
5.4: Passive Transport Across Membranes
- Selective Permeability Plasma membranes are asymmetric, meaning that despite the mirror image formed by the phospholipids, the interior of the membrane is not identical to the exterior of the membrane. ...
- Diffusion Diffusion is a passive process of transport. ...
- Facilitated transport ...
- Osmosis ...
- Tonicity ...
- Section Summary ...
- Art Connections ...
- Contributors and Attributions ...
Full Answer
What is the mechanism of movement of molecules across the plasma membrane?
How does the plasma membrane move?
What is the movement of water from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration?
What is the random movement of molecules down the pathway called?
Why do molecules move down the pathway?
What is the process of transporting solid particles across the plasma membrane?
What happens when a protein moves across the membrane?
See 4 more
About this website
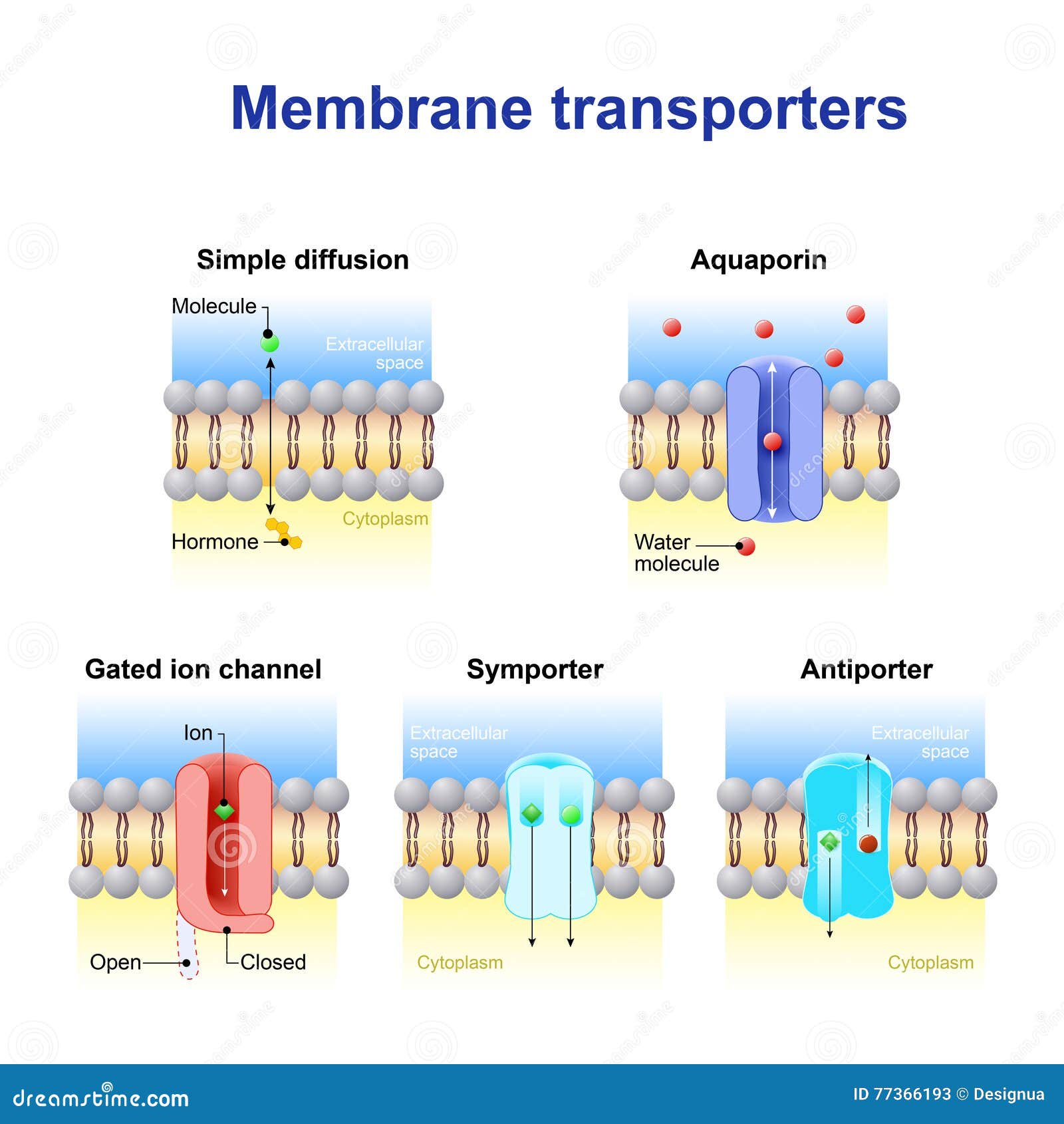
Transport across Cell Membrane: 4 Ways | Biology
ADVERTISEMENTS: Transport across cell membrane is classified into four ways: 1. Diffusion (Passive Transport) 2. Osmosis 3. Active Transport 4. Vesicular Transport. Cell membrane acts as a barrier to most, but not all molecules. Cell membranes are semi-permeable barrier separating the inner cellular environment from the outer cellular environment. Since the cell membrane is made […]
Methods of Transport across a Plasma Membrane Biology - UKEssays.com
Methods of Transport across a Plasma Membrane Biology The plasma membrane is present in both the eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell and is also known as the biological membrane and. It wo
How do molecules move across the plasma membrane? | Socratic
Through diffusion or active transport. Molecules move across the plasma/cell membrane through diffusion. If they are not small enough, they have to broken down by other substances, such as enzymes, which are biological catalysts. If they are small enough, usually, the easiest way for them to move is through diffusion. This means that they will move from a region of higher concentration to a ...
Selective Permeability
Plasma membranes are asymmetric, meaning that despite the mirror image formed by the phospholipids, the interior of the membrane is not identical to the exterior of the membrane. Integral proteins that act as channels or pumps work in one direction.
Diffusion
Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. For example, think about someone opening a bottle of perfume in a room filled with people.
Facilitated transport
In facilitated transport, also called facilitated diffusion, material moves across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transmembrane proteins down a concentration gradient (from high to low concentration) without the expenditure of cellular energy.
Osmosis
Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane according to the concentration gradient of water across the membrane. Whereas diffusion transports material across membranes and within cells, osmosis transports only water across a membrane and the membrane limits the diffusion of solutes in the water.
