Endoplasmic Reticulum Functions
- It is primarily responsible for transportation to another organ of proteins and other carbohydrates, including lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, plasma membrane, etc.
- They also provide cellular reactions with increased surface area.
- They aid in nuclear membrane formation during cell division.
- They play an important role in forming the skeletal structure.
What does the endoplasmic reticulum do in a plant cell?
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure
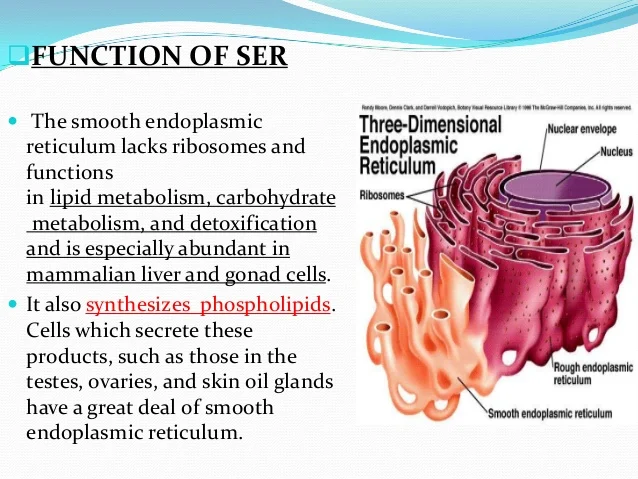
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum, on the other hand, does not have ribosomes.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum has a tubular form.
- It participates in the production of phospholipids, the chief lipids in cell membranes and are essential in the process of metabolism.
What does the endoplasmic reticulum do in an animal cell?
There are 3 main functions of endoplasmic reticulum:
- Lipid Synthesis
- Proper protein folding: This is ensured by variety of modifications like
- Glycosylation
- Disulfide bond formation
- Assembly of multi subunit protiens in ER and proper folding of polypeptide chain
- Specific proteolytic cleavage in the ER.
- Transport of protein, lipids and other substances through the cells. ...
What does a smooth endoplasmic reticulum do?
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum has a tubular form. It participates in the production of phospholipids, the chief lipids in cell membranes and are essential in the process of metabolism. Smooth ER transports the products of the rough ER to other cellular organelles, especially the Golgi apparatus.
What is the role of endoplasmic reticulum in protein synthesis?
Endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes inside a cell through which proteins and other molecules move. Proteins are assembled at organelles called ribosomes. When proteins are destined to be part of the cell membrane or exported from the cell, the ribosomes assembling them attach to the endoplasmic reticulum, giving it a rough appearance.

What are the 4 major functions of smooth ER?
The SER has a variety of functions that are often more prominent in certain cell types whose roles require an enhanced SER ability. Four common functions are the mobilization of glucose from glycogen, calcium storage, drug detoxification, and the synthesis of lipids.
What are the main functions of endoplasmic reticulum Class 9?
It is composed of two forms: RER and SER. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum, SER, is involved in the synthesis of fat and steroid hormones. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum helps in the muscle contraction by the release and uptake of calcium ions. Rough endoplasmic reticulum, RER, provides the surface for protein synthesis.
What is the main function of endoplasmic?
The endoplasmic reticulum performs the following functions: It is responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones. It is also responsible for the synthesis of essential lipids such as phospholipids and cholesterol. It is responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates.
What is endoplasmic reticulum in biology class 11?
The endoplasmic reticulum is the organelle that is present in almost every eukaryotic cell. Endoplasmic reticulum is generally divided into two categories, RER and SER. The endoplasmic reticulum is like a sac in structure. The continuous network of these sacs of membranes is termed cisternae.
What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum and what are their functions?
The two types of endoplasmic reticulum are : Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Their main function is produce proteins in the cells and ribosomes are attached to their surface. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: Their main function is to produce lipids and also detoxify toxins in the body in the liver and kidney cells.
What is a endoplasmic reticulum simple definition?
(EN-doh-PLAZ-mik reh-TIH-kyoo-lum) A network of sac-like structures and tubes in the cytoplasm (gel-like fluid) of a cell.
What are the three forms of endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large membrane-bound compartment spread throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It is divided into three major morphologies that include the nuclear envelope (NE), peripheral ER cisternae, and an interconnected tubular network (Fig. 1A,B).
What is endoplasmic reticulum class 9 science?
It is a cell organelle present in eukaryotic cells. It is a part of the endomembrane system. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network or reticulum of small tubular structures dispersed throughout the cytoplasm.
