions
Ques. What role does absorbance play in determining a solution's concentration? 1 mark
What is Beer Lambert's law?
Beer-Lambert’s law for absorption spectroscopy is a linear relationship between the absorbance and the concentration of an absorbing species. The states imply that type, as well as the concentration of the molecules, are necessary.
Why does Beer Lambert law fail?
Beer-Lambert law fails at higher concentrations because the linearity of the law is limited to chemical and instrumental factors. When the solution has higher concentrations, the proximity between the molecules of the solution is so close that there are deviations in the absorptivity.
Why is the Beer Lambert law nonlinear?
Causes of nonlinearity include: deviations in absorptivity coefficients at high concentrations (>0.01M) due to electrostatic interactions between molecules in close proximity scattering of light due to particulates in the sample.
What is the law of light absorption?
In optics, the Beer–Lambert law, also known as Beer’s law, the Lambert–Beer law, or the Beer–Lambert–Bouguer law relates the absorption of light to the properties of the material through which the light is traveling. The general Beer-Lambert law is usually written as: A = a () * b * c
What is the Beer Lambert law?
In optics, the Beer– Lambert law, likewise called Beer’s law, the Lambert– Beer law, or the Beer– Lambert– Bouguer law relates the absorption of light to the homes of the material through which the light is traveling. The general Beer-Lambert law is generally composed as: A = a () * b * c.
What is the objective of Beer-Lambert Law?
958. Objective: 1. To identify the linear relationship between absorbance and concentration of a taking in species. 2. To study the effects of molecular dissociation complex formation on the applicability of the Beer-Lambert Law. 3.
How is Beer's law applied to a mixture?
Beer’s law can be applied to the analysis of a mixture by spectrophotometry, without the need for extensive pre-processing of the sample. An example is the determination of bilirubin in blood plasma samples. The spectrum of pure bilirubin is known, so the molar absorption coefficient is known.
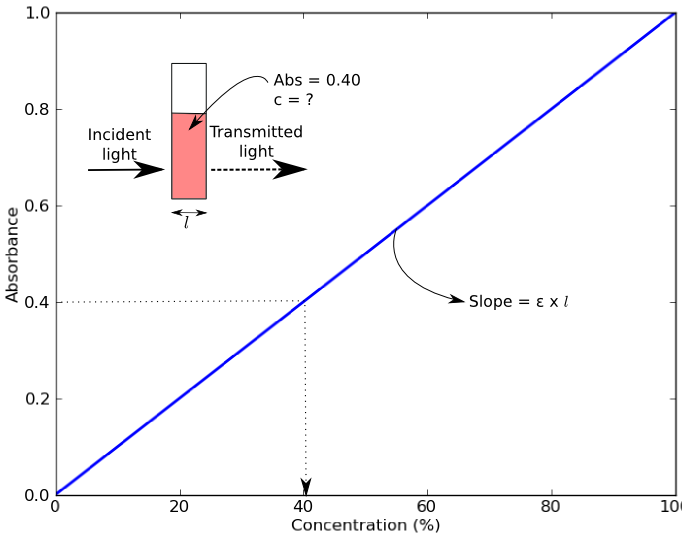
What Is Beer-Lambert Law?
- When a monochromatic light of initial intensity Io passes through a solution in a transparent vessel, some of the light is absorbed so that the intensity of the transmitted light I is less than Io.
- There is some loss of light intensity from scattering by particles in the solution and reflectio…
Derivation of Beer-Lambert Law
- If material bodies are exposed to radiation, part of the incident radiation is absorbed, a part is scattered and a part is transmitted.
- As a result of absorption the intensity of light passing through material bodies, i.e. the intensity of transmitted light, decreases.
- The fraction of incident light absorbed depends on the thickness of the absorbing medium.
- If material bodies are exposed to radiation, part of the incident radiation is absorbed, a part is scattered and a part is transmitted.
- As a result of absorption the intensity of light passing through material bodies, i.e. the intensity of transmitted light, decreases.
- The fraction of incident light absorbed depends on the thickness of the absorbing medium.
- Lambert derived a quantitative relationship between the decrease in intensity of a monochromatic light due to the passage through a homogeneous medium of thickness dx and the intensity of light I....
Other Limitations Include
- The electromagnetic radiation should be monochromatic.
- The light beam should not be scattered.
- The solution should be diluted.
References
- http://life.nthu.edu.tw/~labcjw/BioPhyChem/Spectroscopy/beerslaw.htm
- https://www.slideshare.net/MorshedulHaque/beer-lamberts-law
- https://www.slideshare.net/JALEEL/beer-lambert
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beer%E2%80%93Lambert_law
Beer-Lambert Law Definition
Beer-Lambert Law Equation
Beer-Lambert Law Derivation
Applications of Beer-Lambert Law
Limitations of Beer-Lambert Law
- [Click Here for Sample Questions] The limitations of Beer-Lambert law claim that only under certain situations does the Beer-Lambert law maintain linearity. 1. As the molecules of the analyte have stronger intermolecular and electrostatic interactions due to the smaller amount of space between them, the law will produce false results at high concen...
Things to Remember
What Is The Beer-Lambert Law?
What Is The Molar Extinction coefficient?
Beer-Lambert Law Graph
Applications of The Beer-Lambert Law
Limitations of The Law
- The law tends to become inaccurate at high concentrations. This is due to a combination of different factors. The refractive index of the solution may deviate. There are saturation and aggregation effects possible due to the molecule of interest interacting with each other (not just solvent as is the situation at low concentrations). An excellent w...
Example Problems