What are the potential risks of cloning?
What are the downsides of cloning?
- The process is not entirely safe and accurate. Despite being genetically identical with each other, clones will not be the same regarding behavioral attributes.
- It is regarded as unethical, and the probability of abuse is very high.
- The offspring lack genetic uniqueness.
- It is not yet fully-developed.
What are the benefits and risks of cloning?
Benefits and Risks of Cloning Scientists are picturing a world where animal products are safer, there is less disease among animals, and cloning can be used for studies and medical reasons. However, while they try to make this possible, they must also consider the benefits and risks of cloning.
What are the bad effects of cloning?
What are the disadvantages of gene cloning?
- Expensive.
- Highly inefficient.
- Cloned animals tend to have more compromised immune function, higher rates of infection, tumour growth and other disorders.
- Clones tend to be larger in size, therefore causing them to have shortened lifespans.
What are some potential problems with cloning?
What Are the Risks of Cloning?
- Miscarriage. Most cases of cloning to date -- September 2010 -- have proven unsuccessful. ...
- Health Problems. Cloned embryos that survive pregnancy can be born with a variety of birth defects and other health problems.
- Abnormal Gene Expression. ...

What are the benefits and risks of therapeutic cloning?
Through the process of therapeutic cloning, it would become possible to replace damaged cells with healthy cells that are a direct match to the patient. This practice could prevent disease, limit the risks of future health issues, and control genetic or chromosomal issues that some patients may face.
What is the risk of reproducing by cloning?
Reproductive cloning also carries the risk of psychosocial harm, including violations of privacy and autonomy and the possibility of compromising the cloned child's right to an open future by creating enormous pressures to live up to expectations based on the life of the somatic cell donor.
What are 3 risks of cloning?
These include an increase in birth size and a variety of defects in vital organs, such as the liver, brain and heart. Other consequences include premature aging and problems with the immune system. Another potential problem centers on the relative age of the cloned cell's chromosomes.
What is a disadvantage of cloning?
Disadvantages of Cloning: Losing the diversity of genes. 2. It might be unethical and cause imbalance in the society. 3. Human cloning might pose the danger of human race extinction.
Does cloning cause infertility?
It has nothing to do with infertility ... no one is infertile with cloning, all right. It has nothing to do with couple, because you don't have to be a couple to do this. It's just a technique to make a genetic duplicate.
Why humans should not be cloned?
Moreover, most scientists believe that the process of cloning humans will result in even higher failure rates. Not only does the cloning process have a low success rate, the viable clone suffers increased risk of serious genetic malformation, cancer or shortened lifespan (Savulescu, 1999).
What are the negative effects of cloning to society?
Another health risk attributed to human cloning focuses on cell aging and potential birth abnormalities among successful births. Specifically, cases of increased risks of cancer, brain malfunction, kidney issues, and accelerated biological aging are rampant.
What is therapeutic cloning?
Therapeutic cloning is the process of using person's own stem cells to cure the disease. Though this technology is making its place in the biotech world but still it has many drawbacks...
What are the disadvantages of therapeutic cloning?
Most prominent disadvantage of therapeutic cloning is the use of embryos. Many critics claim that it is the death of a human if embryo is used to extract stem cells. They consider it murder and strictly oppose this act. Some believe that somatic cell nuclear transfer is also responsible for giving life to an embryo.
Why do we use eggs in therapeutic cloning?
Therapeutic cloning uses eggs to perform experiments on. But it is noted that many eggs are used during this process to get the required stem cell. If scientists start using a lot of eggs to get one stem cell, then where would they get all the eggs from? It is a big drawback of therapeutic cloning as well as it is also against the ethics to use eggs. It is believed that if therapeutic cloning is performed for a particular disease, scientists will have to use 1.5 billion eggs. If a woman agrees to donate an egg, she will have to pass through many painful processes and it will be costly too. She will never want her egg to be used in laboratory and scientists perform experiments on it.
How many eggs are used in cloning?
It is believed that if therapeutic cloning is performed for a particular disease, scientists will have to use 1.5 billion eggs. If a woman agrees to donate an egg, she will have to pass through many painful processes and it will be costly too.
Can stem cells cure diseases?