Who discovered endoplasmic reticulum Class 9?
Porter and Thompson discovered the endoplasmic reticulum in 1945. Endoplasmic reticulum is a double membrane and has interconnected cisternae that run through the cytoplasm and has a tubular structure. It is of two types- RER (Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum) and SER (Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum).
What are the functions of cytoplasm Class 9?
What is the important function of cytoplasm? The cytoplasm is responsible for holding the components of the cell and protects them from damage. It stores the molecules required for cellular processes and is also responsible for giving the cell its shape.
What is RER and SER Class 9?
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) It possesses ribosomes attached to its membrane. It does not have ribosomes on its membrane. Formed of cisternae and a few tubules. Formed of vesicles and tubules.
1. What is endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a tubular network of membranes found within the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell.
2. List the types of endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum is classified into two types: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough endoplasmic reticulum
3. List the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum performs the following functions: It is responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones. It is also resp...
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.All e...
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The ER can be classified in two functionally distinct forms: smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The morpholo...
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves important functions particularly in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins. Differen...
When was the endoplasmic reticulum discovered?
The ER was first noted in the late 19th century, when studies of stained cells indicated the presence of some type of extensive cytoplasmic structu...
What is the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum transpires in two forms: a type with a ribosome-studded surface and another with a smooth surface. The latter is called the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and the former is called the rough endoplasmic reticulum. These membranes form continuous folds, eventually joining the outer layer of the nuclear membrane. Except for sperm cells and red blood cells, the endoplasmic reticulum is observed in every other type of eukaryotic cell.
Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum called that?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is named so because of its appearance. It is a series of connected flattened sacs having several ribosomes on its outer surface, hence the name. It synthesizes and secretes proteins in the liver, hormones and other substances in the glands.
What is the difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes embedded within its structure, giving a “rough” appearance. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not have these ribosomes, hence appear “smooth.”
What is the function of the smooth ER?
Smooth ER is also responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones. It is also responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates. The smooth ER store and release calcium ions.
What is the role of the ER?
It is responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones. It is also responsible for the synthesis of essential lipids such as phospholipids and cholesterol. It is responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates. ER releases calcium ions, which are necessary for the nervous system and muscular system.
Which part of the reticulum plays a vital role in protein folding?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum also plays a vital role in protein folding.
What is the role of ER in the nervous system?
ER releases calcium ions, which are necessary for the nervous system and muscular system.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum? What are its functions?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The diverse functions of the ER are performed by distinct domains; consisting of tubules, sheets and the nuclear envelope. Several proteins that contribute to the overall architecture and dynamics of the ER have been identified, but many questions remain as to how the ER changes shape in response to cellular cues, cell type, cell cycle state and during development of the organism. Here we discuss what is known about the dynamics of the ER, what questions remain, and how coordinated responses add to the layers of regulation in this dynamic organelle.
Where are proteins and phospholipids transferred to the endomembrane?
Proteins and phospholipids, which are the major lipid component of membranes, are transferred and biochemically modified in the region of the ER that is in close juxtaposition to the Golgi apparatus [25]. This region, known as the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC), is rich in tubules and vesicles [4]. Once lipids are mobilized to the ERGIC they are distributed throughout the cell through organelle contacts or secretory vesicles [26]. The cis-Golgi, which is the closest structure to the ERGIC, leads to the trans-Golgi network where vesicles carrying newly synthesized secretory proteins from the ER form and bud [4]. The trans-Golgi network has traditionally been viewed as the main sorting station in the cell where cytosolic cargo adaptors are recruited to bind, indirectly or directly, and transport proteins or lipids [27].
What is the ER structure?
While the ER is defined as an interconnected network with a continuous membrane, the different structures that make up the ER perform very diverse and specialized functions within the cell.
What is the role of the ER in the body?
Regulation of ER shape and function . The ER is a complex organelle, involved in protein and lipid synthesis, calcium regulation and interactions with other organelles. The complexity of the ER is reflected in an equally complex physical architecture.
What is the role of calcium in the cell cycle?
Calcium is a widespread signaling molecule that can affect diverse processes including localization, function and association of proteins, either with other proteins, organelles or nucleic acids. Release of Ca2+can result in a wave of Ca2+that moves through the entire cell [40], a gradient of Ca2+from the source of release, or a spatially-restricted wave from clustered channels known as a Ca2+spark [41]. One of the most well-studied Ca2+release events occurs at fertilization following sperm entry [40, 42], but also occurs during muscle contraction and secretion [6] as well as neuronal processes including neurotransmitter release [43]. We will highlight recent evidence that Ca2+may also play a role in reshaping the ER in response to cellular signals.
