
What are the 5 components of the cell membrane?
Cell Membrane Structure
- Phospholipids. Phospholipids are referred to as glycerophospholipids, these phospholipids are part of the cell membrane of living beings as well as a group of lipid compounds; i.e. ...
- Protein. This protein itself is derived from the Greek word “Protos” which means “most importantly”. ...
- Glycolipids and glycoproteins. ...
- Oligosaccharides. ...
- Cholesterol. ...
What are the structural components of the cell membrane?
There are four main types of phospholipids that make up most of the cell membrane in animal cells:
- Phosphatidylcholine
- Phosphatidylethanolamine
- Phosphatidylserine
- Sphingomyelin
What are three characteristics of a cell membrane?
The main functions of the cell membrane are:
- Controls movement of fluids, ions, and other substances, such as organic molecules, in and out of the cells and organelles.
- Facilitate cell adhesion
- Regulate ion conductivity
- Cell signaling
- Attach to glycoproteins and an intracellular network of protein fibers, collectively called the cytoskeleton
What are the main functions of the cell membrane?
- protects the cell by acting as a barrier.
- regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell.
- receives chemical messengers from other cell.
- acts as a receptor.
- cell mobility, secretions, and absorptions of substances.

What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
What are the parts of the cell membrane?
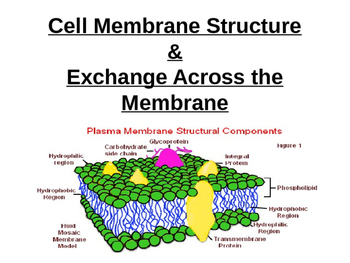
Following are the various parts of the cell membrane. Integral Membrane Proteins: These are structures present on the inside, outside, and also throughout the cell membrane. Fluorescence and electron microscopy can be used in viewing these proteins. These proteins are present on the entire/whole surface of the cell membrane.
What is the membrane of a cell?
Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell (in animals). In plant cells, the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm. This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
How are cell membranes made?
Structure. The cell membrane is made up of two layers that are composed of phospholipids. The bilayer is formed by the arrangement of phospholipids in a manner that their head regions (which are hydrophilic) face external environment as well as the internal cytosolic environment. The (hydrophobic) tails of these phospholipids face each other.
What are some examples of proteins that are attached to the cell membrane?
Examples of these structures include the cadherins, integrins, clathrin-coated pits, desmosomes, caveoles, etc. These proteins are attached/bound to the surface of the membrane by means of hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions.
What is the characteristic of the organelle?
The characteristic feature of this organelle is that it allows only certain substances to pass through. Most of the research carried out for the purpose of studying cell membrane structure makes use of red blood cells (RBCs), as the absence of internal membranes and nuclei in RBCs results into the isolation process being carried out quite easily.
Why is the plasma membrane important?
The plasma membrane is an important part of a cell, as it provides it with protection and also helps in maintaining a proper shape. The cell membrane structure and functions presented in the article should help in knowing more about ...
Which structure is used to anchor proteins to the cell membrane?
The framework or cytoskeleton proves to be useful in the processes of organelles like cilia. Cytoskeleton also helps in anchoring the membrane proteins to the cell membrane. Composition of Cell Membrane:
Cell Membrane
A cell membrane is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds and encloses a cell’s cytoplasm. The membrane also provides a cell structure and allows it to join to neighboring cells to form tissues. In certain animals, the cell membrane also acts as a basis of attachment for the cytoskeleton, whereas in others, it functions as the cell wall.
Structure of Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is composed of two phospholipid-based layers. The bilayer is generated by arranging phospholipids such that their head regions (which are hydrophilic) face both the exterior and internal cytosolic environments. These phospholipids’ (hydrophobic) tails are facing each other.
Functions of Cell Membrane
A cell membrane shields the cell’s structures. Cell membranes are semipermeable, which means that only specific items may flow through them. Cell membranes also form and sustain the cell’s structure.
Chemical composition of the cell membrane
It has a heterogeneous chemical composition that varies according to the type of cell . Anyway and in general it is composed of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Cell membrane structure
Scientists have been based on a model called “ model of the fluid mosaic ” that serves for their study and physiology of the membrane. This model was proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 972 and is made up of 3 layers, two external lines and two internal ones. In the middle of both is the lighter layer called the fluid mosaic pattern.
Attraction of molecules
The attractive force between the molecules allows them to slide from one side to the other.
