Types of Cases
- Cases that raise a "federal question" involving the United States Government , the U.S. Constitution, or other federal laws; and
- Cases involving “diversity of citizenship," which are disputes between two parties not from the same state or country, and where the claim meets a set dollar threshold for damages.
What are the different types of court cases?
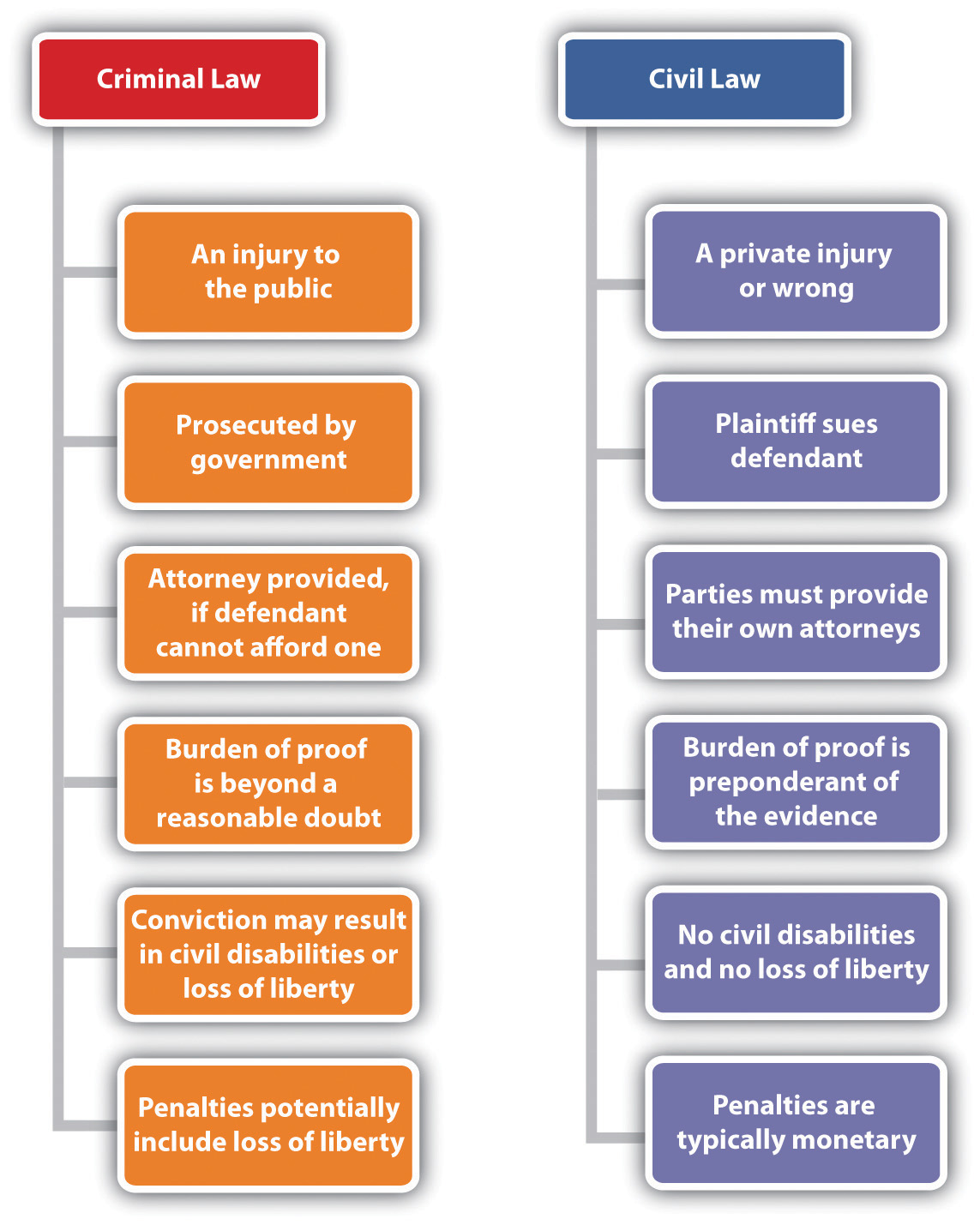
The Types of Court Cases. Criminal Cases; Civil Cases; In criminal cases, the government brings a case against one or more defendants. The defendant in a criminal case is the person being accused of committing a crime by the government.
What are the different types of cases heard by juries?
Types of Cases Heard by Juries. There are two types of judicial proceedings in the federal courts that use juries. Criminal trial: An individual is accused of committing a crime that is considered against society as a whole. Twelve people, and alternates, make up a criminal jury.
