Flowering plant
The flowering plants, also known as angiosperms, Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants, with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are seed-producing plants. Howeve…
Why are angiosperms most successful?
Because angiosperms photosynthesize so much, they are some of the best oxygen makers around. Angiosperms have been so successful because of their compact DNA and cells. Representing hundreds of thousands of species and 96% of all terrestrial vegetation, flowering plants are the most successful land plants on Earth.
What does angiosperm and a gymnosperm have in common?
Angiosperms and gymnosperms are both seed-bearing plants with a few similarities. This is due to the fact that gymnosperms were present for at least 200 million years before the angiosperms evolved and they may have shared a common ancestor. The main difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms is their diversity.
What are the characteristics of an angiosperm?
These include:
- All angiosperms have flowers that act as reproductive organs. ...
- Angiosperm flowers usually have multiple stamen, which are the male reproductive parts.
- The stamen produce small pollen grains. ...
- Most angiosperm flowers also have large, bright petals to attract pollinators — animals (usually insects) that carry pollen from one flower to another.
What is the life cycle of an angiosperm?
The life cycle of angiosperms begin with pollination and end in the formation of fruits which contains seeds that germinate into new plants which mature till they reach the flowering stage, thereby, completing a full circle.
What are the spores in the corolla?
Why are the bracts in my poinsettias brightly colored?
Why do sepals look like leaves?
What is the outermost layer of a flower called?
How many whorls are there in a Bougainvillea?
What is a carpel?
Where does the staminal disc come from?
See 4 more
About this website
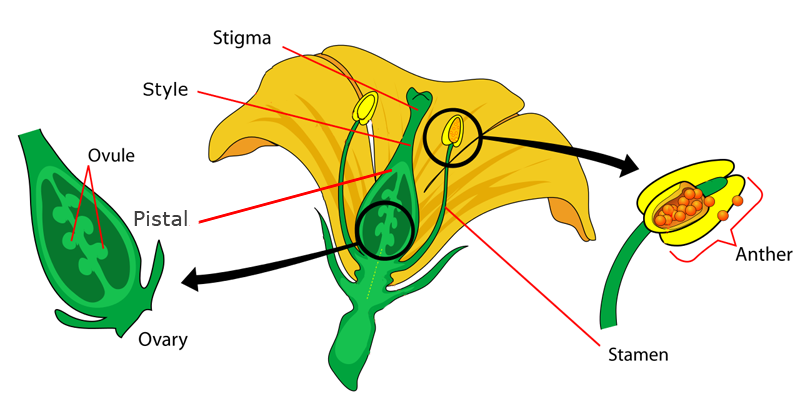
What are the male and female reproductive parts of an angiosperm?
The male reproductive organ of an angiosperm is stamen or androecium and the female reproductive organ of an angiosperm is pistil or carpel or gynoecium. The stamen consists of a filament and another. The anther contains four microsporangia within which microspores or pollens are developed.
What are the male parts of an angiosperm?
Angiosperms have male sex organs called stamens. On the end of the stamen is the anther. This is where pollen is made. The pollen has to be taken to the pistil or the female part of the flower.
What are all the female parts of an angiosperm?
The pistil, or carpel are the female reproductive structures of a flower. It consists of a stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is raised and sticky to help it catch pollen. The style supports the stigma and connects it to the ovary, which contains the egg.
What are the parts of an angiosperm?
The basic angiosperm body has three parts: roots, stems, and leaves. These primary organs constitute the vegetative (nonreproductive) plant body. Together, the stem and its attached leaves constitute the shoot. Collectively, the roots of an individual plant make up the root system and the shoots the shoot system.
What is the female part of the flower?
PistilPistil: The ovule producing part of a flower. The ovary often supports a long style, topped by a stigma. The mature ovary is a fruit, and the mature ovule is a seed. Stigma: The part of the pistil where pollen germinates.
Do angiosperms have male and female cones?
Angiosperms Versus Gymnosperms Double fertilization is a key event in the life cycle of angiosperms, but is completely absent in gymnosperms. The male and female gametophyte structures are present on separate male and female cones in gymnosperms, whereas in angiosperms, they are a part of the flower.
