Comparison Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic ...
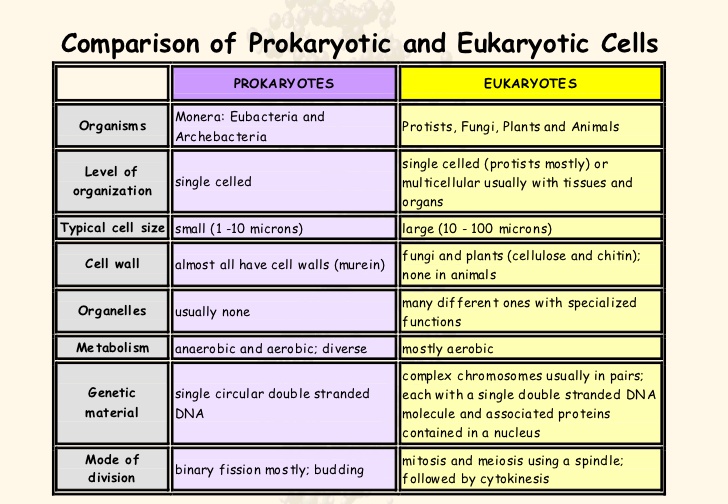
| Characteristic | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| Size of cell | Typically 0.2-2.0 m m in diameter | Typically 10-100 m m in diameter |
| Nucleus | No nuclear membrane or nucleoli (nucleoi ... | True nucleus, consisting of nuclear memb ... |
| Membrane-enclosed organelles | Absent | Present; examples include lysosomes, Gol ... |
What are 5 examples of prokaryotic cells?
- Azotobacter vinelandii
- Bacillus subtilis
- Clostridium tetani
- Diplococcus pneumoniae
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Rhizobium leguminosarum
- Rhodosprillium rubrum
- Salmonella typhi
What is the size range of an eukaryotic cell?
The eukaryotic cell ranges from 5-100 micrometers. How big are eukaryotic plant or animal cells on average? Plant cells can be larger than animal cells. The normal range for an animal cell varies from 10 to 30 micrometers while that for a plant cell stretches from 10 to 100 micrometers.
What is the comparison between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Well, to summarise, prokaryotic cells are unicellular micro-organisms, whereas eukaryotic cells are multi-cellular organisms. The nucleus is present in eukaryotic cells, while there is no nuclei present in prokaryotic cells.
Why do prokaryotic cells have no nucleus?
They have no nucleus; instead their genetic material is free-floating within the cell. They also lack the many membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Thus, prokaryotes have no mitochondria. How do prokaryotic cells survive in the absence of important organelles like mitochondria and nucleus?
Do we (humans) have prokaryotic cells in our bodies?
Ans. We have some bacteria in our mouth and stomach that help to produce vario... Read full
How does the nucleoid stay in one place in a prokaryotic cell where the plasma membrane is absent?
Ans: Nucleoid is made up of DNA and proteins. Proteins are responsible for mai... Read full
How can a prokaryotic cell survive without organelles?
Ans. A transport function is unnecessary in prokaryotic cells since there are ... Read full
Which is a unicellular eukaryote?
Ans. Unicellular eukaryotes are Protists. Example: Paramecium, Chrysophytes, Euglena, Dinoflagellates, Slime moulds,... Read full
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
The most obvious difference between them is that prokaryotes have no nuclei, but there are four major differences between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell: No prokaryotic cell has a nucleus; every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells have no mitochondria;
What is the nucleus of an eukaryotic cell?
The word eukaryote comes from two Greek roots, eu (good, well), and karyon (nut, kernel), so a eukaryote has a well-defined or “good” nucleus (kernel) in its cells.
How do prokaryotic cells recycle nutrients?
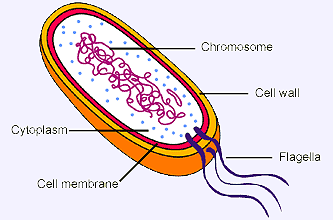
Facts About Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotes help recycle nutrients by decomposing dead organisms. Bacteria in the intestines and mouths of all higher animals help with the digestion of food. The DNA of a prokaryotic cell is tightly coiled in a ‘nucleoid,’ which is not a true nucleus since it has no membrane.
