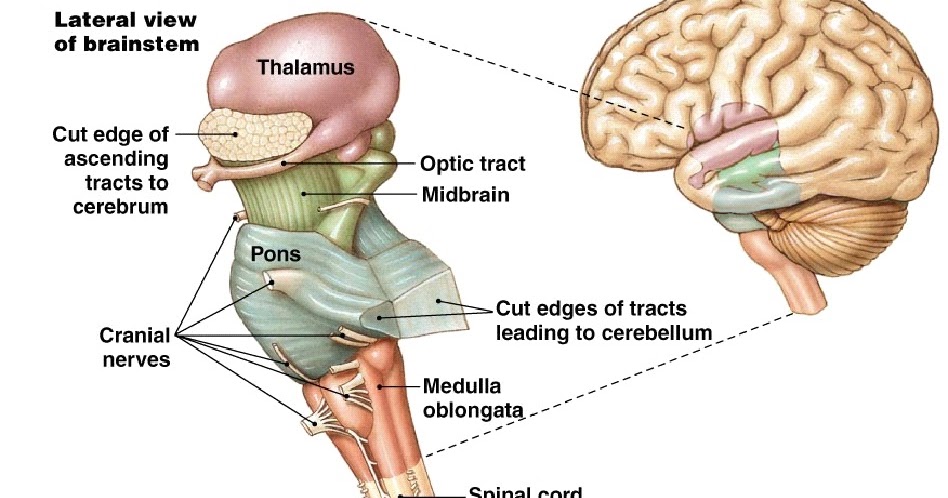
The Brain Stem
- Functions of the Brain Stem. The brainstem regulates vital cardiac and respiratory functions and acts as a vehicle for sensory information.
- Medulla Oblongata. The medulla oblongata controls autonomic functions and connects the higher levels of the brain to the spinal cord.
- Pons. ...
- Midbrain. ...
- Reticular Formation. ...
See more
What is the function of the brainstem?
Your brainstem sends messages between your brain and other parts of your body. Your brainstem helps coordinate the messages that regulate :
What is the brainstem?
Your brainstem is the bottom, stalklike portion of your brain. It connects your brain to your spinal cord. Your brainstem sends messages to the rest of your body to regulate balance, breathing, heart rate and more. Sudden injuries, and brain or heart conditions may affect how your brainstem works.
What is the stalk of the brain?
The brainstem is the stalklike part of your brain that connects your brain to your spinal cord (column of nerve tissue that runs down your spine). It sits toward the bottom of your brain and is part of your central nervous system.
How many cranial nerves are in the brain?
Your brainstem also contains 10 of the 12 cranial nerves (nerves that start in your brain). These nerves control your facial movements, sensations and taste.
How many parts does the brain have?
Your brain has three parts that work together. Each part does specific jobs to help you process information, move and function.
Where is the brain stem located?
Your brainstem is near the bottom of your brain, at the back of your skull. It looks like a flower stalk or stem. It connects your brain to your spinal cord.
Which part of the brain is responsible for regulating eye movements?
Midbrain: The top part of the brainstem is crucial for regulating eye movements.
What are the three structures that make up the brain stem?
There are three structures that make up the brain stem. They include the midbrain, pons, and medulla. Each of these structures have distinct and essential functions to maintain survival, such as breathing, heart rate, and other non-voluntary functions. Below are detailed descriptions of the aforementioned components.
What is the brain stem?