Though scientists are working hard to cure human diseases by using adult stem cells, but they are not getting the desired results like they got in the method of traditional cloning. Though in the beginning it was believed that therapeutic cloning will be helpful in curing the diseases, but as the application of adult stem cells is limited ...
Is cloning a human embryo beneficial?
Through this method a cloned human embryo can be created to use it in different experiments. Everything which is beneficial for humans it has somehow disadvantages as well. For example, if therapeutic cloning helps to make genetically modified nucleus to cure the damaged or diseased tissues, it also has some drawbacks which can also be considered.
Can stem cells be mutated?
Another possibility is that stem cells can be mutated due to which tumors can develop in person's body. When experiments performed on animals, some of them developed tumor in their body so scientists are afraid that same can happen in humans also. They are still performing experiments to make them 100% healthy and usable for people.
How long does it take for embryonic stem cells to form?
After 4-5 days, embryonic stem cells begin to form. These stem cells can then be harvested and used to create cultured stem cells that are genetically identical to the individual with the original somatic cell. Here are some of the pros and cons of therapeutic cloning to consider when evaluating this practice.
What is therapeutic cloning?
February 25, 2018 by Louise Gaille. Therapeutic cloning refers to the removal of a nucleus from almost any cell in an adult body. These are somatic cells and the nucleus contains genetic material. This genetic material can then be transferred to an unfertilized egg that has also had its nucleus removed. Once reconstituted, the egg begins to divide.
Why is therapeutic cloning important?
The process of therapeutic cloning could be directed so that these vital organs could be created. Not only would this process eliminate wait times, it would also reduce costs. Because the DNA from the “cloned” organ is the same as the individual, there would be little threat of organ rejection. 2.
How many people die from cloning every day?
Therapeutic cloning could eliminate lengthy treatment times. About 20 people die every day waiting for an organ. A new patient is added to the national transplant waiting list in the United States, on average, every 10 minutes.
Why are critical organs rare?
Critical organs are few and far between because of the need for a fatality, the ability to preserve the organ at the time of death, and the need for a direct match to the recipient. All of these concerns would go away if therapeutic cloning were to become an accepted and common practice within the medical community. 5.
How many eggs are needed for cloning?
The best estimates of need for therapeutic cloning place the number of needed eggs at over 1 million. In the United States, over the past 20 years, there have been an estimated 400,000 eggs placed into cold storage. That means the supply of eggs would need to double just to begin the process of curing disease.
What to do if playback doesn't begin?
If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
Why are cloned animals so large?
According to the FDA, one phenomenon seen in cloning is that cloned animals tend to be larger than normal at birth, with unusually large organs. Enlarged organs often function improperly, causing problems with circulation, breathing and other bodily functions, sometimes leading to early death.
Why do genes turn on and off?
Cloned cells, however, may lack the programming necessary to tell genes when to turn on and off. The result may be disorganized cell growth or inappropriate cell functioning, both of which can lead an organism to die.
How successful is cloning?
Most cases of cloning to date -- September 2010 -- have proven unsuccessful. Scientists have attempted to clone a variety of animals, and in almost all cases, the embryo has failed to develop properly or survive for more than a short period of time. The Genetic Science Learning Center estimates that the success rate of cloning ranges from only 0.1 percent to 3 percent. A cloned embryo, for example, faces the same challenges as a natural pregnancy plus others that are particular to cloning.
What happens when a cloned cell is not able to tell genes?
Cloned cells, however, may lack the programming necessary to tell genes when to turn on and off. The result may be disorganized cell growth or inappropriate cell functioning, both of which can lead an organism to die. Advertisement.
What is cloning in biology?
Scientist looking into a microscope. Image Credit: View Stock/View Stock/Getty Images. Cloning refers to various techniques of copying genetic information. Reproductive cloning, the most controversial type of cloning, creates copies of whole organisms. While the process of cloning results in two organisms that are genetically identical, ...
What is the success rate of cloning?
The Genetic Science Learning Center estimates that the success rate of cloning ranges from only 0.1 percent to 3 percent. A cloned embryo, for example, faces the same challenges as a natural pregnancy plus others that are particular to cloning. Advertisement.
How many calories are in kale pesto?
This amazing kale pesto is only 210 calories and anti-oxidant rich!