Cell membrane wateriness
Prior to the fluid mosaic model , the membrane was considered to be a solid body , but later it was shown that it behaves like a liquid .
Selective permeability of the cell membrane
The cell membrane is characterized by being semi-permeable . In other words, it allows the membrane to select which molecules must enter and which must exit.
Processes carried out by the cell membrane
If endocytosis captures particles then the process is known as phagocytosis.
Cell membrane asymmetry
Another characteristic of the plasma membrane is that it has an asymmetric structure, since the composition of each layer that forms the cell membrane is different from one another. On the other hand, proteins also vary if they are found in one layer or another. This means that the functions of the layers are different.
What Is a Cell Membrane?
A cell membrane is a thin flexible lipid-based layer situated at the far exterior of cells. The cell membrane is the barrier that separates a cell from its outside environment or from other cells. Its composition makes it semipermeable. It is also called the plasma membrane.
Structure of a Cell Membrane
There is an important cell membrane structure to accomplish its functions and purposes. It is flexible and moveable. The cell membrane surrounds the entire exterior of the cell. As we discuss the specific parts of the cell membrane refer to the cell membrane diagram shown in figure 1.
What makes up the cell membrane?
What makes up the cell membrane? The basic structure of the cell membrane includes a two layers of phospholipids, called the phospholipid bilayer. The phospholipid bilayer also has additional macromolecules that help the membrane do its job. What is the structure of the cell membrane? The structure of the cell membrane can be described by the fluid mosaic model. The fluid mosaic model explains that the components of the cell membrane are fluid and can drift laterally in the bilayer. It also explains how the membrane is flexible and able to move with the cell. The fluid mosaic model also describes how the cell membrane is a mosaic, made of many different macromolecules including:
What is a Cell Membrane?
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that separates the cell from its environment and regulates what enters and leaves the cell, called selective permeability. The cell membrane is important for creating a flexible, semi-permeable barrier around the cell. This allows the cell to create stable, internal conditions that are different from a changing environment. The cell membrane is made of two layers of phospholipids and also includes proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol. Forming a barrier is the main function of the cell membrane, but it also has additional functions including:
What is the role of carbohydrates in the cell membrane?
Carbohydrates also play an important role in helping cells attach to the extracellular matrix in cellular adhesion. The collection of carbohydrates on the outside of the cell is called the glycocalyx. In addition to cell adhesion and cell recognition the glycocalyx also helps to cushion the plasma membrane.
What are the two types of proteins in the cell membrane?
There are two types of proteins in the cell membrane: integral and peripheral proteins. Integral proteins span the cell membrane and exist both outside and in it. These proteins have a hydrophobic core that allows them to interact with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids. Peripheral proteins are located on the outside of the cell membrane. These proteins are hydrophilic and attach to the phospholipid heads.
What is the amphipathic structure of a phospholipid?
Phospholipids are a type of amphipathic lipid that make up the cell membrane. Phospholipids have a hydrophobic tail made of two fatty acid chains and a hydrophilic head made of a phosphate group. The head and tail are connected with a glycerol molecule. Because phospholipids have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts, they are called amphipathic. The amphipathic nature of phospholipids contributes to their arrangement in a bilayer in the membrane.
Why is the cell membrane important?
The cell membrane is also important for cell movement and adhesion to the extracellular matrix and other cells. Integral proteins are embedded in the membrane that bind to both internal components of the cell, such as the cytoskeleton, and to external components like the extracellular matrix. These connections can be remodeled as cells need to grow, divide and move throughout the body.
What is the role of the cell membrane in cell signaling?
The cell membrane is also crucial for cell signaling and acts like a transducer, converting chemical signals in the environment to changes inside the cell. Signaling molecules outside the cell bind to proteins which cause changes in protein activation inside the cell. This can lead to changes in cell behavior and trigger protein synthesis. For example, growth hormone is produced during times of growth and repair in the body. It binds to receptors on the outside of the cell which cause changes in signal transduction. These signaling systems ultimately create changes in gene transcription which promote cell growth and division.
What is the cell membrane?
Definition. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. a 3D diagram of the cell membrane.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Function of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane gives the cell its structure and regulates the materials that enter and leave the cell. It is a selectively permeable barrier, meaning it allows some substances to cross, but not others. Like a drawbridge intended to protect a castle and keep out enemies, the cell membrane only allows certain ...