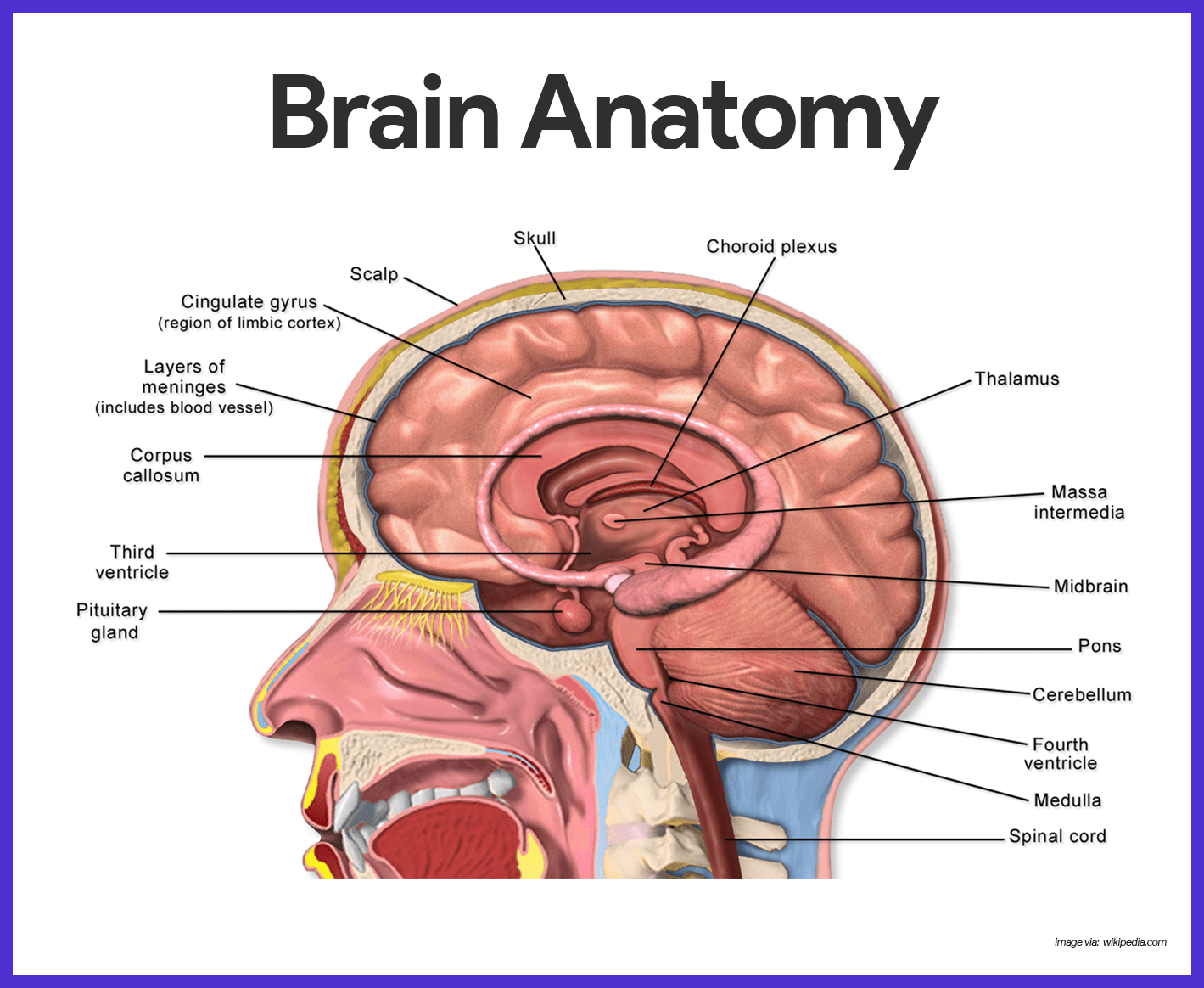
Thus, the brain stem is the base of the whole brain. It consists of three essential components: the midbrain, pons, and medulla (also known as the medulla oblongata). The brain stem is responsible for several vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, sleep, and even consciousness.
What is the upper part of the brain?
The midbrain is the upper-most structure of the brain stem, and it is also the widest component. Cerebral peduncles make up the anterior part of the midbrain , connecting the brainstem to the thalamus and other important brain regions. The brain stem is further sectioned into the tectum, Latin for "roof" and the tegmentum, Latin for "covering". Four major bumps can be seen on the tectum, and they represent the superior and inferior colliculi, responsible for visual and auditory processing, respectively.
What is the medulla?
