
What is the place where the vocal folds are attached?
The vocal folds are attached at the front of the larynx to the thyroid cartilage and at the back to the arytenoid cartilages. The arytenoid cartilages can be made to rotate in a swivelling movement and to slide apart along the cricoid cartilage on which they are located.
What are the true vocal cords made of?
The vocal cords are composed of twin infoldings of 3 distinct tissues: The outer layer is squamous, non-keratinizing epithelium. Below this is the superficial layer of the lamina propria, a gel like layer, which allows the vocal fold to vibrate and produce sound.
What is another word for vocal folds?
Synonyms for vocal folds include vocal cords, esophagus, larynx, pharynx, throat, voice, oesophagus, voice box, vocal bands and vocal processes. Find more similar words at wordhippo.com!
What structure contains the vestibular and vocal folds?
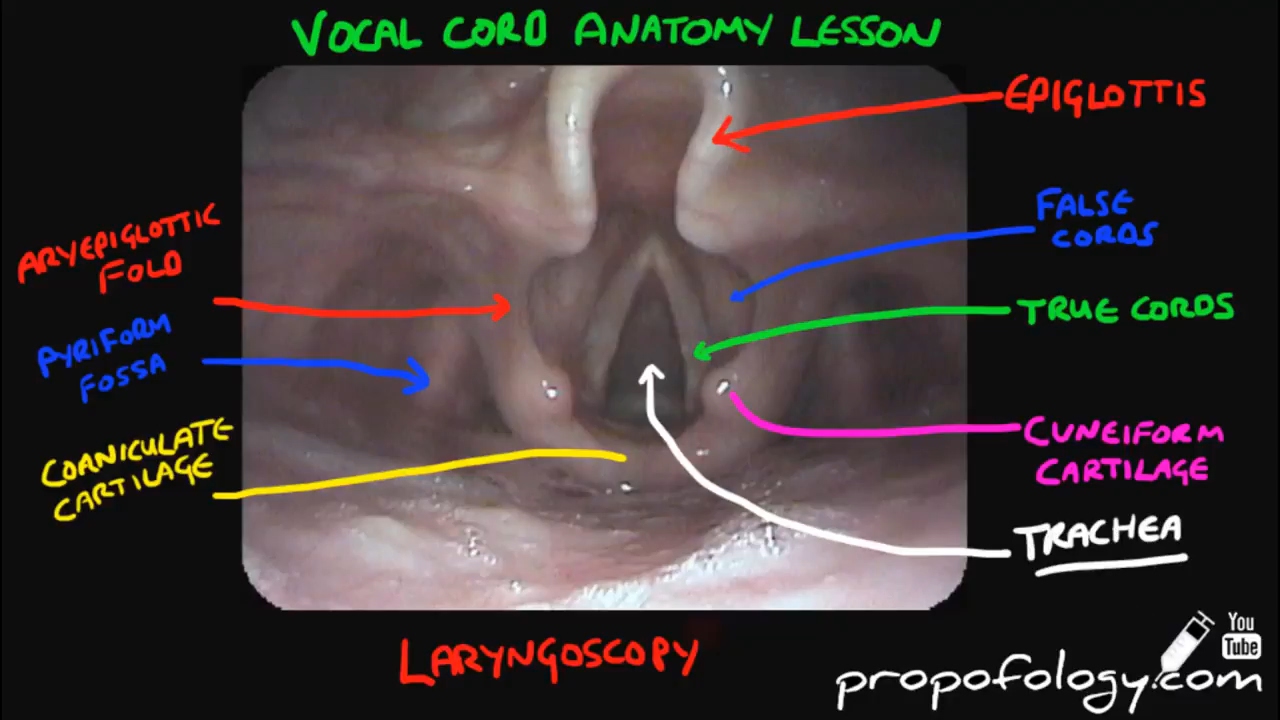
the pharynx name the structure that contains the vestibular and vocal folds. the larynx what protective function do the vestibular and vocal folds have the vestibular and vocal folds help prevent foreign particles including food from entering the lower respiratory system the vocal folds are also known as? why? the true vocal cords.
