What are the 7 monocular depth cues?
- relative size.
- interposition.
- linear perspective.
- aerial perspective.
- light and shade.
- monocular movement parallax.
What are the different types of monocular cues?
Understanding of Monocular Cues
- Motion Parallax. When we observe a moving object, at that time, the stationary objects against or in the background can give us a hint about the relative distance.
- Absolute Size. ...
- Depth from Motion. ...
- Kinetic Depth Effect. ...
- Linear Perspective. ...
- Relative Size. ...
- Familiar Size. ...
- Aerial Perspective. ...
- Accommodation. ...
- Texture Gradient. ...
Is an example of a monocular cue?
Is an example of a monocular cue? An example of a monocular cue would be what is known as linear perspective. Some other monocular depth cues are interposition, the partial overlap of objects, and the relative size and closeness of images to the horizon.
What are the disadvantages of monocular vision?
List of the Pros of Monovision Cataract Surgery
- Fixed-focus monofocal lenses will give you better vision at a distance, so you might still need reading glasses. ...
- Accommodating monofocal lenses can shift from near to far vision at the response of your ciliary muscles. ...
- Toric lenses can help you to deal with an issue of astigmatism.
What are the two binocular depth perception cues?
What is visual depth perception: Monocular cues and Binocular cues?
- Monocular cues. Monocular cues of visual depth perception operate when a person is looking with only one eye. ...
- Binocular cues. These are the cues that are provided by both the eyes working together. They are important visual depth cues in three dimensional spaces.
- Conclusion. The image of an object projected on our retina is two-dimensional. ...

What are the 4 monocular depth cues?
These monocular cues include:relative size.interposition.linear perspective.aerial perspective.light and shade.monocular movement parallax.
What are the monocular cues for depth perception?
Monocular cues include relative size (distant objects subtend smaller visual angles than near objects), texture gradient, occlusion, linear perspective, contrast differences, and motion parallax.
What are monocular cues and give two examples?
A monocular cue is a visual cue for depth perception that only requires one eye. People with vision loss in one eye can still rely on these cues to navigate the world, although their depth perception will be impaired. Some examples include motion parallax, interposition, and linear perspective.
What are the monocular depth cues AP Psychology?
a binocular cue for perceiving depth: the greater the difference (disparity) between the two images the retina receives of an object, the closer the object is to the viewer. a binocular cue for perceiving depth; the extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object.
What are the 5 depth cues?
The psychological depth cues are retinal image size, linear perspective, texture gradient, overlapping, aerial perspective, and shades and shadows.
What are the monocular cues of depth perception explain any three?
Important monocular cues are relative size and height, interposition, linear and aerial perspective, light and shade, texture gradient, and motion parallax. The binocular cues of depth perception are provided by both the eyes in three-dimensional spaces.
What are monocular cues quizlet?
Monocular Cues. Depth cues, such as interposition and linear perspective, available to either eye alone.
What is an example of the monocular cue linear perspective?
Linear perspective is a monocular cue because the effects are manifested as actual differences in distance and size that require only a single eye to perceive. In this image, for example, the white road lines and the broken white center line are parallel, but seem to converge in the distance.
What is an example of the monocular cue motion parallax?
This is a motion parallax example, and a monocular cue. The cows appear to be passing by the car slower because the person is able to observe them for longer, due to their relative far-away position. The speed limit sign, however, is closer and does not stay in the person's field of vision for as long.
What is monocular cues in psychology?
The word “monocular” means “with one eye.” Monocular cues are all the ways that a single eye helps you see and process what you're looking at. Monocular cues play a huge role in how you perceive the world around you.
Is an example of monocular cue quizlet?
The moon changing size is an example of what monocular cue? Moon Illusion: The sky at the horizon is perceived to be (closer/farther) than the sky directly overhead. So for the moon to subtend the same visual angle, it must be (smaller/larger) when directly overhead and (closer/farther).
Which of the following is not a monocular depth cue?
Which of the following is not a monocular depth cue? Explanation: “Retinal disparity” is a binocular depth cue, not a monocular cue.
What is monocular cue?
The word “monocular” means “with one eye.”. Monocular cues are all the ways that a single eye helps you see and process what you’re looking at. Monocular cues play a huge role in how you perceive the world around you. Keep reading to learn how different types of monocular cues help you interpret and understand what you’re seeing.
How does monocular cue work?
It works by judging how big or small the object is and what that means in relation to other objects you’ve interacted with in the past.
What do binocular cues mean?
Together, your two eyes combine to give you binocular cues. This refers to visual information you get from the overlapping of each eye’s monocular cues. As Vrotsos explained, “With binocular cues, images are interpreted as three-dimensional.
What are the eye and monocular cues in the real world?
That is your eye and monocular cues in the real world — things that are closer are larger and move faster; things in the background are smaller and move slower.”. That’s the high-level idea behind monocular cues.
How to do monocular motion parallax?
The monocular motion parallax happens when you move your head and objects that are farther away appear to move at a different speed than those closer to you. Try it out by looking at something far away. Then, slowly turn your head from left to right and back again.
What is depth cue?
This cue involves awareness of objects' movement in respect to each other. It uses the premise that closer objects will move faster than more distant objects when in motion, such as in the case of a car. For instance, while driving, the trees on the side of the road move faster that the mountains in the background. Here is an example of this depth cue.
What is the cue used to determine the spatial position of objects relative to one another?
Overlapping or interposition is another cue that can be used to determine spatial positioning of objects relative to one another. By simply being able to distinguish which of the objects is in front of the other, a person can immediately gain an understanding of the perspective to determine which objects are closer or further away. Here is an example of using overlapping as a depth cue in determining object positioning.
What is monocular vision?
By definition, monocular vision is to view something with one eye. Be it through a device such as a long distance monocular or telescope, or having lost the ability to use an eye. In this article we take a look at the various ways in which our brain perceives depth, size, and perspective when presented with visual information from just one eye.
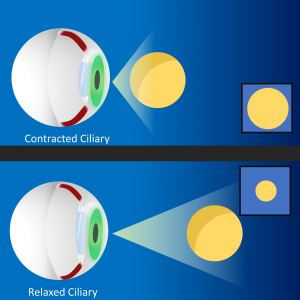
What muscles are used to change the shape of the eye lens?
Our ciliary muscles are used to change the shape of the eye lens so that we can focus on objects at varying distances. Accomodation refers to the amount of work that are eye muscles have to do to focus on an object.
Can you calculate depth and distance with two eyes?
It’s certainly a lot easier for our brains to accurately calculate depth and distances when using two eyes. Binocular cues are based upon the different images that two separate eyes produce. They each see something from a slightly different angle, which makes computing things like depth and distance much easier.
What are the oculomotor and monocular depth cues?
Oculomotor and Monocular Depth Cues. Oculomotor depth cues are proprioceptive information from oculomotor muscles and ciliary muscles. Oculomotor muscles are the muscles that rotate the eyeballs for them to converge at a depth (fig.10.6.1). Ciliary muscles are the muscles that change the focal length by compressing the lens of the eye.
Which muscles rotate the eyeballs for them to converge at a depth?
Oculomotor muscles are the muscles that rotate the eyeballs for them to converge at a depth (fig.10.6.1). Ciliary muscles are the muscles that change the focal length by compressing the lens of the eye. Fig. 10.6.1.
Development of Depth Perception
Since the time of the ancient Greeks, a recurring issue in the study of perception has been whether perceptual processes are acquired (based on prior experience) or innate (existent or potential at birth).
Monocular Cues for Depth Perception
Monocular cues are what they’re called. These are cues that may be utilized to aid depth perception when just one eye is employed.
How Monocular Cues Are Used in Depth Perception
Many of these monocular signals work together to give us a sense of depth while seeing the world around us.
Relative Size
The term “relative size” alludes to the fact that the farther away an item is, the smaller its picture on the retina will be.
Absolute Size & Familiar Size
The sense of depth is also influenced by absolute size or the actual size of an item. More minor things will appear farther away than many objects in the exact location, even if we don’t know how big they are.
Elevation
The location of an item concerning the horizon can likewise be used as a monocular cue. Objects closer to the horizon are viewed as farther away, whereas those farther out are perceived as more intimate.
Texture Gradient
The use of texture to assess depth and distance is another crucial monocular signal. When gazing at an item that stretches into the distance, such as a grassy field, the texture gets less noticeable as you get further away from it.
What are monocular cues?
Monocular cues are actually a collection of cues that help us see an object properly using just one eye. These are as follows: –. 1. Absolute Size, not knowing the size of an object is problematic for us, in such cases, the smaller object is considered at a greater distance than larger objects at the same location. 2.
Why are monocular cues important?
Monocular cues play an important role in detecting depth. It uses one eye and image can be presented in two dimensions. As such, many of the monocular cues are used in art to create an illusion of depth in a two-dimensional space.
What is the ability of both eyes to perceive an object in three-dimensional space?
Binocular cues are defined as the ability of both of our eyes to perceive an object in three-dimensional space. It’s much easier for our brains to accurately calculate the depth and distance of objects when we use both eyes. These cues are based on different images that our two separate eyes produce.
What is motion perception?
Motion Perception. Motion perception is the process of inferring with the direction and speed of elements in a scene based upon visual input. Monocular cues, or what we see from one eye, can detect nearby motion; but depth perception isn’t up to the mark. As such, binocular cues are better at perceiving m otion from distance.
How do binocular cues help us?
While binocular cues help us to expand in more than one perspective in the form of an object in order to get apt depth perception. Monocular cue sensitivity, on the other hand, depends on the visual field location, which is relative to the stimulating.
What is the difference between monocular and binocular cues?
Monocular cues provide depth information when viewing a scene with one eye while Binocular cues provide information taken when viewing a scene with both the eyes. In this article, we learn about depth perception, What are Monocular cues and Binocular cues, the Difference between them and, how we can use them.
What is binocular summation?
7. The binocular summation is one factor that results in faster reaction times when we are viewing something using both our eyes. 8.