Which type of cell has intracellular structures?
Intracellular structures are common to both types of cells. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have:
Which type of cell has circular DNA?
Prokaryotic cells have circular strands of DNA; eukaryotic cells have multiple molecules of double-stranded, linear DNA.
Where do eukaryotes store DNA?
Eukaryotic cells store chromatin (DNA and proteins) in a gel-like fluid called the nucleoplasm, inside the nucleus.
Why do all living things use cellular organization?
All living organisms use cellular organization to create structures to conduct life processes. Cells organize into tissues, which organize into organs, which organize into amazing life forms like plants, fungi, dogs, ducks, and people.
Which is larger, prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are either archaea or bacteria. Their cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes include larger, more complex organisms such as plants and animals. Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus. Prokaryotes divide via using binary fission, while eukaryotic cells divide via mitosis.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Differences in Organization. Prokaryotic cells engage in reproduction through a process of cell division called binary fission. Eukaryotic cells use a different process of cell division called mitosis, which involves a constant cycle of cell growth and development.
Why are prokaryotic cells different from eukaryotic cells?
The reason for the difference in cell sizes between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells belongs to the different structure and organization between the two types of cells. The lack of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotes might be the most noticeable difference. While eukaryotic cells contain organelles enclosed in membranes – two examples ...
What are the two main categories of cells?
All of these cells, whether they operate as a solitary bacterial cell or as part of a complex system such as the human body, can be sorted into two main categories: eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells .
How do eukaryotes reproduce?
Eukaryotes reproduce sexually through meiosis, which allows for genetic variance. Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, copying themselves. Despite this, gene transfer processes still allow for genetic variance. One of these is transduction in which viruses move DNA from one bacterium to another.
Which domain has eukaryotic cells?
Eukarya. The organisms in Archaea and Bacteria are prokaryotes, while the organisms in Eukarya have eukaryotic cells. The Archaea domain has subcategories, but scientific sources differ on whether these categories are phyla or kingdoms. They are:
Where does DNA store in a prokaryote?
Instead, most of their DNA is in one chromosome-like structure that sits in an area of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. This nucleoid does not have a membrane of its own.
Which is smaller, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Scientists speculate that these organisms gave rise to the eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are comparatively smaller and much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The other defining characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that it does not possess membrane-bound cell organelles such as a nucleus.
What is the meaning of eukaryotic cell?
The term “ Eukaryotes ” is derived from the Greek word “ eu “, (meaning: good) and “ karyon ” (meaning: kernel), therefore, translating to “ good or true nu clei .”. Eukaryotes are more complex and much larger than the prokaryotes. They include almost all the major kingdoms except kingdom monera.
What are the structures that help in cellular respiration?
It is also one of the smallest components within the cell. Some prokaryotic cells contain special structures called mesosomes which assist in cellular respiration.
What is the nucleus of a cell?
The nucleus contains DNA, which is responsible for storing all genetic information. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Within the nucleus exists the nucleolus, and it plays a crucial role in synthesising proteins. Eukaryotic cells also contain mitochondria, which are responsible for the creation of energy, which is then utilized by the cell.
Which type of cell has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the smallest part of a cell?
Right below the protective coating lies the cell wall, which provides strength and rigidity to the cell. Further down lies the cytoplasm that helps in cellular growth, and this is contained within the plasma membrane, which separates the interior contents of the cell from the outside environment. Within the cytoplasm, ribosomes exist and it plays an important role in protein synthesis. It is also one of the smallest components within the cell.
Which kingdoms have cell walls?
They include almost all the major kingdoms except kingdom monera. Structurally, eukaryotes possess a cell wall, which supports and protects the plasma membrane. The cell is surrounded by the plasma membrane and it controls the entry and exit of certain substances.