What is the vocal fold called?
vocal cordsThe vocal folds, also known as vocal cords, are located within the larynx (also colloquially known as the voice box) at the top of the trachea. They are open during inhalation and come together to close during swallowing and phonation.
What is the main function of the vocal folds?
Vocal cords: Your vocal cords, or vocal folds, open, close and vibrate as air passes through to create sounds and speech.
What is vocal folds in music?
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice.
What are the vocal folds and how do they work?
The vocal folds (vocal cords) are attached within the larynx to the largest of the laryngeal cartilages known as the thyroid cartilage or "Adam's apple". The vocal folds produce sound when they come together and then vibrate as air passes through them during exhalation of air from the lungs.
What are vocal folds made of?
The vocal folds are a pair of rubber band-like tissues located in your larynx (voice box) directly above the windpipe (trachea). They're made of up several layers of cells, including muscle and an elastic layer, known as the mucosa.
What are the 5 layers of the vocal folds?
The vocal fold comprises five layers (deep to superficial layers as follows): thyroarytenoid muscle, deep lamina propria, intermediate lamina propria, superficial lamina propria, and the squamous epithelium. The deep and intermediate lamina propria both are grouped to form the vocal ligament mentioned above.
Where are the vocal folds located?
larynxThe vocal cords (also called vocal folds) are two bands of smooth muscle tissue found in the larynx (voice box). The vocal cords vibrate and air passes through the cords from the lungs to produce the sound of your voice.
Do your vocal folds close when you hold your breath?
In the inhale/easy breath-hold group, true VFC occurred in 62%, and closure of both folds occurred in 46%. In the hard breath-hold group, true VFC occurred in 86%, and closure of both folds occurred in 64%.
How do vocal folds move?
As air passes through a constriction (or venturi), it speeds up and creates a suction in its wake. This suction draws in the pliable mucosa from each vocal fold, which meet in the midline only to be pushed aside by more air from the lungs. This cycle creates a repeating undulation which is known as the mucosal wave.
How do the vocal folds open and close?
Vocal folds vibrate when excited by aerodynamic phenomena; they are not plucked like a guitar string. Air pressure from the lungs controls the open phase. The passing air column creates a trailing “Bernoulli effect,” which controls the close phase.
What are the main vocal organs?
The main articulators are the tongue, the upper lip, the lower lip, the upper teeth, the upper gum ridge (alveolar ridge), the hard palate, the velum (soft palate), the uvula (free-hanging end of the soft palate), the pharyngeal wall, and the glottis (space between the vocal cords).
How do vocal folds change pitch?
Returning to our guitar-strings-in-gelatin analogy, when one string is plucked, the entire gel-fiber set shakes along with it. The muscles in the larynx further modulate the sound the cords produce, lengthening and shortening the cords to change the pitch.
Where are the vocal folds located?
VOCAL FOLDS. The vocal folds are to separate structures which are located in the larynx or voice box. Humans have two vocal folds which open and close during normal breathing, and during sound production, or phonation, the vocal folds come together and vibrate.
What is the outer layer of the vocal fold?
The vocal folds are intricately layered, which is the reason for unique sound production. The outer layer is squamous, non-keratinizng epithelium. Just deep to this is the superficial layer of the lamina propria. This is a gel like layer, which allows the vocal fold to vibrate and produce sound.
Why do vocal folds remain open?
If you have vocal fold paralysis, the paralyzed fold or folds may remain open, leaving the air passages and lungs unprotected.
How to change the position of the vocal fold?
The most common procedures change the position of the vocal fold. These may involve inserting a structural implant or stitches to reposition the laryngeal cartilage and bring the vocal folds closer together. These procedures usually result in a stronger voice.
What causes vocal fold paralysis?
Vocal fold paralysis may be caused by injury to the head, neck, or chest; lung or thyroid cancer; tumors of the skull base, neck, or chest; or infection (for example, Lyme disease). People with certain neurologic conditions such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's disease, or who have sustained a stroke, may experience vocal fold paralysis. In many cases, however, the cause is unknown.