The medulla, also known as the medulla oblongata, is the narrowest and lowest structure within the brain stem. It contains two key divisions: the basilar portion, which contains the pyramids and olives, and the medullary tegmentum, which contains four cranial nerve nuclei and other important structures. The medulla is also where the spinal cord connects to the brain stem, and so it has important roles in transmitting signals between the two structures pertaining to heartbeat, respiration, and other vital functions.
What is the function of the pons?
The pons is responsible for automatic functions like controlling breathing in addition to sleep cycles. Furthermore, several important cranial nerves, or nerves that control movements of the head and neck, are found in the pons. Some are listed below.
Which nerve is responsible for sensation and movements associated with the head and neck?
Housing the cranial nerve nuclei, which are responsible for sensation and movements associated with the head and neck. Examples are listed above, whereby eight cranial nerves are divided between the pons and medulla.
Which part of the brain controls reflexes?
Several important reflexes are controlled by the medulla, such as vomiting, coughing, swallowing, and sneezing. For the aforementioned reasons, the medulla is also considered the most important segment of the brain stem due to it being necessary for vital functions.
Why is the brainstem important?
All of these brainstem functions are enabled because of its unique anatomy ; since the brainstem houses cranial nerve nuclei and is a passageway for many important neural pathways.
What are the parts of the brain?
The brainstem is widest at its proximal end and becomes narrower toward the distal end. There are three parts of the brainstem: 1 the medulla oblongata is the narrowest and most distal part 2 the pons lies anteriorly and in the middle segment of the brainstem 3 and the midbrain is the widest and most superior segment.
What is the narrowest part of the brain?
The medulla ob longata or medulla is the narrowest and most caudal part of the brainstem. It is a funnel-like structure that extends from the decussation of the great pyramids, passes through the foramen magnum (which is the largest of all the foramina and fissures of the skull ), to the inferior pontine sulcus ( pontomedullary groove ). As the medulla continues upward in the posterior cranial fossa, it terminates at the inferior pontine sulcus (anteriorly) and the medullary striae of the fourth ventricle (posteriorly).
What is the division of the midbrain?
Most textbooks divide the midbrain into tectum and tegmentum, but the division is actually extended caudally into other brainstem segments. The tectum (Latin word for roof) and tegmentum (Latin word for covering) are used in relation to the developing central cavity of the neural tube .
Where does the brainstem begin?
The brainstem begins at the level of the cerebral peduncles (anteriorly) and the corpora quadrigemina or quadrigeminal plate (posteriorly) or tectal plate. It continues along a slight posteroinferior course until it ends at the decussation of the pyramids (at the level of the foramen magnum of the skull ).
What part of the brain is connected to the rest of the body?
Similarly, the majority of brain tissue is connected to the rest of the body via the brainstem . The brainstem is a stalk-like projection extending caudally from the base of the cerebrum.
Which part of the brain is the widest?
The brainstem is widest at its proximal end and becomes narrower toward the distal end. There are three parts of the brainstem: and the midbrain is the widest and most superior segment. The brainstem is be divided horizontally (as above) and vertically.
What is the function of the brain stem?
The brain stem handles the most basic functions required for survival; things like, heart rate, reflexes, breathing, digestion, and regulating sleep. There is a substantial amount of evidence that the brainstem plays an integral role in regulating consciousness and awareness.
How to tell what functions certain parts of the brain stem perform?
As is often the case in neuroanatomy, one way of figuring out exactly which functions certain parts of the brain stem perform is to see what happens when those parts of the brain are damaged. Sometimes, seeing what happens when a machine malfunctions can give clues regarding its internal organization and structure.
Why is the Medulla important?
The medulla is important for 2 major reasons; First, the medulla controls the most basic and crucial functions needed for life. The medulla controls these things automatically so we do not even have to think of them . Without the medulla, the body could not regulate its own heartbeat, blood pressure or breathing. Autonomic functions are regulated by the medulla using chemoreceptors. For example, the brain stem regulates breathing by chemoreceptors that detect changes in the acidity of the blood. when blood acidity reaches a certain level, the medulla sends electric signals to the intercostal and phrenical muscles to increase the rate of lung contraction.
What is the midbrain?
