
The symptoms of hepatitis in dogs are the following:
- Excessive thirst
- Jaundice, that is, yellowing of the eyes and mucous membranes
- Blood in the mucous membranes
- Abdominal pain that can lead to immobility
- Fever
- Seizures due to liver failure
- Loss of appetite
- Increase in nose and eye secretion
- Vomiting
- Subcutaneous edema
- Watery discharge from eyes and nose.
- Congestion.
- Slight fever.
- Deficiency of blood clotting.
- Blindness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Thirst.
- Enlarged tonsils.
What causes acute hepatitis in dogs?
Acute hepatitis in dogs is often caused by a viral infection called canine adenovirus 1. This viral organism infects other different organs like the spleen, kidneys, blood vessel walls, but causes the most damage to the liver. This is a contagious disease in dogs that are usually spread through bodily discharges like saliva, feces, or urine.
What are the symptoms of canine liver cancer?
The following symptoms are typically only seen once dog liver cancer is in the advanced stages:
- Lethargy
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite ( anorexia)
- Paleness (anemia) or yellowness ( jaundice) of the skin
- Weight loss
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Swollen abdomen, especially uneven swelling
Does canine hepatitis affect humans?
The hepatitis B virus is prevalent in humans and affects animals alike, but canine hepatitis is not caused in humans. In fact, the HBV virus is the leading cause of hepatitis B. CAV1 is responsible for chanical hepatitis caused by Adenoviruses 1. There is no human transmission of canine hepatitis, however two or more dogs can carry the virus.
What are the advanced symptoms of canine distemper?
Signs associated with dogs infected with canine distemper
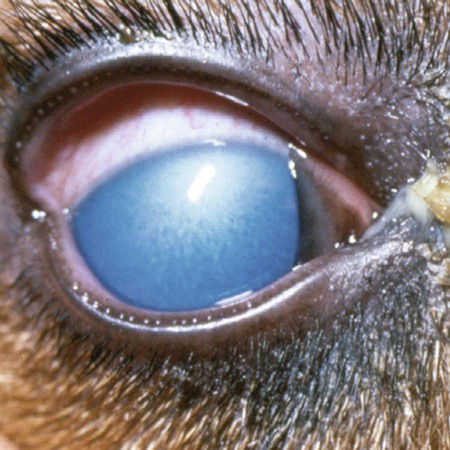
- Anterior uveitis (inflammation of the front chamber of the eye; may cause the cornea to appear cloudy and/or cause changes in the appearance of the iris)
- Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS = dry eye)
- Optic neuritis (inflammation of the optic nerve-may cause sudden blindness)
- Retinal degeneration or separation (may cause vision impairment)
Is canine hepatitis curable?
Though some cases of acute hepatitis can be cured, chronic hepatitis cannot be cured. Dogs with chronic hepatitis will need monitoring and treatment so they can enjoy good quality of life and longevity, with minimal clinical signs.
What is the treatment for hepatitis in dogs?
Hospitalization, intravenous fluid therapy, and supportive care may be necessary in severe cases. Immunosuppressive or anti-inflammatory medications are most commonly prescribed. Dietary modifications may be needed in some patients.
What causes a dog to get hepatitis?
Infectious Canine Hepatitis Hepatitis C in dogs is an acute contagious disease in dogs caused by the canine adenovirus 1. The virus targets the infected pet's liver, lungs, kidneys, spleen, the lining of blood vessels, and occasionally other organs.
Is canine hepatitis contagious to humans?
Infectious Canine Hepatitis (ICH) is a type of hepatitis caused by a virus, specifically the canine adenovirus type 1 (or CAV-1). The CAV-1 is not contagious to humans or cats. Thanks to the success of vaccinations, it's a rather rare disease in the U.S. now.
How long do dogs live with hepatitis?
Prognosis. The prognosis for dogs with chronic hepatitis varies. Median survival durations of 18.3 to 36.4 months have been reported. However, patients with hypoalbuminemia, hypoglycemia, prolonged clotting times, bridging fibrosis, and ascites have shorter survival times.
How long does dog hepatitis last?
6 monthsHepatitis in Dogs - Causes Dogs that are recovered from the condition will shed the virus in their urine for at least 6 months. In some cases, dogs can develop severe chronic hepatitis as a result of damage caused by the accumulation of copper in the liver's cells.
Can a vaccinated dog get hepatitis?
YES! The canine version of the illness is called infectious canine hepatitis, which is caused by the canine adenovirus 1. If your dog comes into contact with saliva, urine, or feces of an infected dog, they can contract the virus and become ill.
Can dogs be vaccinated against hepatitis?
Regular vaccination can protect your dog from infectious diseases such as canine parvovirus, canine distemper, canine hepatitis, leptospirosis, canine parainfluenza and rabies.
How do you know when to put a dog down with liver failure?
As a general rule, I suggest euthanasia to my clients if their dog in liver failure stops eating for more than 48 hours. Other signs of poor quality of life include an inability to sleep well, repeated seizures, constant pain, soiling themselves and not wanting to interact with the family.
What do you feed a dog with chronic hepatitis?
Good proteins to feed for liver disease are eggs for the most bioavailable protein and choline content, poultry and a little fish such as sardines, salmon and cod. Proteins to reduce or avoid would be red meats high in phosphorus.
Does liver disease in dogs cause panting?
Symptoms of Liver Disease in Dogs Dogs often have other signs not specific to the liver. These can include changes in behavior such as sleeping more than usual, decreased activity, panting, weakness, or increased drinking and urination.
What animals carry hepatitis?
Spontaneous hepatitis A infection has been reported to occur in captive non-human primates including the great apes (chimpanzee) as well as Old World (cynomolgus, African vervet, stump-tailed) and New World (aotus) monkeys.
Can a vaccinated dog get hepatitis?
YES! The canine version of the illness is called infectious canine hepatitis, which is caused by the canine adenovirus 1. If your dog comes into contact with saliva, urine, or feces of an infected dog, they can contract the virus and become ill.
Is there a vaccine for hepatitis in dogs?
NOBIVAC® CANINE 1-DAPPv This product has been shown to be effective for vaccination of healthy dogs 6 weeks of age or older against canine distemper virus, canine adenovirus type 1 (hepatitis), canine adenovirus type 2 (respiratory disease), canine parainfluenza virus and canine parvovirus.
Can dogs survive acute liver failure?
Because the liver is an organ that has the ability to regenerate, pets can sometimes return to perfectly normal lives even after near-death acute liver failure experiences.
How do you know when to put a dog down with liver failure?
As a general rule, I suggest euthanasia to my clients if their dog in liver failure stops eating for more than 48 hours. Other signs of poor quality of life include an inability to sleep well, repeated seizures, constant pain, soiling themselves and not wanting to interact with the family.