How is vocal fold paralysis treated?
The most common treatments for vocal fold paralysis are voice therapy and surgery. Some people's voices will naturally recover sometime during the first year after diagnosis, which is why doctors often delay surgery for at least a year. During this time, your doctor will likely refer you to a speech-language pathologist for voice therapy, which may involve exercises to strengthen the vocal folds or improve breath control while speaking. You might also learn how to use your voice differently, for example, by speaking more slowly or opening your mouth wider when you speak. Several surgical procedures are available, depending on whether one or both of your vocal folds are paralyzed. The most common procedures change the position of the vocal fold. These may involve inserting a structural implant or stitches to reposition the laryngeal cartilage and bring the vocal folds closer together. These procedures usually result in a stronger voice. Surgery is followed by additional voice therapy to help fine-tune the voice.
What research is being done on vocal fold paralysis?
The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) supports research studies that explore the causes of vocal fold paralysis as well as better ways to treat the disorder. One surgical procedure, called medialization laryngoplasty, inserts a structural implant into the larynx to return voice quality. However, close to a quarter of the people who receive this treatment must return for repositioning surgery to fine-tune the placement of the implant. An NIDCD-supported researcher currently is developing a pre-operative planning system that uses 3-D computer modeling to determine the best location for, and configuration of, the implant. The surgery also uses an image-guided system that allows the surgeon to visualize the precise location of the vocal fold to ensure exact placement of the implant. Researchers hope this new system will reduce the need for repeated surgeries and lower the cost and risk of surgical complications from the procedure.
What is the term for a voice disorder that occurs when one or both of the vocal folds don't open?
Structures involved in speech and voice production. Vocal fold paralysis (also known as vocal cord paralysis) is a voice disorder that occurs when one or both of the vocal folds don't open or close properly. Single vocal fold paralysis is a common disorder.
How do you know if you have a paralysis of your vocal folds?
Symptoms of vocal fold paralysis include changes in the voice, such as hoarseness or a breathy voice; difficulties with breathing, such as shortness of breath or noisy breathing; and swallowing problems, such as choking or coughing when you eat because food is accidentally entering the windpipe instead of the esophagus (the muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach). Changes in voice quality, such as loss of volume or pitch, also may occur. Damage to both vocal folds, although rare, usually causes serious problems with breathing.
What are vocal folds?
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of tissue in the throat that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice.
What is the meaning of vocal folds?
Vocal folds (open) Vocal folds (speaking) In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of tissue in the throat that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech or singing, ...
What is the vocal cord made of?
The vocal cords are composed of twin infoldings of 3 distinct tissues: an outer layer of flat cells that do not produce keratin ( squamous epithelium ). Below this is the superficial layer of the lamina propria, a gel-like layer, which allows the vocal fold to vibrate and produce sound. The vocalis and thyroarytenoid muscles make up the deepest portion. These vocal folds are covered with a mucous membrane and are stretched horizontally, from back to front, across the larynx .
How many formants does a female voice have?
In females, the voice is three tones lower than the child's and has five to twelve formants, as opposed to the pediatric voice with three to six. The length of the vocal fold at birth is approximately six to eight millimeters and grows to its adult length of eight to sixteen millimeters by adolescence.
How do male and female voices differ?
Males and females have different vocal fold sizes. Adult male voices are usually lower-pitched due to longer and thicker folds. The male's vocal folds are between 1.75 cm and 2.5 cm (approx 0.75" to 1.0") in length, while females' vocal folds are between 1.25 cm and 1.75 cm (approx 0.5" to 0.75") in length. The vocal folds of children are much shorter than those of adult males and females. The difference in vocal fold length and thickness between males and females causes a difference in vocal pitch. Additionally, genetic factors cause variations between members of the same sex, with males' and females' voices being categorized into voice types .
How do vocal cords affect pitch?
