What are the three membranes of the meninges?
The meninges are composed of three membrane layers known as the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater . Each layer of the meninges serves a vital role in the proper maintenance and function of the central nervous system.
What is the outer layer of the meninges?
It is composed of tough, fibrous connective tissue. Dura mater that surrounds the brain consists of two layers. The outer layer is called the periosteal layer and the inner layer is the meningeal layer.
How does the arachnoid membrane get its name?
The arachnoid membrane loosely covers the brain and spinal cord and gets its name from its web-like appearance. The arachnoid mater is connected to the pia mater through tiny fibrous extensions that span the subarachnoid space between the two layers.
What is the meninges?
Updated July 02, 2019. The meninges is a layered unit of membranous connective tissue that covers the brain and spinal cord. These coverings encase central nervous system structures so that they are not in direct contact with the bones of the spinal column or skull.
Which layer of the brain connects the dura mater to the skull?
The outer periosteal layer firmly connects the dura mater to the skull and covers the meningeal layer. The meningeal layer is considered the actual dura mater. Located between these two layers are channels called dural venous sinuses.
Which layer of the spinal column is composed of the meningeal layer and does not contain a perio
The dura mater of the spinal column is composed of the meningeal layer and does not contain a periosteal layer. Arachnoid Mater: This middle layer of the meninges connects the dura mater and pia mater. The arachnoid membrane loosely covers the brain and spinal cord and gets its name from its web-like appearance.
What is the function of the meninges?
Evelyn Bailey. The meninges functions primarily to protect and support the central nervous system (CNS). It connects the brain and spinal cord to the skull and spinal canal. The meninges forms a protective barrier that safeguards the sensitive organs of the CNS against trauma. It also contains an ample supply of blood vessels ...
What happens if the meninges is damaged?
For example, blood (e.g. due to damage caused by trauma) can collect in spaces between the layers of the meninges, creating a hematoma that can put pressure on the brain as it expands. Such an infection can cause meningitis, which is characterized by an inflammation of the meninges.
Where is the dura located?
The dura mater is the top layer of the meninges, lying beneath the bone tissue. This material at times opens into sinus cavities (spaces) located around the skull.
What is a Meninge?
The meninges is a layered unit of membranous connective tissue that covers the brain and spinal cord. These coverings encase central nervous system structures so that they are not in direct contact with the bones of the spinal column or skull.
What is dura mater made of?
Dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. The other two meningeal layers are the arachnoid mater and the pia mater.
What are the meninges layers?
The meninges refer to the membranous coverings of the brain and spinal cord. There are three layers of meninges, known as the dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. These coverings have two major functions: Provide a supportive framework for the cerebral and cranial vasculature.
Where is CSF made?
CSF is produced mainly by a structure called the choroid plexus in the lateral, third and fourth ventricles. CSF flows from the lateral ventricle to the third ventricle through the interventricular foramen (also called the foramen of Monro).
How do the meninges protect the brain?
The brain is protected from injury by the skull, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid and the blood-brain barrier. The function of the meninges is to cover and protect the brain itself. It encloses and protects the vessels that supply the brain and contains CSF between the pia mater and arachnoid maters.
What are the three layers of the meninges?
There are three layers of meninges, called the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
What is the master gland of the pituitary gland?
Another fact often overlooked: the tentorium covers the sella turcica (an indentation of the sphenoid bone), which houses the pituitary gland. This gland, called the master gland, controls all hormonal actions in the body. Trauma to the head may distort this part of the tentorium and thus exert pressure on the pituitary gland, potentially resulting in a variety of hormonal disturbances, including menstrual irregularities and associated pain/discomfort.
What is the dura of the cerebellum?