Why is cloning controversial?
However, the topics of cloning and gene editing further open up controversial discussions about how this work could create more divides in the society between the rich and the poor (Weintraub, 2019). For example, there is the possibility of babies whose genes have been selected or altered, also known as “designer babies.” If we give scientists the ultimate power to clone humans, what terrifying things would they do next? What will our future look like? How far are we willing to go for science?
What is the goal of eugenics?
Eugenics aim are to “breed out” diseases, “disabilities and so-called undesirable characteristics from the human population ” (“Eugenics — HISTORY”, 2019). The practice of cloning would not only violate a person’s right to individuality but it would also “reduce diversity in the human gene pool” (Savulescu, 1999 and Green, 1999).
What is the Fung Fellowship?
The Fung Fellowship is shaping a new generation of entrepreneurial leaders focused on transforming health and wellness.
What is therapeutic cloning?
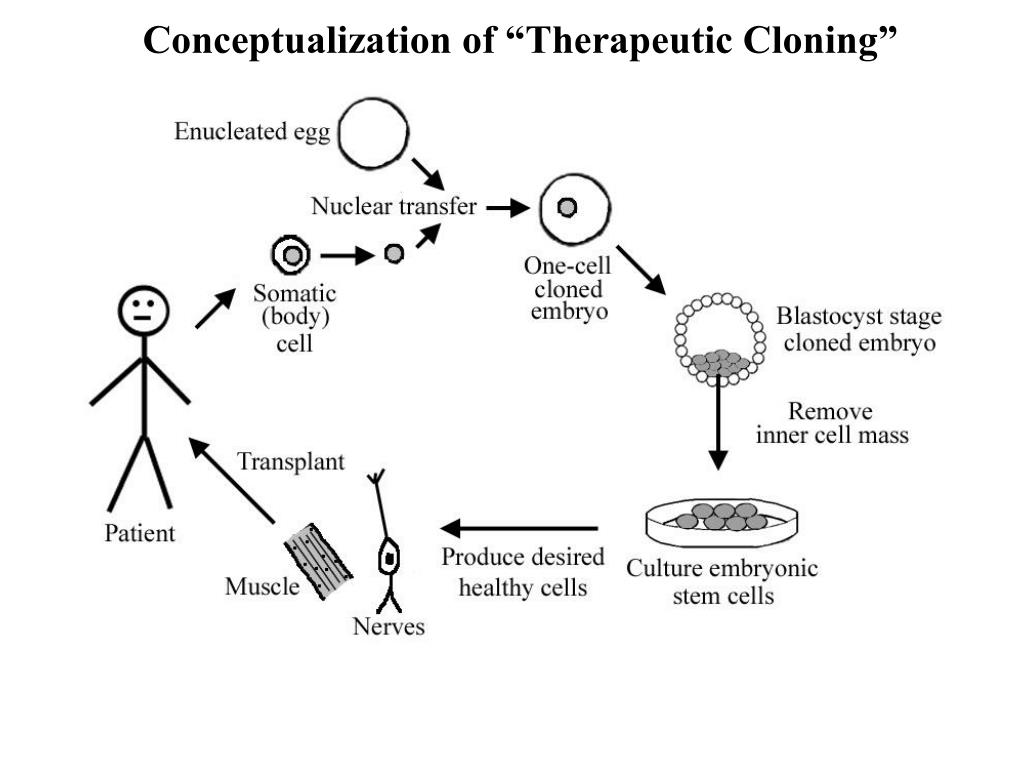
Therapeutic cloning is used to produce embryonic stem cells in order to replace or repair damaged tissues or organs (“Therapeutic Cloning”, 2019). The diagram below summarizes the process of reproductive cloning.
What is an op-ed in E295?
This op-ed is part of a series from E295: Communications for Engineering Leaders. In this course, Master of Engineering students were challenged to communicate a topic they found interesting to a broad audience of technical and non-technical readers.
Can humans be cloned?
After Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute near Edinburgh in Scotland successfully cloned Dolly the sheep from the udder cells of an ewe in 1996, it became possible to envision having hundreds of cloned human babies in the very near future. Although this technology and the ongoing research to clone mammals (and thus humans) is at work in order to potentially cure certain diseases and give infertile couples the opportunity to have children, the topic of cloning humans has raised a lot of controversy as well as scientific, ethical and moral concerns. Just because we can does not mean that we should. Human beings should not be cloned for several reasons that are going to be further discussed in this op-ed: cloning is a risky, imperfect procedure, it does not create an exact copy of an individual, and it poses ethical concerns by using human beings as a means to an end, opening up possibilities for abuse and allowing eugenic selection.
Does cloning a sheep have a low success rate?
Not only does the cloning process have a low success rate , the viable clone suffers increased risk of serious genetic malformation, cancer or shortened lifespan (Savulescu, 1999). The likelihood of pregnancy losses and abnormal births are very high, and this was observed by Wilmut and his team after cloning Dolly the sheep.
Why is therapeutic cloning so controversial?
Therapeutic cloning is so controversial, because it is tied to ethical issues that are connected to life and death. To get a better understanding of therapeutic cloning, you must be more informed about the pros and cons of this medical advancement.
What is therapeutic cloning?
Therapeutic cloning is replicating cells and tissue to use for medical purposes. This type of cloning is very controversial and individuals feel strongly on both sides of this issue. The medical use of replicated cells and body tissue are wide ranging and include organ growth and scientific research. Therapeutic cloning is so controversial, ...
Why are embryos used for cloning?
Embryos are often used for therapeutic cloning, because they have the ability to transform and grow into any type of organ and cell. This offers incredible lifesaving possibilities, but it also calls into question a matter of ethics.
What to do if playback doesn't begin?
If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
Is therapeutic cloning successful?
Many scientific researches against therapeutic cloning suggest that it is not very successful. Many of the cells that are cloned develop very serious defects. This is seen to defeat the purpose of growing new cells. If the cells simply become defective and die there is no real benefit gained.
Can cloning be beneficial?
Many of the cells that are cloned develop very serious defects. This is seen to defeat the purpose of growing new cells. If the cells simply become defective and die there is no real benefit gained. Although some are against therapeutic cloning for many different reasons, there are some benefits that can be gained.
Does cloning reduce rejection?
Patients that receive organ transplants are often faced with high percentages of rejection. However. Therapeutic cloning reduces the risk of rejection due to the fact that the new organs are created using the patient’s own cells.
What sort of cloning research is going on at NHGRI?
Gene cloning is the most common type of cloning done by researchers at NHGRI. NHGRI researchers have not cloned any mammals and NHGRI does not clone humans.
What are the potential drawbacks of cloning animals?
For instance, Dolly was the only clone to be born live out of a total of 277 cloned embryos. This very low efficiency, combined with safety concerns, presents a serious obstacle to the application of reproductive cloning.
What is therapeutic cloning?
Therapeutic cloning involves creating a cloned embryo for the sole purpose of producing embryonic stem cells with the same DNA as the donor cell. These stem cells can be used in experiments aimed at understanding disease and developing new treatments for disease. To date, there is no evidence that human embryos have been produced for therapeutic cloning.
What are the potential applications of therapeutic cloning?
Researchers hope to use embryonic stem cells, which have the unique ability to generate virtually all types of cells in an organism, to grow healthy tissues in the laboratory that can be used replace injured or diseased tissues. In addition, it may be possible to learn more about the molecular causes of disease by studying embryonic stem cell lines from cloned embryos derived from the cells of animals or humans with different diseases. Finally, differentiated tissues derived from ES cells are excellent tools to test new therapeutic drugs.
What are some of the ethical issues related to cloning?
However, both reproductive and therapeutic cloning raise important ethical issues, especially as related to the potential use of these techniques in humans.
Do clones ever occur naturally?
Yes. In nature, some plants and single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, produce genetically identical offspring through a process called asexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction, a new individual is generated from a copy of a single cell from the parent organism.
How are genes cloned?
The procedure consists of inserting a gene from one organism, often referred to as "foreign DNA," into the genetic material of a carrier called a vector. Examples of vectors include bacteria, yeast cells, viruses or plasmids, which are small DNA circles carried by bacteria. After the gene is inserted, the vector is placed in laboratory conditions that prompt it to multiply, resulting in the gene being copied many times over.