What is an example of the judicial branch?
For example, the judicial branch decides everything from criminal and civil cases and applies the laws of the jurisdiction, as well as the Constitution to them. The most important arm of this important branch is the United States Supreme Court. To explore this concept, consider the following judicial branch definition.
What kind of case is civil or criminal?
Criminal Cases. Civil Cases. In criminal cases, the government brings a case against one or more defendants. The defendant in a criminal case is the person being accused of committing a crime by the government.
Which court has jurisdiction over cases involving the United States Government?
What type of cases can be appealed?
About this website

8 types of cases federal courts can hear Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Case 1, Case 2, Case 3 and more.
What kinds of cases are handled in Federal Court?
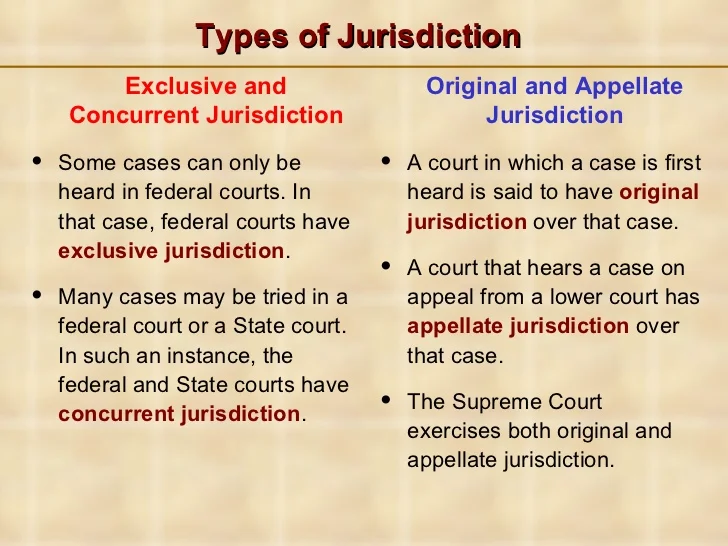
Federal court jurisdiction is limited to certain types of cases listed in the U.S. Constitution. For the most part, federal court jurisdictions only hear cases in which the United States is a party, cases involving violations of the Constitution or federal law, crimes on federal land, and bankruptcy cases.
What type of cases are heard in the US District Court? - Quora
Answer (1 of 3): The district courts are courts or original jurisdiction, meaning they would be the court where the case is first brought and tried. Generally the courts of appeals and Supreme Court are courts of appellate jurisdiction. They review the decisions of the lower courts such as the di...
Types of Cases in Federal Court | CONNECTIONS - United States Courts
U.S. district courts hear cases over which they have jurisdiction granted by the U.S. Constitution or by federal statute. The federal courts have jurisdiction over:
What Kinds of Cases Can Federal Courts Decide? - FindLaw
There are two parallel systems of courts in the United States: federal courts and state courts. Each system typically hears different cases to ensure that each court decides the law that it knows best.
Which court has jurisdiction over cases involving the United States Government?
The federal courts have jurisdiction over. Cases that raise a "federal question" involving the United States Government , the U.S. Constitution, or other federal laws; and. Cases involving “diversity of citizenship," which are disputes between two parties not from the same state or country, and where the claim meets a set dollar threshold ...
What type of cases can be appealed?
More specifically, federal courts hear criminal, civil, and bankruptcy cases. And once a case is decided, it can often be appealed .
Who decides if there is enough evidence to charge you?
The police then submit a report on their investigation to the criminal and penal prosecuting attorney, who will decide if there is enough evidence to charge you.
What is the duty of a criminal lawyer?
Moreover, it is the duty of the criminal lawyer to ensure that each client understands the process. It is therefore very important to consult us quickly following an arrest. 1. STAGES PROCEDING THE JUDICIAL PROCESS.
Why do you meet with a criminal defense attorney?
The meeting with the criminal attorney is essential to determine whether a defense can be invoked, in which case a trial date will be set, or if there is a possibility to avoid a criminal record. If this is not the case, the defense attorney has a duty to mitigate the consequences of a guilty plea or conviction.
Who is a person who has committed an indictable offense?
a person who has committed an indictable offense or who, on reasonable grounds, he believes has committed or is about to commit an indictable offense; a person whom he finds committing a criminal offense; or. a person in respect of whom he has reasonable grounds to believe that a warrant of arrest is in force.
Who accepts joint submissions?
