The different types of transport mechanisms across cell membranes are as follows:
- Simple diffusion
- Facilitated diffusion
- Osmosis
What are the three types of cell transport?
What are the 3 types of transport?
- Passive Transport. Passive transport is the movement of molecules across the cell membrane and does not require energy.?
- Facilitated Diffusion. Subsequently, one may also ask, what are the four types of active transport? ...
- Passive transport. ...
- different. ...
What are two types of transport through a membrane?
Types of Transport through cell membranes, Active transport, Simple & Facilitated diffusion
- Transport of substances through cell membranes. The extracellular fluid contains a large amount of sodium and chloride ions but only a small amount of potassium.
- Passive Transport. ...
- Facilitated diffusion. ...
How are large molecules transported across a cell membrane?
There are two ways in which molecules are transported across the cell membrane: passive transport and active transport. The passive transport methods are simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion osmosis - these rely on the natural kinetic energy of molecules. Active transport requires energy in the form of ATP.
What facilitated passive transport across a cell membrane?
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that allows substances to cross membranes with the assistance of special transport proteins. Some molecules and ions such as glucose, sodium ions, and chloride ions are unable to pass through the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes .
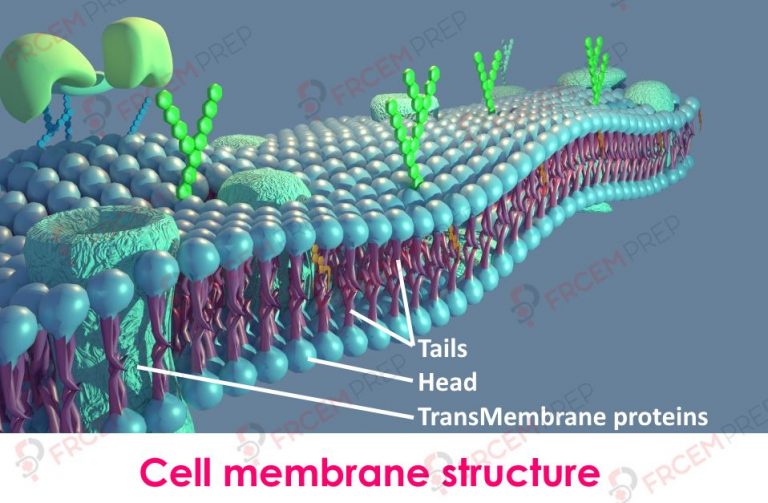
What are the names of 2 types of active transport?
There are two main types of active transport: Primary (direct) active transport – Involves the direct use of metabolic energy (e.g. ATP hydrolysis) to mediate transport. Secondary (indirect) active transport – Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient.
What is the transport in the cell membrane?
Membrane transport refers to the movement of particles (solute) across or through a membranous barrier. These membranous barriers, in the case of the cell for example, consist of a phospholipid bilayer.
Which 2 transport methods use transport proteins?
Both active transport and facilitated diffusion do use proteins to assist in transport. However, active transport works against the concentration gradient, moving substances from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration. In addition, the types of proteins that they use are different.
What are the two types of cell transport quizlet?
MatchWhat are the three types of cell transport? simple diffusion. ... Simple Diffusion. ... Osmosis. ... Hypotonic Solution. ... Isotonic Solution. ... Hypertonic Solution. ... Facilitated Diffusion aka Passive Transport. ... Active Transport.More items...
What is active and passive transport?
Active transport moves molecules and ions from lower concentration to higher concentration with the help of energy in the form of ATP. On the other hand, passive transport moves molecules and ions from a higher concentration to lower concentration without any energy.
What are the two main components of the cell membrane?
Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments.
What are the three types of transport across the cell membrane?
Basic types of membrane transport, simple passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion (by channels and carriers), and active transport [8].
What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion?
In simple diffusion, the substance passes between the phospholipids; in facilitated diffusion there are a specialized membrane channels. Charged or polar molecules that cannot fit between the phospholipids generally enter and leave cells through facilitated diffusion.
How are facilitated diffusion and active transport different?
Facilitated diffusion takes place down the gradient of concentration. Active transport takes place toward the gradient of concentration. Facilitated diffusion is a passive method and needs no energy. An active method is an active transport.
What is the difference between active and passive transport quizlet?
Passive transport doesn't require energy (ATP), active transport does require energy. Passive transport moves molecules WITH the concentration gradient (high to low), while active transport moves molecules AGAINST the concentration gradient (Low to High).
What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion quizlet?
Diffusion is different from facilitated diffusion because it is where particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Facilitated diffusion, on the other hand, is the process in which molecules cannot be directly diffused across the membrane pass through special protein channels.
What are the types of passive transport?
There are four types of passive transport:Simple Diffusion.Facilitated Diffusion.Filtration.Osmosis.
What are 4 types of active transport?
CONTENTSAntiport Pumps.Symport Pumps.Endocytosis.Exocytosis.
Is the cell membrane active or passive transport?
Some substances (small molecules, ions) such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2), can move across the plasma membrane by diffusion, which is a passive transport process.
What are the 6 types of transport?
Therefore; an essential part of transportation management lies in building an efficient supply chain from the six main modes of transportation: road, maritime, air, rail, intermodal, and pipeline. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each mode is paramount to building an effective supply chain.
What is transported across a membrane during osmosis?
Osmosis is a type of simple diffusion in which water molecules diffuse through a selectively permeable membrane from areas of high water concentration to areas of lower water concentration.
Why do carriers move across the cell membrane?
Ans: The Carrier proteins facilitate passive movement across the cell membrane. This is possible due to the concentration gradient across the membrane.
What is the energy used to transport across the membrane?
However, in the next methods, transport across the membrane occurs through the use of energy (ATP).
How do solute molecules move down the concentration gradient?
Small molecules move down the concentration gradient through the plasma membrane by diffusion.
Why do cells have transport proteins?
Ans: The cell membrane has transport proteins to facilitate the movement of molecules by passive facilitated diffusion or active transport. Molecules like glucose move by transport protein by the passive process.
How do potassium and sodium ions move across the nerve membrane?
In contrast, potassium and sodium ions move across the nerve membrane against the concentration gradient through transport proteins by active process.
Why is the cell membrane semipermeable?
However, it is semipermeable due to which certain substances can still move in and out of the cell. Based on the mechanism of movement, the transport across the cell membrane is classified as.
How do carrier proteins help move substances?
For this, specialized carrier protein molecules help in moving substances from one side of the membrane to the other. When the substance molecules bind , the carrier protein changes its shape so that the molecules move to the other end of the channel in the protein.
When a substance to be transported binds to a carrier protein on one side, there is a conform?
When a substance to be transported binds to a carrier protein on one side there is conformational change in the shape of the protein which carries the substance to the interior of the cell by opening to other side of membrane. It also obeys the law of diffusion (higher to lower concentration).
Which substances are highly soluble and diffuse through the membrane?
Substance like oxygen and carbon dioxide and alcohols are highly lipid soluble and dissolve in the layer easily and diffuse through the membrane. The rate of diffusion is determined by the solubility of the substance. For example, exchange of gases in the lungs.
How many potassium ions are drawn in every 3 sodium ions?
For every three sodium ions expelled out of cell, two potassium ions are drawn in. Thus, there is a net loss of positive charge (ion) out of the cell, which initiates osmosis of water out of the cell as well as prevents any cell from swelling.
What are the four ways of transport?
Transport across cell membrane is classified into four ways: 1. Diffusion (Passive Transport) 2. Osmosis 3. Active Transport 4. Vesicular Transport. Cell membrane acts as a barrier to most, but not all molecules. Cell membranes are semi-permeable barrier separating the inner cellular environment from the outer cellular environment. ...
How does the osmosis pump work?
The function is to pump out excess Na + from the intracellular fluid and to draw in K + into the cell. Since there are 3 sites for Na + and 2 sites for K +, the pump gets activated only when three Na + ion and two K + ion attaches to the interior and exterior surface of the cell respectively. For every three sodium ions expelled out of cell, two potassium ions are drawn in. Thus, there is a net loss of positive charge (ion) out of the cell, which initiates osmosis of water out of the cell as well as prevents any cell from swelling.
Where does sodium glucose transport?
Sodium glucose co-transport in proximal convoluted tubule of nephron ― Here carrier protein undergoes conformational change and ready for transporting only when sodium and glucose attaches to it and both moves in same direction. The energy is obtained from the stored energy due to sodium transport by Na + K + pump on the basolateral membrane of the tubule. This creates a high concentration gradient for sodium ion inside the tubular cell. Thereby the stored energy due to the gradient is used for sodium as well as glucose transport along with it along the luminal side of the tubule.
What is the net movement of a substance (liquid or gas) from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration without?
It is the net movement of a substance (liquid or gas) from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration without expenditure of energy is called diffusion.
What are the types of transport through the cell membrane?
Types of Transport through cell membranes, Active transport, Simple & Facilitated diffusion. Cells are bathed in the interstitial fluid that is derived from the blood. The interstitial fluid contains thousands of ingredients, nutrients, vitamins, hormones, ions, and waste products. The cell membrane consists almost entirely of a lipid bilayer, ...
Which layer of the cell membrane transports substances?
It is the transport of substances either through the lipid bilayer or through the channel proteins of the cell membrane along the electrochemical gradient & according to the physicochemical laws.
Why is the lipid bilayer important?
Therefore, it constitutes a barrier against the movement of water and water-soluble substances between the extracellular and intracellular compartments.
Why is facilitated diffusion important?
Facilitated diffusion is important to transport the polar and/or large molecules such as sugars and amino acids. Facilitated diffusion depends on the availability of the carrier, high concentration gradient of the substance through the membranes, rapid combination and splitting of the carrier with the transported substance, and saturation of the carrier. As glucose is normally in higher concentrations in the blood than in the cells, it can be transported from the blood into the cells in association with a specific carrier.
What is passive transport?
Passive Transport means random molecular movement through intermolecular spaces in the membrane or in combination with a carrier protein, from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, by the aid of the kinetic energy of the molecules. The molecules diffuse along down, their concentration gradient, ...
How is glucose transported into cells?
Glucose and amino acids are transported into most cells against large concentration gradients by the co-transport mechanism. The excess sodium outside the membrane always attempts to diffuse to the interior, uses the stored energy to pull other substances along with it through the membrane. This is achieved by means of a carrier protein that serves as an attachment point for both the sodium ion and the substance to be co-transported.
Where does active transport occur?
Active transport occurs only through the lipid layer of the cell membrane where the transported substance combines with a specific carrier protein. It requires energy derived directly from the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) or another high-energy phosphate compound (creatine phosphate). This leads to the conformational change in the carrier and it pumps the carried substance across the membrane. The most important example of a primary active transport is the sodium-potassium (Na+-K+) pump.
What are the two types of transport that the cell membrane provides?
Cell membrane provides structure for the cell, protects cytosolic contents from the environment, and allows cells to act as specialized units.The two types of transport are Active and passive transport.
What is the role of active transport in the cell membrane?
B) Active transport - requires the cell to use energy, usually in the form of ATP. Active transport creates a charge gradient in the cell membrane. It keeps unwanted ions or other molecules out of the cell that are able to diffuse through the cell membrane.
What is the transporter of proteins in the vacuole membrane?
Recently, a team of researchers in UCLA found that the transmembrane protein transport is mediated by a specific malarial protein called “PTEX”. PTEX is a transporter protein anchored on the vacuole membrane. When malarial proteins are being transported, they are unwound into long peptides, which allows them to get passed through the narrow channel of PTEX. The unwound proteins then fold back into their native forms in the host cell cytoplasm. Researchers not only solved the 3D structure of PTEX , but also found a small segment of peptide trapped in the channel, indicating that proteins are indeed “squeezed” through it.
What is the thickness of a biomembrane?
The thickness of biomembrane is 75 angstrom . It is phospholipid bilayer with extrinsic& intrinsic proteins,carbohydrates. Lipids posses one hydrophilic polar head and two hydrophobic non-polar tail. Hence, lipids are amphipathic. The bilayer is arranged in such a way that tail is sandwiched between head.
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
On the other hand, passive transport moves biochemicals from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration; so it does not require energy.
Which bilayer of the cell contains cholesterol?
Cell membranes also contain cholesterol in the phospholipid bilayer. In some membranes there are only a few cholesterol molecules, but in others there are as many cholesterols
What is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane?
The movement of water across a semi permeable membrane. Osmosis is the movement of water (red dots) through a semipermeable membrane to a higher concentration of solutes (blue dots).
What ions are used to produce more ATP in ETC?
The hydrogen ions will separate from NAHD and FADH2 which are then used to produce more ATP in ETC. (Oxidation-Reduction or a redox reaction)
What are the main products of the Krebs cycle?
The main products of the Krebs cycle are 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, CO2, and 2 ATP. (It goes through this process twice because of the 2 ATP made in glycolysis) making a total of 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, CO2, and 4 ATP. Therefore there is not much energy made in the Krebs cycle, most ATP is made in the ETC.
How much ATP is produced in aerobic respiration?
For aerobic respiration, glucose makes in total 36-38 ATP and in anaerobic respiration 2 ATP are produced (since it uses 2 ATP to start the process). In each step of the process, a different amount of ATP are produced.
What is the function of ATP synthase?
ATP synthase is a protein that is responsible for creating ATP in the mitochondria. ATPase is an enzyme/protein that uses ATP as a power source to produce function. (-ase = enzyme)
Where does glycolysis occur?
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and the Krebs cycle ad electron transport chain both occur in the mitochondria. The Krebs cycle more specifically occurs in the matrix and the electron transport chain occurs in the Cristae.
Can ions cross the plasma membrane?
Ions cannot freely cross the lipid portions of the plasma membrane, they can enter and exit the cell only through membrane channels. The distinction may be based on size, electrical charge, molecular shape, lipid solubility, or other factors.
Is simple diffusion mediated or unassisted?
Simple diffusion is unassisted diffusion. Solutes transported this way are either: 1. Lipid - soluble or 2. Small enough to pass through the membrane pores. Channel mediated diffusion is where membrane channels act as very small passageways created by transmembrane proteins. Whether an ion can cross a particular membrane channel depends on many factors including the size and charge of the ion, size of the hydration sphere, and interactions between the ion and the channel walls.