Tonicity
Tonicity describes the amount of solute in a solution. The measure of the tonicity of a solution, or the total amount of solutes dissolved in a specific amount of solution, is called its osmolarity.
Section Summary
The passive forms of transport, diffusion and osmosis, move material of small molecular weight. Substances diffuse from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, and this process continues until the substance is evenly distributed in a system.
Art Connections
Figure 5.4. 3: A doctor injects a patient with what he thinks is isotonic saline solution. The patient dies, and autopsy reveals that many red blood cells have been destroyed. Do you think the solution the doctor injected was really isotonic?
What is the mechanism of movement of molecules across the plasma membrane?
A third mechanism for movement across the plasma membrane is facilitated diffusion. Certain proteins in the membrane assist facilitated diffusion by permitting only certain molecules to pass across the membrane. The proteins encourage movement in the direction that diffusion would normally take place, from a region with a higher concentration of molecules to a region of lower concentration.
How does the plasma membrane move?
The final mechanism for movement across the plasma membrane into the cell is endocytosis, a process in which a small patch of plasma membrane encloses particles or tiny volumes of fluid that are at or near the cell surface. The membrane enclosure then sinks into the cytoplasm and pinches off from the membrane, forming a vesicle that moves into the cytoplasm. When the vesicle contains solid particulate matter, the process is called phagocytosis. When the vesicle contains droplets of fluid, the process is called pinocytosis. Along with the other mechanisms for transport across the plasma membrane, endocytosis ensures that the internal cellular environment will be able to exchange materials with the external environment and that the cell will continue to thrive and function. Exocytosis is the reverse of endocytosis, where internally produced substances are enclosed in vesicles and fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the contents to the exterior of the cell.
What is the movement of water from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration?
Osmosis is the movement of water from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. Osmosis occurs across a membrane that is semipermeable. A semipermeable membrane lets only certain molecules pass through while keeping other molecules out.
What is the random movement of molecules down the pathway called?
Diffusion is a random movement of molecules down the pathway called the concentration gradient. Molecules are said to move down the concentration gradient because they move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. A drop of dye placed in a beaker of water illustrates diffusion as the dye molecules spread out ...