If an agreement is reached, the joint submission will be presented to the judge, who will accept it unless he or she believes that the sentence is unreasonable.
What is the duty of a defense lawyer in a bail hearing?
If the Crown prosecutor objects, it is the duty of the defense lawyer to bring forth all the necessary arguments in front of a judge in what is know as a bail hearing . 2. THE JUDICIAL PROCESS.
Which court deals with civil cases?
Like criminal cases, the majority of civil disputes are left to the state courts to settle. The federal courts only deal with civil cases that either:
What are some examples of civil disputes?
Some examples of civil disputes that could be filed in federal court are: Suing for civil rights violations or discrimination. Suing for first amendment violations of free speech, free expression of religion, etc. Suing people for a loss they caused, if they are from another state.
What is the right to counsel for a felony?
Anyone accused of a federal felony has a right to be assisted by a lawyer for every step of the process, even if they can’t afford one. (A felony is a crime carrying a jail term of more than one year.) The right to counsel is guaranteed by the 6 th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution.
What does the judicial branch do?
What Courts Do. The judicial branch must apply the existing laws to each individual situation, to be sure justice is administered fairly. This includes punishing those who are guilty of breaking the law, and keeping the rest of the community safe from crime.
Who represents the government in a criminal case?
At the U.S. District Court level, the government is represented by the United States Attorney (or an Assistant United States Attorney), ...
Can a defendant represent themselves in a federal court?
Defendants are also allowed to represent themselves, and this is called pro se. Most crimes are a violation of state law, not federal law, and thus would be prosecuted in the state court system. Only crimes that break a law of the U.S. government will be prosecuted in the federal courts.
Is a civil suit a federal case?
Though you have the right to sue someone in federal court, not every civil law suit is a federal case. See below to figure out which civil cases might be heard in federal court. Though the U.S. Constitution gives everyone a right to have an attorney if accused of a crime, there is no such guarantee for civil cases.
Typical Steps in the Judicial Process
Concern Reported: The process begins when someone files a concern with the Office of Community Standards (OCS).
Uncontested vs. Contested Cases
Judicial Panel hearings follow a different format for cases in which the responding student accepts responsibility (uncontested cases) and for cases in which the student disputes the charges (contested).
Key Figures in the Judicial Process
In addition to the responding student, there are a several key participants in the process.
What is the judicial process?
The judicial process is a set of interrelated procedures and roles for deciding disputes by an authoritative person or persons whose decisions are regularly obeyed. The disputes are to be decided according to a previously agreed upon set of procedures and in conformity with prescribed rules. As an incident, or consequence, of their dispute-deciding function, those who decide make authoritative statements of how the rules are to be applied, and these statements have a prospective generalized impact on the behavior of many besides the immediate parties to the dispute. Hence the judicial process is both a means of resolving disputes between identifiable and specified persons and a process for making public policies.
What are the staples of research concerning the judiciary?
In contrast, and in response to the formal model, the main staples of research concerning the judiciary are the evidence presented, the arguments before the courts, and the judge’s formally stated reasons for his decision. The judicial decision is approached as a product of a controlled debating contest.
Why do authorities disagree on judicial review?
Authorities tend to disagree on whether judicial review exists in a given country, largely because no two scholars appear to hold identical views as to what judicial review is or how it should be define d (cf., e.g., Abraham 1962; Black 1960; Corwin 1932; Haines 1914). Nevertheless, some definition is essential as a point of departure. The following is offered as somewhat less troublesome than most: Judicial review is the process whereby a judicial body determines the constitutionality of activity undertaken by a country’s national legislature and by its chief political executives.
How did the appellate judges program start?
The pioneer project was the Appellate Judges Seminar, inaugurated by the Institute of Judicial Administration in 1957 and held for two weeks each summer. Each year it provides a pro-gram for 20 to 25 of the appellate judges of the nation. In 1962, under the aegis of the Joint Committee for the Effective Administration of Justice, an organization sponsored by 14 national organizations interested in judicial administration and headed by Justice Tom C. Clark of the United States Supreme Court, the same idea was extended on a large scale to trial judges of state courts of general jurisdiction. It has held many two-day or three-day seminars throughout the nation. Other seminars are held for new federal district judges under the auspices of the Judicial Conference of the United States; and still others are conducted for juvenile court judges, traffic court judges, and justices of the peace. The movement is continuing to grow and expand, as is evidenced by the establishment in 1964, on what was hoped to be a permanent basis, of the College of Trial Judges, to be conducted four weeks each year for new judges of state trial courts of general jurisdiction. Further in the future is the possibility of establishing a training program for lawyers who are not yet judges, but who have ambitions in that direction.