Do angiosperms have separate male and female plants?
Separate male and female flowers are present on the same individual plant. The green female inflorescence projects upward on the left side of the branch. The male catkin hangs below the branch on the right. Individual flowers with their two stigmas can be seen in this closeup of the female inflorescence.
What is the male part of the flower?
The male parts are called stamens and usually surround the pistil. The stamen is made up of two parts: the anther and filament. The anther produces pollen (male reproductive cells). The filament holds the anther up.
What are the male and female gametophyte in angiosperms?
The female gametophyte is also commonly called the embryo sac or megagametophyte. The male gametophyte, also called the pollen grain or microgametophyte, develops within the anther and consists of two sperm cells encased within a vegetative cell (Gifford and Foster, 1989).
What are the two main parts of the angiosperm?
While flowers are the reproductive organ, the non-sexually-reproductive body parts are roots, stems, and leaves. The two main parts of the structure of the angiosperm are root systems and shoot systems.
What are the two reproductive parts of an angiosperm?
The success of angiosperms is due to two novel reproductive structures: flowers and fruit. The function of the flower is to ensure pollination. Flowers also provide protection for the ovule and developing embryo inside a receptacle. The function of the fruit is seed dispersal.
What are the 2 divisions of angiosperms?
Angiosperm diversity is divided into two main groups, monocot and dicots, based primarily on the number of cotyledons they possess.
What are the male plant parts?
stamensThe male parts are called stamens and usually surround the pistil. The stamen is made up of two parts: the anther and filament. The anther produces pollen (male reproductive cells). The filament holds the anther up.
What are male gametes in angiosperms?
The male gametes of angiosperms consist of two sperm cells within a pollen grain or a pollen tube. They are derived from a single generative cell, which is formed as the smaller cell by unequal cell division in the microspore after meiosis.
What are the male gametes of angiosperms called?
The male gametophyte (pollen) of angiosperms is among the most reduced independent multicellular organisms in biology. Pollen is comprised largely of a vegetative cell that forms a pollen tube, which conveys the non-motile sperm cells that it contains into the female gametophyte.
What are the 3 male reproductive parts of a flower?
If you were to zoom in on a flower, you may notice some male reproductive organs, which are the structures involved in producing and distributing the male reproductive cells and include the anther, the filament, the stamen, and the pollen.
Reproduction in Angiosperm and Reproductive structures
Angiosperm: Reproductive structures General features of reproductive structures: In Angiosperms, there is a wide range of morphology and structure of the reproductive organs of the plant.
How many megaspores are there in angiosperms?
In the majority of angiosperms, one megasporocyte develops in the megasporangium (often called the nucellus) of the ovule, and a tetrad of megaspores is formed as a result of meiosis. Three megaspores (nearest the micropyle) degenerate; only one enlarges, and then it undergoes divisions to form the eight-nucleate, seven-celled female gametophyte (“embryo sac”). Of the three cells of this gametophyte near the micropyle, one functions as an egg. As the pollen tube discharges its contents into the female gametophyte, the egg nucleus is fertilized by one of the sperm cells, and the other unites with the two nuclei ( polar nuclei) within the large central cell of the female gametophyte. The resultant nucleus, which has three sets of chromosomes, is the primary endosperm nucleus. This process, double fertilization, occurs only in angiosperms.
What is the life cycle of angiosperm?
Life cycle of a typical angiosperm. The angiosperm life cycle consists of a sporophyte phase and a gametophyte phase. The cells of a sporophyte body have a full complement of chromosomes (i.e., the cells are diploid, or 2 n ); the sporophyte is the typical plant body that one sees when one looks at an angiosperm.
How do angiosperms open their anther?
Opening of the anther may be by longitudinal or transverse fissures or by terminal pores. The reproductive cycle in angiosperms can be traced from before the shedding of pollen. The microspores begin their development of male gametophytes, which involves formation of a small generative cell and a tube cell.
What is the difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms?
Angiosperms. Although the angiosperms are known as flowering plants, they are difficult to distinguish from gymnosperms solely on the basis of bearing flowers, for, like the strobilus, a flower is a compressed stem , with crowded spore-bearing appendages .