Midbrain. ADVERTISEMENT. The midbrain (also called the mesencephalon) is the highest and first part of the brain stem. The midbrain consists of three general parts. The tectum (Latin: roof) is the highest part of the brain stem and forms the tissue that connects the brain stem to the lowest parts of the cerebellum.
What is the role of the tectum?
The main role of the tectum is to regulate reflex activity in response to visual and auditory stimuli and engage in basic level visuoauditory processing. A cross section of the midbrain. Credit; WikiCommons CC BY-SA 3.0. The tegmentum is the second part of the midbrain and is much larger than the tectum.
What is the function of the pons?
The pons performs many different functions. Most importantly, neural pathways in the pons are responsible for regulating respiration. The pons is the part of the brain that ensures you keep breathing even when you are asleep or not consciously paying attention. The pons also contains a number of cranial nerves and is implicated in swallowing, facial expressions, facial sensation, and eye movement. Damage to the pons can impair any of these functions. For example, Central pontine myelinolysis is a condition caused by damage to the myelin sheath of cells in the pons and is characterized by difficulties in swallowing, speaking, and breathing. The pons also serves as a message center that relays signals between the cerebellum and cerebrum.
What is the oldest part of the brain?
Since the brain stem is the lowest part of the vertebrate brain, it is considered the “oldest” part of the brain, evolutionarily speaking. Rudimentary versions of the brain stem appear in the evolutionary record somewhere between 600 to 420 million years ago; roughly contemporaneous with the emergence of complex eukaryotic life. Regarding the current function of brain structures, the brain stem generates arousal, reward, and stress; the most basic elements necessary for memory formation and immediate survival.
What is the function of the brainstem?
Function. The brainstem contains nerves and tracts (nerve pathways) that provide motor and sensory functions throughout the body. Nerve tracts are composed of a sequence of nerves that rapidly send messages along a specific route. Major nerve pathways in the brainstem include: Spinothalamic: This tract runs at the outer portion of the brainstem, ...
How does the brainstem work?
Some of the structures located in the brainstem work by coordinating with neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) and structures in other parts of the brain and throughout the body to control complex functions.
What is the brainstem composed of?
Medulla: Cranial nerves nine through 12. The deeper portion of the brainstem is composed of grey matter, and the remaining nerve pathways of the brainstem are primarily are composed of white matter, which is more heavily myelinated (protected by a type of fat that insulates nerves). In an average size adult, the brainstem measures approximately 3 ...
What nerves control movement?
The cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem—controlling movement and sensation in and around the face. A number of conditions can affect the brainstem, and the symptoms can vary, often including dizziness, double vision, and/or problems with physical movement. Hank Grebe / Getty Images.
Where are the cranial nerves located?
Cranial nerve roots are located in the brainstem , and each pair of the 12 cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem. The cranial nerve levels are: Cerebrum: Cranial nerves one and two. Midbrain: Cranial nerves three and four. Pons : Cranial nerves five through eight. Medulla: Cranial nerves nine through 12.
What is the fluid that flows between the brain and the meninges?
Outside the meninges, the brainstem is shielded by the lower part of the skull. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows between the meninges and the brainstem, providing nourishment and protection.
Which part of the brain is responsible for controlling the heart and breathing?
Associated Conditions. Tests. The brainstem is the part of the brain that directly connects with the spinal cord. It contains regions that modulate breathing and heart function, as well as pathways for communication between the brain and the spinal cord. The cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem—controlling movement and sensation in ...
What are the three structures that make up the brain stem?
Definition. The brain stem (or brainstem) contains three structures- the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata - that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It has several roles in the autonomic nervous system, with ascending pathways to receive sensory information for brain processing and descending pathways to send motor information back to ...
Which part of the brain contains descending and ascending pathways?
The brain stem contains ascending pathways and descending pathways. The ascending pathways process sensory information while the descending pathways create motor responses to the sensory information received.
Why is the reticular system important?