Why do molecules move down the pathway?
This movement occurs because the molecules are constantly colliding with one another. The net movement of the molecules is away from the region of high concentration to the region of low concentration. Diffusion is a random movement of molecules down the pathway called the concentration gradient. Molecules are said to move down ...
What is the process of transporting solid particles across the plasma membrane?
When the vesicle contains solid particulate matter, the process is called phagocytosis. When the vesicle contains droplets of fluid, the process is called pinocytosis. Along with the other mechanisms for transport across the plasma membrane, endocytosis ensures that the internal cellular environment will be able to exchange materials with ...
What happens when a protein moves across the membrane?
When active transport is taking place, a protein moves a certain material across the membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. Because this movement is happening against the concentration gradient, the cell must expend energy that is usually derived from a substance called adenosine triphosphate, ...
How does water move across the plasma membrane?
Water moves across plasma membranes by a specific type of diffusion called osmosis. The concentration gradient of water across a membrane is inversely proportional to the concentration of solutes; that is, water moves through channel proteins called aquaporins from higher water concentration to lower water concentration.
What are the characteristics of plasma membranes?
This characteristic helps the movement of some materials through the membrane and hinders the movement of others. Lipid-soluble material with a low molecular weight can easily slip through the hydrophobic lipid core of the membrane. Substances such as the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K readily pass through the plasma membranes in the digestive tract and other tissues. Fat-soluble drugs and hormones also gain easy entry into cells and are readily transported into the body’s tissues and organs. Similarly, molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide have no charge and so pass through membranes by simple diffusion.
How does diffusion work?
Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across a space. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. For example, think about someone opening a bottle of ammonia in a room filled with people. The ammonia gas is at its highest concentration in the bottle; its lowest concentration is at the edges of the room. The ammonia vapor will diffuse, or spread away, from the bottle, and gradually, more and more people will smell the ammonia as it spreads. Materials move within the cell’s cytosol by diffusion, and certain materials move through the plasma membrane by diffusion (Figure 5.8). Diffusion expends no energy. On the contrary, concentration gradients are a form of potential energy, dissipated as the gradient is eliminated.
What is the most direct form of membrane transport?
The most direct forms of membrane transport are passive. Passive transport is a naturally occurring phenomenon and does not require the cell to exert any of its energy to accomplish the movement. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
How do channel proteins and carrier proteins work?
Channel and carrier proteins transport material at different rates. Channel proteins transport much more quickly than do carrier proteins. Channel proteins facilitate diffusion at a rate of tens of millions of molecules per second, whereas carrier proteins work at a rate of a thousand to a million molecules per second.
What is facilitated transport?
However, these materials are polar molecules that are repelled by the hydrophobic parts of the cell membrane. Facilitated transport proteins shield these materials from the repulsive force of the membrane, allowing them to diffuse into the cell.
What is the purpose of plasma membranes?
Plasma membranes must allow certain substances to enter and leave a cell, and prevent some harmful materials from entering and some essential materials from leaving. In other words, plasma membranes are selectively permeable —they allow some substances to pass through, but not others. If they were to lose this selectivity, the cell would no longer be able to sustain itself, and it would be destroyed. Some cells require larger amounts of specific substances than do other cells; they must have a way of obtaining these materials from extracellular fluids. This may happen passively, as certain materials move back and forth, or the cell may have special mechanisms that facilitate transport. Some materials are so important to a cell that it spends some of its energy, hydrolyzing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), to obtain these materials. Red blood cells use some of their energy doing just that. Most cells spend the majority of their energy to maintain an imbalance of sodium and potassium ions between the interior and exterior of the cell.
What are the types of movement across the cell membrane?
1. TYPES OF MOVEMENT ACROSSTHE CELL MEMBRANE. 2. Passive Transport Passive transport is the movement of molecules across the cell membrane and does not require energy. It is dependent on the permeability of the cell membrane. There are three main kinds of passive transport - Diffusion, Osmosis and Facilitated Diffusion. 3.
What is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane?
Osmosis The movement of water across a semi permeable membrane. Osmosis is the movement of water (red dots) through a semipermeable membrane to a higher concentration of solutes (blue dots). 6.
What is the role of active transport in the cell?