What is the orthodox theory of judicial process?
According to what is variously called the “mechanical,” “slot-machine,” “photographic,” “formalistic,” “conceptual,” or “orthodox” theory of the judicial process, judges , like doctors or scientists, are trained technicians who apply their specialized knowledge to discover answers to legal disputes.
How are judges elected?
One approach toward de-emphasizing political considerations (without eliminating them entirely) is to require that a judicial appointment be made from a list presented to the governor (or other appointing official) by a non-partisan nominating commission; and to require that after a probationary period of service, the appointee shall run against his own record, not against any other candidate. The choice that ap-pears on the ballot is simply whether Judge X shall, or shall not, be retained in office. This plan is known by various names, the most familiar of which is the Missouri plan, Missouri being one of the first states to put it into effect. Similar plans are now in operation in Kansas, Alaska, California, Alabama, and Iowa; and movements are under way for the adoption of the idea in still other states.
How does tenure affect the judiciary?
The tenure of judicial office is one of the factors affecting recruitment of the proper men to become judges , because an office that carries tenure for life or for a long period of years is obviously more attractive than one that carries a short tenure. At the same time, it is important that men do not remain on the bench after their powers have failed or if they have demonstrated by their conduct that they are not fit to hold office. The direction of reform, therefore, has been toward making tenure long, but at the same time providing for retirement or removal under the proper conditions and by a simple and effective procedure. Impeachment, involving legislative accusation and trial, has proved to be a cumbersome and generally ineffective method of getting rid of unfit judges and, consequently, has in some states been replaced or supplemented by removal machinery operated and controlled by the highest judicial officers of the state.
How are civil cases similar to criminal cases?
Civil cases are similar to criminal ones, but instead of arbitrating between the state and a person or organization, they deal with disputes between individuals or organizations. In civil cases, if a party believes that it has been wronged, it can file suit in civil court to attempt to have that wrong remedied through an order to cease and desist, alter behavior, or award monetary damages. After the suit is filed and evidence is gathered and presented by both sides, a trial proceeds as in a criminal case. If the parties involved waive their right to a jury trial, the case can be decided by a judge; otherwise, the case is decided and damages awarded by a jury.
How many Supreme Court Justices are there?
Even the number of Supreme Court Justices is left to Congress — at times there have been as few as six, while the current number (nine, with one Chief Justice and eight Associate Justices) has only been in place since 1869.
How long can a justice stay in office?
Justices may remain in office until they resign, pass away, or are impeached and convicted by Congress. The Court’s caseload is almost entirely appellate in nature, and the Court’s decisions cannot be appealed to any authority, as it is the final judicial arbiter in the United States on matters of federal law.
What is the power of the federal courts?
Federal courts enjoy the sole power to interpret the law, determine the constitutionality of the law, and apply it to individual cases. The courts, like Congress, can compel the production of evidence and testimony through the use of a subpoena.
How can a federal judge be removed?
Federal judges can only be removed through impeachment by the House of Representatives and conviction in the Senate. Judges and Justices serve no fixed term — they serve until their death, retirement, or conviction by the Senate.
What is the highest court in the United States?
The Supreme Court of the United States. The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest court in the land and the only part of the federal judiciary specifically required by the Constitution. The Constitution does not stipulate the number of Supreme Court Justices; the number is set instead by Congress.
Which branch of government has the power to establish courts inferior to the Supreme Court?
The Constitution also grants Congress the power to establish courts inferior to the Supreme Court, and to that end Congress has established the United States district courts, which try most federal cases, and 13 United States courts of appeals, which review appealed district court cases.
What is a civil court case?
Landlord/tenant issues. Civil courts handle disputes arising between landlords and tenants. Cases where a landlord is trying to evict a tenant from a rental property or a tenant has moved out and is suing a landlord for the return of a security deposit are examples.
What is criminal case?
Criminal Cases. Criminal cases involve enforcing public codes of behavior, which are codified in the laws of the state. In criminal cases, the government prosecutes individuals for violating those laws (in other words, for allegedly committing a crime).
What is tortious action?
Very broadly, civil cases may involve such things as, for example, Tort claims. A "tort" is a wrongful act (sometimes called a "tortious" act), other than a breach of contract, that results in injury to someone's person, property, reputation, or the like, for which the injured person is entitled to compensation.
What is the post trial stage?
During the post-trial stage, one or both of the parties might appeal the judgment that was entered at trial, or the winning party might try to collect the judgment that was entered.