What is a tulip in flower?
A tulip ( Tulipa) in flower. Yellow corymbs, a type of inflorescence, of yarrow ( Achillea aegyptiaca ). An individual flower may be complete, in that a given floral receptacle produces sepals (often greenish and leaflike), petals (often white or coloured other than green), stamens, and a pistil (or pistils).
What does it mean when a flower is incomplete?
If sepals or petals are lacking, the flower is said to be incomplete. Although incomplete, a flower that has both stamens and a pistil is said to be perfect; lacking either of these parts, it is imperfect. flower anatomy. Diagram of the flower of a typical flowering plant (angiosperm). Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
What is the name of the cell that produces the egg?
An eight-celled megagametophyte (called the embryo sac) produces the egg. Fertilization occurs with the fusion of a sperm with an egg to produce a zygote, which eventually develops into an embryo. After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed, and the ovary develops into a fruit. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
What is Angiosperm?
The word Angiosperm originates from a Greek word where “angeion” means vessel and “sperma” means seed. Flower bearing plants are called as Angiosperms. Belonging to the plants group. Along with the flower, it also bears seeds. It is one of the vast group of plants, with 453 families and 260,000 species within. In the category of Angiosperms are 80% of green plants.
What are monocots called?
In 1703, they were first discovered by Ray. In the seed presence of a single cotyledon are called as monocots. These monocots phylogenetic studies have been done in 19th century. They consist of fibrous system of roots. The flowers in monocots consist of three parts and are called as Trimerous. Woody tissues are either absent or only present in few cases. A vital feature seen in monocots is the presence of a single layer of pollens, which is even seen today. Examples of monocots plant are orchid, lilies, grasses and others, whereas monocot crops are sugarcane, pineapple, corns and others.
What are some examples of non-flowering plants?
Example are grains, fruits, vegetables and others. Gymnosperms are non-flowering plants and their examples are juniper, pine, cedar and fir. Accumulation of gymnosperms form, cones whereas the accumulation of angiosperm forms flowers. Angiosperms are mostly unisexual whereas the gymnosperms are bisexual. In angiosperms there are various flowering parts such as style, stigma, petals and sepals. Archegonia is found in gymnosperms and is absent in angiosperms. On the stalk are the angiosperms present. Angiosperms and gymnosperms also vary in the cotyledon number. Angiosperms have application in food, ornament, timber and pharmaceutical, whereas gymnosperms in making of ply, paper and lumber.
Why are angiosperms important to humans?
Thus, angiosperms are very vitals as various crops are available to humans because of them.
What are the two types of angiosperms?
On the basis of the leaves, angiosperms can be divided into eudicots and the monocots. On the embryo surface there are seed leaves which contain protein, lipid and sugars. There exist three species of angiosperm and they are where on the flower, stamen and pistil are present is the hermaphroditic. Monecious, where both the stamen and pistil are on the same plant but different flower. When both stamens and pistil are present on different plants and different flower it is called as dioecious.
What is the process of pollination?
Pollination occurs when the pollen from the male reaches the female part. There are two types of pollination; self-pollination and cross pollination. Pollination agents are insects, invertebrates, mammals and wind.
How old are angiosperms?
Modern and molecular techniques have been used to determine the origin of flowering plants and has said that they are 5-45 millions years old. Various researchers have worked on the finding of origination of angiosperm using various tools and techniques and have found that the age of angiosperm is 165-199 Ma and for other plants as well have been found.
What Is an Angiosperm?
Angiosperms are flowering vascular plants and are the most common type of plant found on Earth. Angiosperms are incredibly diverse, making up approximately 80% of all the known species of plants on Earth. The word "angiosperm" is derived from two root words: "angio" meaning vessel, and "sperm" meaning seed.
Angiosperm Structure
The angiosperm structure has distinct parts and characteristics. Though each species of angiosperm varies widely, from the largest oak tree to the smallest dandelion, the flower structure has recognizable parts that are specialized for specific functions.