What happens when a protein is translated into the ER?
If the protein is not destined to be integrated into the membrane, but instead enter the secretory pathway or the lumen of membrane-bound organelles, the protein begins the process of transport. Once translation is complete and the signal peptide has been cleaved the ribosomes are released back into the cytosol [16, 17]. For mRNAs translated by stably-bound ER ribosomes, mRNAs are released and ribosomes may remain bound to the ER and participate in multiple rounds of translation [18, 19]. For cytosolic proteins translated on ER-bound ribosomes it is not clear how these mRNAs are recruited to the ER or what populations of ribosomes are utilized to initiate translation, although a recent study indicates that the ER-resident protein p180 may play a role in the translation-independent recruitment of mRNAs to the ER [20].
What is the function of the ER?
One of the major functions of the ER is to serve as a site for protein synthesis for secreted and integral membrane proteins [8] , as well as a subpopulation of cytosolic proteins [1]. Protein synthesis requires localization of ribosomes to the cytosolic face of the ER, and the canonical pathway that regulates protein synthesis involves co-translational docking of the mRNA:ribosome complex on the ER membrane. Translation of secretory or integral membrane proteins initiates in the cytosol, then ribosomes containing these mRNAs are recruited to the ER membrane via a signal sequence within the amino terminus of the nascent polypeptide that is recognized and bound by the signal recognition particle (SRP) [9, 10]. The complex of mRNA:ribosome:nascent polypeptide:SRP is targeted to the ER where it docks on the SRP receptor [11, 12]. Translation continues on the ER and the emerging polypeptide can co-translationally enter the ER through the translocon [2], which is a channel that contains several Sec proteins and spans the lipid bilayer [13].
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. All eukaryotic cells contain an ER. In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell. The ER can be classified in two functionally distinct forms: ...
Who introduced the term "endoplasmic reticulum"?
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, Porter and colleagues Helen P. Thompson and Frances Kallman introduced the term endoplasmic reticulum to describe the organelle. Porter later worked with Romanian-born American cell biologist George E. Palade to elucidate key characteristics of the ER. Kara Rogers.
What is the ER in eukaryotic cells?
All eukaryotic cells contain an endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell. Differences in certain physical and functional characteristics distinguish the two types of ER, known as rough ER and smooth ER. Rough ER is named for its rough appearance, ...
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the liver?
In cells of the liver, it contributes to the detoxification of drugs and harmful chemicals. The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a specialized type of smooth ER that regulates the calcium ion concentration in the cytoplasm of striated muscle cells. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content.
What is the role of SER in the liver?
In cells of the liver, SER contributes to the detoxification of drugs and harmful chemicals.
What percentage of the membrane content of an animal cell is ER?
In animal cells, the ER usually constitutes more than half of the membranous content of the cell.
Where are proteins transported to the Golgi apparatus?
Proteins targeted for transport to the Golgi apparatus are transferred from ribosomes on rough ER into the rough ER lumen , which serves as the site of protein folding, modification, and assembly. endoplasmic reticulum; organelle.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules and flattened sacs that serve a variety of functions in plant and animal cells . The two regions of the ER differ in both structure and function. Rough ER has ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Smooth ER lacks attached ribosomes.
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum serves as a transitional area for transport vesicles. It also functions in carbohydrate and lipid synthesis. Cholesterol and phospholipids are examples.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells?
It plays a major role in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and lipids. The ER produces transmembrane proteins and lipids for its membrane and many other cell components including lysosomes, secretory vesicles, ...
How are proteins sent to the Golgi apparatus?
Some proteins are sent to the Golgi apparatus by special transport vesicles. After the proteins have been modified in the Golgi, they are transported to their proper destinations within the cell or exported from the cell by exocytosis .
Which structure helps support the cell and aids in organelle movement?
Cytoskeleton: a network of fibers throughout the cytoplasm that helps support the cell and aids in organelle movement.
Which protrusions from a cell aid in movement and cellular locomotion?
Cilia and flagella: protrusions from a cell that aid in movement and cellular locomotion.
Is the endoplasmic reticulum only one component of a cell?
The endoplasmic reticulum is only one component of a cell. The following cell structures can also be found in a typical animal eukaryotic cell:
