Which is the best description of a psychomotor objective? Psychomotor Psychomotor learning is the relationship between cognitive functions and physical movement. Behavioral examples include driving a car, throwing a ball, and playing a musical instrument. In psychomotor learning research, attention is given to the learning of coordinated activity involving the arms, hands, fingers, and feet, while verbal processes are not emphasized.Psychomotor learning
What is an example of a psychomotor objective?
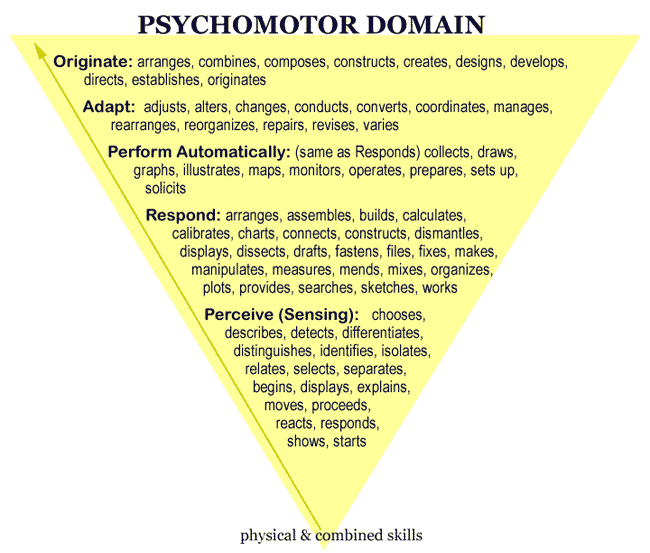
Demonstrate correct use of personal protective equipment (psychomotor—guided response)....The Psychomotor Domain.PSYCHOMOTOR DOMAINACTION VERBS for OBJECTIVESEXAMPLEPerception: observation of behaviors involved in completing a taskObserve, attend to, ask, describe, participate, answerObserve correct technique for conducting a pelvic exam4 more rows
What are psychomotor learning objectives?
Psychomotor Learning Learning in this domain includes physical movement, coordination, and use of the motor-skill areas. These might focus on speed and efficiency, precision, procedures, or techniques in execution.
What are the examples of psychomotor domains?
Psychomotor Skills Examples Characteristics of psychomotor skills include movement, coordination, dexterity, strength, flexibility, and speed.
What are the 5 psychomotor domain?
Five Levels of Skills Imitation: Learner watches actions of another person and imitates them. Manipulation: Learner performs actions by memory or by following directions. Precision: Learner's performance becomes more exact. Articulation: Learner can perform several skills together in a harmonious manner.
What are basic psychomotor skills?
Psychomotor learning is demonstrated by physical skills such as movement, coordination, manipulation, dexterity, grace, strength, speed—actions which demonstrate the fine or gross motor skills, such as use of precision instruments or tools, and walking.
What are the 3 domains of objectives?
The three domains of learning are cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. There are a variety of methods in professional development events to engage the different learning domains. Effective professional development events, such as webinars, should follow adult learning principles to engage learners.
What is a psychomotor activity?
Psychomotor activity is defined as motor/physical activity that is secondary to or depen- dent on a psychic component and is mostly non-goal-directed. 2 For example, manic, psychotic, and anxious patients would demonstrate increased psychomotor activity.
What is psychomotor in lesson plan?
Psychomotor domain is the learning and combination of old and new skills that involves physical movements. Once you understand the behavior of your learners you will be able to adapt your learning objectives according.
What are the four main domains of psychomotor development?
Psychomotor Domain TaxonomyPerception - Sensory cues guide motor activity.Set - Mental, physical, and emotional dispositions that make one respond in a certain way to a situation.Guided Response - First attempts at a physical skill. ... Mechanism - The intermediate stage in learning a physical skill.More items...
What is psychomotor domain in learning?
The psychomotor learning domain involves our physicality and how that develops from basic motor skills to intricate performance. How do the Domains of Learning impact professional development? Each domain represents a continuum of processes that begins with the most simple and ends with the most complex process.
What is an example of affective objective?
Example: Given the opportunity to work in a team with several people of different races, the student will demonstrate a positive increase in attitude towards non-discrimination of race, as measured by a checklist utilized/completed by non-team members.
What are the 3 types of domain?
The domains of learning can be categorized as cognitive domain (knowledge), psychomotor domain (skills) and affective domain (attitudes). This categorization is best explained by the Taxonomy of Learning Domains formulated by a group of researchers led by Benjamin Bloom along with in 1956.
What is an example of psychomotor learning?
psychomotor learning, development of organized patterns of muscular activities guided by signals from the environment. Behavioral examples include driving a car and eye-hand coordination tasks such as sewing, throwing a ball, typing, operating a lathe, and playing a trombone.
What is psychomotor in lesson plan?
Psychomotor domain is the learning and combination of old and new skills that involves physical movements. Once you understand the behavior of your learners you will be able to adapt your learning objectives according.
What are the four main domains of psychomotor development?
Psychomotor Domain TaxonomyPerception - Sensory cues guide motor activity.Set - Mental, physical, and emotional dispositions that make one respond in a certain way to a situation.Guided Response - First attempts at a physical skill. ... Mechanism - The intermediate stage in learning a physical skill.More items...
What is a psychomotor domain of learning?
The psychomotor learning domain involves our physicality and how that develops from basic motor skills to intricate performance. How do the Domains of Learning impact professional development? Each domain represents a continuum of processes that begins with the most simple and ends with the most complex process.
What is a mentor in psychomotor objectives?
A mentor or a coach is often needed to provide an outside perspective on how to improve or adjust as needed for the situation. Here are key verbs for each level you can use when writing psychomotor objectives: bend.
What is the second step in learning a psychomotor skill?
Other mental activity, such as reading may be a part of the observation process. Imitating. Attempted copying of a physical behavior. The second step in learning a psychomotor skill. The learner is observed and given direction and feedback on performance.
What is set in psychology?
Set - Mental, physical, and emotional dispositions that make one respond in a certain way to a situation.
What is skilled movement?
Skilled movements - Activities where a level of efficiency is achieved.
What is the meaning of "manipulation"?
Manipulation - Guided via instruction to perform a skill.
Who developed the taxonomy of involuntary responses?
Harrow (1972) developed this taxonomy. It is organized according to the degree of coordination including involuntary responses and learned capabilities:
How are psychomotor habits mediated?
Psychomotor habits are mediated primarily by the sensory and motor cortex of the brain and by the neural fibres that connect the two cerebral hemispheres. According to the majority of theoreticians, learning outcomes can be correlated with the amount or duration of rewarded practice. The effects of associative and motivational factors are believed to enhance learning, while inhibitory and oscillation (variability) factors are thought to detract from the learning of psychomotor skills.
How does a complex coordinator work?
One device, a complex coordinator, measures the learner’s ability to make prompt, synchronized adjustments of handstick and foot-bar controls in response to combinations of stimulus lights. Another device, a discrimination reaction timer, requires that one of several toggle switches be snapped rapidly in response to designated distinctive spatial patterns of coloured signal lamps. In performing on a manual lever, a blindfolded subject must learn how far to move the handle on the basis of numerical information provided by the experimenter. With a mirror tracer, a six-pointed star pattern is followed with an electrical stylus as accurately and quickly as possible, the learner being guided visually only by a mirror image. The multidimensional pursuitmeter requires the learner to scan four dials and to keep the indicators steady by making corrections with four controls (similar to those found in an airplane cockpit). On a rotary pursuitmeter the learner must hold a flexible stylus in continuous electrical contact with a small, circular metal target set into a revolving turntable.
What is a skill in movement?
The term skill denotes a movement that is reasonably complex and the execution of which requires at least a minimal amount of practice —reflex acts such as sneezing are excluded. Research shows that the performance of complex skills can be influenced by sensations arising from the things the performer looks at, sensations from the muscles that are involved in the movement itself, and stimuli received through other sensory organs. Thus the term sensorimotor skill is used to denote the close relationship between movement and sensation involved in complex acts.
What is psychomotor learning?
Psychomotor learning, development of organized patterns of muscular activities guided by signals from the environment. Behavioral examples include driving a car and eye-hand coordination tasks such as sewing, throwing a ball, typing, operating a lathe, and playing a trombone. Also called sensorimotor and perceptual-motor skills, ...
How are skills measured?
For example, skills may be measured by time intervals. In the laboratory, a subject’s reaction time is measured as the time between the presentation of some kind of stimulus and the performer’s initial response. The individual’s speed of reaction depends upon a number of variables, including the intensity of the stimuli. For example, a person will initiate a movement more quickly to increasingly louder sounds until a limit is reached. When the sounds become too loud, however, the noise delays the onset of the movement. A longer reaction time will also be recorded if the subject must choose among a number of stimuli before initiating a movement (such as moving only if one of a number of various coloured lights is turned on) or if the required act involves a complex movement.
How many instruments are used in psychomotor learning?
Hundreds of electrical and mechanical instruments have been developed for research in psychomotor learning, but only about two dozen are used with any regularity.
What is the difference between gross and fine motor skills?
Gross motor skills refer to acts in which the larger muscles are commonly involved, while fine motor skills denote actions of the hands and fingers. Most skills incorporate movements of both the larger and the smaller muscle groups. The basketball player uses his larger skeletal muscles to run and jump while drawing on fine motor skills such as accurate finger control when dribbling or shooting the ball.
How many groups does Krathwohl classify affective objectives into?
Krathwohl classify affective objectives into 5 groups. This grouping also is hierarchical with the introduction of the lowest level (simple) and practice the highest level. The higher rate of objectives in the hierarchy, the greater the person's involvement and commitment to that objective.
What domain is to be assessed?
1. Choose the affective domain is to be assessed, ex: attitudes or interests.
What are some examples of learning objective affective domain?
Examples of learning objective affective domain of in physics. - Students are willing to discuss lab results determining the specific heat of substances. - Students willing to participate actively in extracurricular activities. - Students are willing to practice using the oscilloscope. 3.
What is the objective expects of philosophy?
The objective expects students were able to show that the practice associated with organizing and integrating the values into a personal value system. This is shown through the behavior of the lower level, but have been integrating these values into a philosophy of life is complete and convincing, and consistent behavior will always primarily to the philosophy of life. Philosophy of life is part of the character.
What is appreciation value?
Appreciation Value. The objective expects students to understand the value of respect for a belief or a feeling assumption that an idea, object or a particular way of thinking has value. In this case the student is consistently behaves in accordance with a value even if there are no teachers who request or require.
What is movement accuracy?
Movement accuracy (precision) Learning objectives at this level expect students to perform a behavior without the use of visual examples and instructions in writing, and do it with smooth, precise, balanced and accurate. In performing the behavior less likes to make mistakes, because students can do it correctly.
How to make a check list for students?
The steps in preparing a check list are: 1). Look for indicators of mastery of the skills tested, 2) . Arrange these indicators in order of appearance, 3) . Make observations of the students being assessed to see the appearance of the indicator in question, 4) . If this indicator appears, then made the sign of √ or write words in the space provided.
Five Levels of Skills
Dave’s five levels of “skill” represent not so much different kinds of skills but rather different degrees of competence in performing a skill. The five levels, in order from most basic to most advanced, are:
How to Write Learning Objectives
Get this free guide to learn all you need to know to write learning objectives, create better training, and help improve workplace performance.
What are the three domains of learning?
These domains of learning are the cognitive (thinking), the affective (social/emotional/feeling), and the psychomotor (physical/kinesthetic) domain , and each one of these has a taxonomy associated with it.
What is affective objective?
Like cognitive objectives, affective objectives can also be divided into a hierarchy (according to Krathwohl). This area is concerned with feelings or emotions (and social/emotional learning and skills). Again, the taxonomy is arranged from simpler feelings to those that are more complex.
What is the original cognitive domain?
Based on the 1956 work, The Handbook I-Cognitive Domain, behavioral objectives that dealt with cognition could be divided into subsets. These subsets were arranged into a taxonomy and listed according to the cognitive difficulty — simpler to more complex forms.
When was the cognitive taxonomy first described?
In examining the three domains of learning it is interesting to note that while the cognitive taxonomy was described in 1956, and the affective in 1964, the psychomotor domain was not fully described until the 1970s.
How many editions of Bloom's Bloom are there?
There are 3 editions of the revisions of Bloom’s from Anderson and Krathwohl and others, or from Anderson.
How can students gain appreciation for the culture or country of origin?
For instance, students can gain appreciation (an affective objective) for the culture or country of origin through conducting investigations or listening to stories while learning the dances from other countries. Learning dance steps would fall under “skilled movements” in the psychomotor domain.
What is the meaning of organization in learning?
Organization. This refers to the learner’s internalization of values and beliefs involving (1) the conceptualization of values; and (2) the organization of a value system. As values or beliefs become internalized, the leaner organizes them according to priority. examine clarify systematize. create integrate.
What are the domains of learning?
The domains of learning are a series of learning objectives created in 1956 by educational psychologist Dr. Benjamin Bloom. They involve three categories of education, and each one requires a different instruction style to achieve its intended outcomes. Each domain has specific features and objectives designed to engage students who learn to solve problems, process information and build their skills using different perspectives. This helps make learning easier and more enjoyable.
What is Bloom's taxonomy?
This concept became known as Bloom's Taxonomy. For each skill, Bloom refers to active verbs that describe how individuals apply what they've learned. The original Bloom's Taxonomy includes the following skills, from the most basic to the most complex:
Why are domains of learning important?
The domains of learning give educators the knowledge to establish teaching methods that emphasize the distinctive strengths of each student. These concepts have influenced the field of education by encouraging a more holistic approach to learning. Holistic educational methods allow students to grow not only academically but also professionally. In this article, we discuss what the domains of learning are, why they're important and the stages of each domain that students use to process information and develop skills.
What is the psychomotor domain?
The psychomotor domain focuses on physical skills, such as the development of hand-eye coordination and the use of motor skills. Psychomotor skills help people perform physical tasks in daily life and at work. The areas of this domain include:
What are the verbs that represent the cognitive domain?
Instructional verbs that represent this foundational level of the cognitive domain include write, list, label, name and state.
What is affective domain?
The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate emotional responses. In this domain, individuals understand and develop their feelings, attitudes and values. Like the cognitive domain, Bloom arranged the five areas of emotional response from simple to complex:
What is an analysis verb?
Analysis: An individual understands the assumptions made by a statement or question and uses them to make conclusions. Instructional verbs include compare, contrast and analyze.