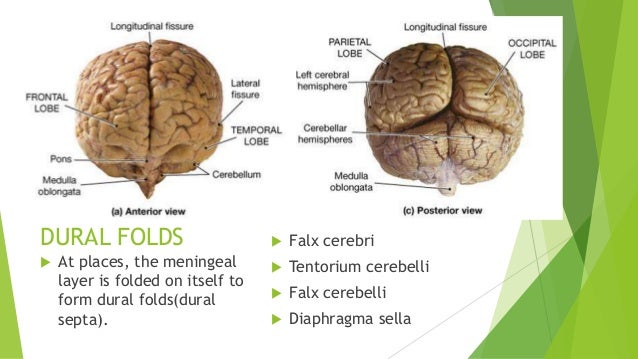
an upper one (two rooms) which houses the two hemispheres, and a lower one, which contains the cerebellum. The two rooms upstairs are created as the dura separates the cerebral cortex into the two hemispheres. This portion of the dura is called the FALX CEREBRI. The dura also supports the two hemispheres by forming a tent-like structure , the TENTORIUM, above the cerebellum. Thus, the dura separates the cerebral cortex from the cerebellum. Moreover, the dura partially divides the cerebellum into two hemispheres. This structure is the FALX CEREBELLI. A pretty complicated but elegant affair.
What fluid is in the subarachnoid space?
The cerebrospinal fluid, which buffers, nourishes, and detoxifies the brain and spinal cord, flows through the subarachnoid space, between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. The smooth flow of this fluid, or lack thereof, can dramatically affect one’s health.
Dura Mater
The dura mater, which translates to "hard matter," is the outermost meningeal layer. It resides just below the bone composing the skull and is superficial to the arachnoid mater. The dura mater is thick and tough, appearing and feeling very similar to leather. The main dura mater function is to provide protection to the brain.
Arachnoid Mater
The arachnoid mater is just below the dura mater. The term "arachnoid" comes from the word "arachnid," meaning "spider." This name is in reference to the appearance of the arachnoid mater, which resembles the stringy, white fibers of a spider web. The most important function of the arachnoid mater is to house the arachnoid space.
Pia Mater
The pia mater, which translates to "tender matter," is the thinnest and deepest meninge of the brain. This thin, clear layer adheres to the surface of the brain and follows the natural hills and valleys (called gyri and hillocks) of the surface of the brain. The pia mater functions to contain cerebrospinal fluid within its proper pathway.
Spinal Meninges
The meninges are also found in the spinal cord. Each layer is observed in the cross section.
Various Spaces in Meninges
The individual spaces that occur within the meningeal layers were described above as relative to their position. Here is a brief overview of each type of space:
How many meninges are there in fish?
In fish, there is a single membrane known as the primitive meninx. Amphibians, and reptiles have two meninges, and birds and mammals have three. In the early 1900s, Giuseppe Sterzi, an Italian anatomist, carried out comparative studies on the meninges from the lancelet to the human.
What is the function of the meninges?
The primary function of the meninges is to protect the central nervous system.
What is the difference between the dura mater and the pia mater?
The dura mater is attached to the skull, whereas in the spinal cord, the dura mater is separated from the vertebrae by a space called the epidural space, which contains fat and blood vessels. The arachnoid is attached to the dura mater , while the pia mater is attached to the central nervous system tissue.
What is the arachnoid mater?
Arachnoid mater. Main article: Arachnoid mater. Diagram of section of top of brain showing the meninges and subarachnoid space. The middle element of the meninges is the arachnoid mater, or arachnoid membrane, so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. It cushions the central nervous system.
What is the name of the arachnoid that is connected to the pia?
Because the arachnoid is connected to the pia by cob-web like strands, it is structurally continuous with the pia, hence the name pia-arachnoid or leptomeninges.
What are the conditions that affect the meninges?
Other medical conditions that affect the meninges include meningitis (usually from a fungal, bacterial, or viral infection) and meningiomas that arise from the meninges, or from meningeal carcinomatoses ( tumors) that form elsewhere in the body and met astasize to the meninges.
What is the name of the membrane that adheres to the surface of the brain and spinal cord?
Pia mater. Main article: Pia mater. The pia mater ( Latin: tender mother) is a very delicate membrane. It is the meningeal envelope that firmly adheres to the surface of the brain and spinal cord, following all of the brain's contours (the gyri and sulci ).