14. Active Transport Active Transport requires the cell to use energy , usually in the form of ATP. Active Transport creates a charge gradient in the cell membrane. For example in the mitochondrion, hydrogen ion pumps pump hydrogen ions into the intermembrane space of the organelle as part of making ATP. 15.
Which process does not require ATP but does require cell membrane proteins?
Facilitated diffusion This process does not require ATP but does require cell membrane proteins which are called carrier proteins to carry the molecules across the cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. 5.
What is exo cytosis?
EXOCYTOSIS-Exo (exit) cytosis (cell) ) is a process in which a substance is exited from the cell without passing through the cell membrane.• . Examples of things that migth be exited include secretion of proteins like enzymes, hormones and antibodies. 14.
What is the mechanism of movement of molecules across the plasma membrane?
A third mechanism for movement across the plasma membrane is facilitated diffusion. Certain proteins in the membrane assist facilitated diffusion by permitting only certain molecules to pass across the membrane. The proteins encourage movement in the direction that diffusion would normally take place, from a region with a higher concentration of molecules to a region of lower concentration.
How does the plasma membrane move?
The final mechanism for movement across the plasma membrane into the cell is endocytosis, a process in which a small patch of plasma membrane encloses particles or tiny volumes of fluid that are at or near the cell surface. The membrane enclosure then sinks into the cytoplasm and pinches off from the membrane, forming a vesicle that moves into the cytoplasm. When the vesicle contains solid particulate matter, the process is called phagocytosis. When the vesicle contains droplets of fluid, the process is called pinocytosis. Along with the other mechanisms for transport across the plasma membrane, endocytosis ensures that the internal cellular environment will be able to exchange materials with the external environment and that the cell will continue to thrive and function. Exocytosis is the reverse of endocytosis, where internally produced substances are enclosed in vesicles and fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the contents to the exterior of the cell.
What is the movement of water from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration?
Osmosis is the movement of water from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. Osmosis occurs across a membrane that is semipermeable. A semipermeable membrane lets only certain molecules pass through while keeping other molecules out.
What is the random movement of molecules down the pathway called?
Diffusion is a random movement of molecules down the pathway called the concentration gradient. Molecules are said to move down the concentration gradient because they move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. A drop of dye placed in a beaker of water illustrates diffusion as the dye molecules spread out ...
Why do molecules move down the pathway?
This movement occurs because the molecules are constantly colliding with one another. The net movement of the molecules is away from the region of high concentration to the region of low concentration. Diffusion is a random movement of molecules down the pathway called the concentration gradient. Molecules are said to move down ...
What is the process of transporting solid particles across the plasma membrane?
When the vesicle contains solid particulate matter, the process is called phagocytosis. When the vesicle contains droplets of fluid, the process is called pinocytosis. Along with the other mechanisms for transport across the plasma membrane, endocytosis ensures that the internal cellular environment will be able to exchange materials with ...
What happens when a protein moves across the membrane?
When active transport is taking place, a protein moves a certain material across the membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. Because this movement is happening against the concentration gradient, the cell must expend energy that is usually derived from a substance called adenosine triphosphate, ...

Diffusion
Osmosis
- Another method of movement across the membrane is osmosis. Osmosisis the movement of water from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. Osmosis occurs across a membrane that is semipermeable. A semipermeable membrane lets only certain molecules pass through while keeping other molecules out. Osmosis is really a type of diffusion …
Facilitated Diffusion
- A third mechanism for movement across the plasma membrane is facilitated diffusion.Certain proteins in the membrane assist facilitated diffusion by permitting only certain molecules to pass across the membrane. The proteins encourage movement in the direction that diffusion would normally take place, from a region with a higher concentration of molecules to a region of lower …
Active Transport
- A fourth method for movement across the membrane is active transport.When active transport is taking place, a protein moves a certain material across the membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. Because this movement is happening against the concentration gradient, the cell must expend energy that is usually derived from a substanc…
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
- The final mechanism for movement across the plasma membrane into the cell is endocytosis, a process in which a small patch of plasma membrane encloses particles or tiny volumes of fluid that are at or near the cell surface. The membrane enclosure then sinks into the cytoplasm and pinches off from the membrane, forming a vesicle that moves into the ...