What is an equitable claim?
Equitable claims. An "equitable claim" asks the court to order a party to take some action or stop some action.
What are the stages of civil litigation?
Stages Of A Civil Case. Most civil lawsuits can be divided into the stages listed below: Pre-filing. During the pre-filing stage, the dispute arises and the parties make demands, try to negotiate a resolution, and prepare for the possibility of a court action. Initial pleading.
What is breach of contract?
Breach of contract claims. A breach of contract case typically results from a person's failure to perform some term of a contract, whether the contract is written or oral, without some legitimate legal excuse. Cases involving claims for such things as not completing a job, not paying in full or on time, failing to deliver goods sold or promised, and many others, are all examples.
What is the judicial process?
The judicial process is a system of procedures used by an individual with authority, like a judge, to decide disputes between parties. The judge relies on previously established case law when applying the judicial process to a case. Sometimes, a judge may also make a decision on a case that affects the judicial process going forward by either creating a rule that had never existed before, or by modifying a rule that needed updating. This is the concept of “setting precedent.”
What is the Judicial Branch Meaning?
This government organization is comprised of a system of courts and judges. The purpose of this system is to interpret the laws that the legislative branch creates, and that the executive branch enforces. Heading up this branch is the U.S. Supreme Court, which is the most powerful Court in the country . It is comprised of nine justices, and it has the final say when it comes to making a decision in a civil or criminal case.
What is the power of the judicial branch to strike down laws?
In this case, the high Court made precedent by creating the process of “ judicial review ,” which is the power of the American court system to strike down any laws or statutes that work in violation of the Constitution. Another of these judicial branch examples is Clinton v. City of New York (1998).
Which branch of government drafts laws?
Of these branches of government, the legislative branch is the one that drafts up the laws. The executive branch either vetoes or approves these laws, and the judicial branch interprets the laws passed by the executive branch and applies them to future civil and criminal cases. The legislative branch consists of the Senate and the House ...
How many justices are there in the Supreme Court?
Heading up this branch is the U.S. Supreme Court, which is the most powerful Court in the country. It is comprised of nine justices, and it has the final say when it comes to making a decision in a civil or criminal case.
What is the role of the Supreme Court?
Namely, the U.S. Supreme Court is the final judge when deciding cases involving Congress, as well as those concerning questions of constitutional rights.
Which case was the Supreme Court able to rule that the Constitution was violated?
Ultimately, the Court ruled that he had indeed violated the Constitution. Still another of these judicial branch examples is Griswold v. Connecticut (1965), wherein the U.S. Supreme Court set precedent once again by interpreting the Constitution.
How many types of judicial proceedings are there?
There are two types of judicial proceedings in the federal courts that use juries. Criminal trial: An individual is accused of committing a crime that is considered against society as a whole. Twelve people, and alternates, make up a criminal jury.
Who determines the appropriate law to be applied to a case?
The judge determines the appropriate law that should be applied to the case and the jury finds the facts in the case based on what is presented to them during the proceedings. At the end of a trial, the judge instructs the jury on the applicable law.
What is the standard of proof in civil cases?
The jury must come to a unanimous decision unless specified otherwise. The standard of proof is a “preponderance of the evidence,” or “more true than not.”. Settlement negotiations reduce the need for juries in civil cases.
What is jury service?
Jury service is a way for U.S. citizens to participate in the judicial process.
What is the unanimous decision in a criminal case?
A unanimous decision must be reached before a defendant is found “guilty.”. The government must prove the crime was committed “beyond a reasonable doubt.”. Guilty pleas and plea negotiations reduce the need for juries in criminal cases.
Who can be excused by the judge?
Members of the panel who know any person involved in the case, who have information about the case, or who may have strong prejudices about the people or issues involved in the case , typically will be excused by the judge. The attorneys also may exclude a certain number of jurors without giving a reason.
Can you serve on a jury?
Being summoned for jury service does not guarantee that a person will actually serve on a jury. When a jury is needed for a trial, the group of qualified jurors is taken to the courtroom where the trial will take place.
Which court has jurisdiction over cases involving the United States Government?
The federal courts have jurisdiction over. Cases that raise a "federal question" involving the United States Government , the U.S. Constitution, or other federal laws; and. Cases involving “diversity of citizenship," which are disputes between two parties not from the same state or country, and where the claim meets a set dollar threshold ...
What type of cases can be appealed?
More specifically, federal courts hear criminal, civil, and bankruptcy cases. And once a case is decided, it can often be appealed .