Angiosperm Reproduction
To understand angiosperm reproduction, it is important to understand that plants have a life cycle that is referred to as the alternation of generations. This means that within the angiosperm life cycle, there are two distinct stages where the cells and the number of chromosomes within the cell vary.
What is the female reproductive structure of angiosperms?
In angiosperms, the pistil is the female reproductive structure found in flowers, and consists of the stigma, style, and ovary. There are two parts to an angiosperm: a male part and a female part. The male gametophyte consists of 2 or 3 cells contained within a pollen grain; the female gametophyte consists of eight cells contained within an ovule. The stamen is the male reproductive structure of a flower; usually consisting of slender, thread-like filaments topped by anthers, which contain the pollen.
What organ does a flower have?
The flower has a male reproductive organ stamen and a female reproductive organ pistil (or carpel). Stamen produces pollen grains which fertilize with ova to form zygote.
Where are the reproductive parts of angiosperm located?
The reproductive parts of an angiosperm are located in the flowers. A flower of an angiosperm usually consists of four whorls namely calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium. Androecium and gynoecium represents the male and female reproductive whorls of the flower, respectively. Furthermore, stamens are the units of androecium while carpels are the units of gynoecium. Stamen consists of two parts namely anther and the filament. The pollen grains are produced in the anthers. Carpel on the other hand side consists of three parts namely stigma, style and ovary. The ovary of carpel contains ovules
What does pedal commander do?
Pedal Commander eliminates the delay from your gas pedal, allowing your car to have instant acceleration.
Why are immature parts of plants protected?
Immature parts of plants generally protected by something because immature parts are prone to damage mechanically or by other means. They act like shield and other immature parts remain protected inside.
Where does the majority of food come from?
The vast majority of our food comes directly or indirectly from angiosperms. For example:- all cereal grains and most vegetables, fruits, and nuts are obtained from angiosperms,- most spices are obtained from angiosperms, and- most non-alcoholic and alcoholic beverages are made from angiosperms.
Does Wagmo cover animals?
Wagmo's health insurance for animals is reimbursement based. Our plans reimburse you right away!
What are the spores in the corolla?
Internal to the corolla are the stamens, spore-producing structures (microsporophylls) that are collectively called the androecium. In most angiosperms, the stamens consist of a slender stalk (the filament) that bears the anther (and pollen sacs), within which the pollen is formed. Small secretory structures called nectaries are often found at the base of the stamens and provide food rewards for pollinators. In some cases the nectaries coalesce into a nectary or staminal disc. In many cases the staminal disc forms when a whorl of stamens is reduced into a nectiferous disc, and in other cases the staminal disc is actually derived from nectary-producing tissue of the receptacle.
Why are the bracts in my poinsettias brightly colored?
Bracteoles in the inflorescence of Bougainvillea also are brightly coloured to attract pollinators (see photograph ).
Why do sepals look like leaves?
The sepals (collectively called the calyx) most resemble leaves because of their generally green colour. From their base and along most of their length, sepals remain either separate (aposepalous, or polysepalous) or marginally fused (synsepalous), forming a tube with terminal lobes or teeth (see photograph ).
What is the outermost layer of a flower called?
The sepals, the outermost layer, are usually green, enclose the flower bud, and collectively are called the calyx. Petals are the next layer of floral appendages internal to the calyx; they are generally brightly coloured and collectively are called the corolla. The calyx and corolla together compose the perianth.
How many whorls are there in a Bougainvillea?
When the petals are missing and bracts appear coloured and petaloid as in the Bougainvillea, one of the three whorls is missing: there are only two whorls of five organs instead of the three whorls of five organs described above.
What is a carpel?
Carpels are megasporophylls that enclose one or more ovules, each with an egg. After fertilization, the ovule matures into a seed, and the carpel matures into a fruit. Carpels, and thus fruit, are unique to angiosperms. A complete flower contains all four organs, while an incomplete flower is missing at least one.
Where does the staminal disc come from?
In many cases the staminal disc forms when a whorl of stamens is reduced into a nectiferous disc, and in other cases the staminal disc is actually derived from nectary-producing tissue of the receptacle. At the centre of the flower are the carpels, collectively called the gynoecium.