What is the technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane?
The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. Structure of the cell membrane and its associated components.
What is the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic phospholipids?
When in water or an aqueous solution (including inside the body) the hydrophobic heads of phospholipids will orient themselves to be on the inside, as far away from the water as possible. In contrast, the hydrophilic heads will be on the outside, making contact with the water. The result is that a double layer of phospholipids is formed, with the hydrophobic heads clustering together in the center, and the hydrophilic tails forming the outside of the structure. The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer.
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid Bilayer. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are lipid molecules made up of a phosphate group head and two fatty acid tails. Importantly, the properties of phospholipid molecules allow them to spontaneously form a double-layered membrane. The phosphate group head of a phospholipid is hydrophilic, ...
How does the cell control the rate of diffusion of substances?
Another way the cell membrane can bring molecules into the cytoplasm is through endocytosis. The reverse process, where the cell delivers contents outside the membrane barrier, is called exocytosis. Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) ...
What is the process of endocytosis?
Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) and pinocytosis (“cell drinking”). During these processes, the cell membrane forms a depression, surrounding the particle that it is engulfing. It then “pinches off” to form a small sphere of membrane called a vesicle that contains the molecule and transports it to wherever it will be used in ...
Plasma Membrane Structure
The accepted and currently used model for representing the structure of the plasma membrane is called the fluid mosaic model. It was first proposed by S. J. Singer and G. L. Nicolson in the year 1972.
Plasma Membrane Components
The cell membrane is composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrate groups that get attached to some of the lipids and proteins. The lipids include phospholipids and cholesterol.
Cell Membrane Function
Cell membranes act as a barrier between two different regions and gatekeepers. They are semi-permeable in nature, which means that few molecules are allowed to diffuse across the lipid bilayer. Small hydrophobic molecules and gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide can cross the membranes rapidly.
Diversity of Cell Membrane
In contrast to the single-celled or prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells along with plasma membrane, also have intracellular membranes that can surround various organelles. In these cells, the plasma membrane is part of an extensive endomembrane system. This system includes the (ER) endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear membrane, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane (Plasma membrane) The outer thin membrane or the layer of the living cell is known as the cell membrane. It is also known as the plasma membrane in animal cells. In the plant cells, it is known as plasmalemma. The term cell membrane was given by Nageli and Cramer (1885) for the membrane covering of the protoplast.
How many types of cell membranes are there?
There are two types of cell membrane. They are:
What are the three types of lipids in the cell membrane?
Most of the cell membrane is composed of 40-50 % protein and 50-60 % lipids. Membrane lipids are of three types: a) Phospholipids b) Glycolipids c) Steroids. In the different membrane, the proportion of the lipid varies:
Which model suggests that the cell membrane is a solid and stable structure?
It was proposed by James Danielli and Hugh Davsan in the year 1935. This model suggests the cell membrane as the solid and the stable structure. Four molecular layers are present in it i.e. two phospholipids and two protein layers. It consists of the phospholipid.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Cell membrane helps to maintain homeostasis. It provides protection to all the internal organelles of the cell.
What is the interaction between lipids and proteins?
Between the lipids and the proteins, there is interaction which results in the fluidity of the membrane.
Which structure is present in the amoeba?
In the amoeba, pseudopodia are present for locomotion which is the modified structure of the cell membrane.
Cell Membrane
Structure of Cell Membrane
- The cell membrane is composed of two phospholipid-based layers. The bilayer is generated by arranging phospholipids such that their head regions (which are hydrophilic) face both the exterior and internal cytosolic environments. These phospholipids’ (hydrophobic) tails are facing each other. Electrostatic, van der Waals, non-covalent interactions, ...
Functions of Cell Membrane
- A cell membrane shields the cell’s structures. Cell membranes are semipermeable, which means that only specific items may flow through them. Cell membranes also form and sustain the cell’s structure. 1. To keep the cell’s physical integrity that is, to physically surround the contents of the cell and to govern the passage of particles, such as ions or molecules, into and out of the cell. 2…
Conceptual Questions
- Question 1: Write any three major functions of a cell wall. Answer: Question 2: Where do chromosomes reside in a cell? Explain what they do? Answer : Question 3: What is the cell membrane’s function? Answer: Question 4: Which chemical is found in both the cell membrane and space? Answer: Question 5: What do you mean by cytoplasm? Answer: Question 6: What is t…