The Reticular Formation: The most important role of the reticular formation is to filter sensory information relayed to the brain, allowing the conscious to pay attention to the most important senses present. As a result, this region is important for maintaining overall attention and alertness. In addition, the reticular formation is important for cardiovascular systemic control, respiratory regulation, and its relation to consciousness during the waking and sleeping cycles. Furthermore, it contains networks for mood and pain modulation. All of these networks start at the brain stem in the core and branch throughout the brain’s entirety, with ascending pathways into the thalamus and cortex and descending pathways into the spinal cord.
What is the nervous system made of?
The nervous system is made up of individual nerve cells (or neurons ), which recognize signals from the body and its environment. The neurons pass along these signals to their respective destinations in the brain almost instantly via electrical signaling. When one nerve passes the signal to the next nerve, a synapse occurs. This is where electrical signals become chemical in the spaces between two neurons, before becoming electrical again at the next neuron.
What are the four regions of the brain?
The brain itself is made up of four regions: the cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, and brain stem. While each region has distinct differences and roles in relation to the rest of the body, there are many interconnected pathways and neural connections that can pass through multiple structures.
What are the two subsystems of the nervous system?
Neurons make up the entirety of the nervous system, which is broken into two physical sub-systems: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system . The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system includes all other neurons throughout the body.
Which part of the midbrain contains the corpora quadrigemina?
The midbrain’s posterior (the tectum) contains the corpora quadrigemina, which is a pair of protrusions on the midbrain. This pair includes the superior colliculi, which is the visual reflex center, and the inferior colliculi, which is the auditory relay center.
How many functions does the brain stem have?
To summarize, you can say that all the individual roles of the brain stem can be summed up into three main functions. These include:
Why is the brain stem important?
Why? The brain stem is a vital part for your brain and body to function. It controls your body’s breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. In addition, It also controls your consciousness and autonomic functions, which are absolute requirements to sustain life.
Where Is The Location Of The Brain Stem?
Located just above the spinal cord, the brain stem connects the spinal cord to the cerebellum part of the brain. Its connection is made up of three pairs of nerve bundles known as cerebellar peduncles.
What is the structure of the brain stem?
Underneath them is the spinal cord, which can be observed as the root. It consists of three major divisions: the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain.
What is the oldest part of the brain?
The brain stem is the oldest, most primitive part of the human brain. This tube-shaped region is about three inches long and made up entirely out of nervous tissue. The brain stem forms a bridge between the brain and the spinal cord and plays the most vital role of all.
How does physical activity help the brain?
Several studies have shown that physical activity, particularly leg exercises, can support the production of new neurons by stimulating the brain stem pathways.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the movement of the eye?
This part of the brain stem is home to many vital nerves. These include the abducens nerve (eye movement), the facial nerve (facial expressions), and the trigeminal nerve (feeling in the face).

Parts of The Brain Stem
Functions of Brain Stem
- The ascending pathways in the brain stem are sensory pathways like spinothalamic tracts for pain and temperature, dorsal column to communicate touch, vibration, two point discrimination, proprioception from skin and joints, fasciculus gracilis, cuneatus for touch and pressure sensation. The descending path carries motor signals from brain to lower ...
Brain Stem Disease and Symptoms
- Brain stem damage is revealed by symptoms such as abnormal sleeping habits, insomnia, nausea, balance issues, inability to cough, difficulty in eating and drinking and slurred speech. Leukoencephalopathy denotes damage of white matter of the brain, which forms the myelin sheath which in turn covers the nerve fibers. This myelin sheath is inevitable for transmitting sig…
Causes
- LBSL is caused due to an abnormal variant of DARS2 gene. When mutation of gene occurs, The proteins become faulty, insufficient, absent or excess in amount. Depending upon the function of the protein, among many organs of the body, the brain stem may also be possibly damaged. Degeneration of brain parenchyma or functional tissue of the brain originates and affects brain s…
Treatment
- Brain stem damage can be handled by addressing symptoms and prompting neuroplasticity which is the brain’s natural healing process. Neuroplasticity enables the brain to form new pathways which enable undamaged parts of the brain to take over functions of damaged parts. Physical therapies like passive range of motion exercises, electrical stimulation, task specific ex…
Conclusion
- With the advent of science, brain stem damage might appear irreversible but is not as hopeless as estimated.