The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech or singing, the folds are controlled via the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve. They are composed of twin infoldings of mucous membrane stretched horizontally, from back to front, across the larynx.
Where are vocal folds located?
The vocal folds are located within the larynx at the top of the trachea. They are attached at the back to the arytenoid cartilages, and at the front to the thyroid cartilage. They are part of the glottis. Their outer edges are attached to muscle in the larynx while their inner edges form an opening called the rima glottidis. They are constructed from epithelium, but they have a few muscle-fibres in them, namely the vocalis muscle which tightens the front part of the ligament near to the thyroid cartilage. They are flat triangular bands and are pearly white in color. Above both sides of the glottis are the two vestibular folds or false vocal folds which have a small sac between them.
What are the vocal folds?
Housed within the larynx are two band-like structures, which stretch horizontally across the opening of the trachea (windpipe). These bands are called the vocal folds, also referred to as vocal cords . Both names are correct, though in the medical world the former title is more accurate. Larynx from the top.
Where is the V shape of the vocal folds?
The vocal folds form a ‘V’ shape, with the narrow end towards the front of the larynx i.e. throat side and the broad end towards the spine.
What muscles are used when singing?
The Thyroarytenoid (TA) and Cricothyroid (CT) muscles are major players when it comes to singing. The TA is more dominant in the lower end of our range (sometimes called the chest register) and the CT muscles help us to access the upper part of our range (also called the head register). When we speak we are mainly using the TAs and if we make a high “Wheee” sound then the CTs have been engaged.
Why does the larynx move down when we swallow?
A flap called the epiglottis (see The larynx, home of the voice! for more info) moves down over the top of the vocal folds to help them keep food and fluid out of the trachea, and ultimately the lungs. This is vital for our survival. If the swallowing mechanism is faulty we could choke and ultimately die – bad thing!
How to produce wide range of pitches?
In order to produce the wide range of pitches used in singing the vocal folds need to: vibrate at different speeds. shorten and thicken. lengthen and thin. Vocal fold density and length is achieved through a complex set of movements made by several sets of paired muscles attached to and around the vocal folds.
What is the normal frequency of the vocal folds?
At middle C (4) the vocal folds oscillate at 261Hz. The normal speaking voice of a male they oscillate between 85-105Hz and a female between 165Hx-255Hz. So as you can see when we speak the demand on the vocal folds is much lower than in singing.
How many times can a vocal fold move?
The vocal folds are made up of a very special tissue, which can withstand vibratory movement, known as oscillations, of over 1000 times per second (Hertz/Hz). Imagine if you rubbed two fingers together at such speeds, you would end up with a friction burn.
What is vocal fold atrophy?
Vocal fold atrophy refers to a gradual change in the vocal folds as people age. The vocal fold muscle can become thinner and/or less taut overtime. The soft outer layer of the vocal folds can also lose bulk over time. These tissue changes affect the ability of the vocal folds to vibrate regularly and can cause an abnormal gap between the vocal folds.
What is the most common symptom of vocal fold atrophy?
The voice can be affected during speaking, singing or both. Often, roughness/hoarseness will be associated with an increased effort to talk and subsequent fatigue or tiring of the voice with continued use.
What is the best way to diagnose vocal fold atrophy?
a. Careful examination of the vocal folds is essential for making the diagnosis of vocal fold atrophy. Examination is typically performed using a flexible laryngoscope with a stroboscopic light source.
Why is a stomoscope used for vocal folds?
Stroboscopy is used to quantify the gap between the vocal folds and to evaluate vocal fold vibratory qualities. It is essential in diagnosis and treatment planning.
How does voice therapy help?
Voice therapy helps the patient improve vocal symptoms through techniques geared at improving the way the body (muscles, lungs etc.) work together to create voice. These techniques are geared to help the patient produce voice in the most efficient way possible, despite changes in muscles tissue from vocal fold atrophy. Sometimes, voice therapy is only partially effective due to inherent limitations in the vocal mechanism.
Is vocal fold atrophy treatable?
Vocal fold atrophy is a treatable condition; however, it is not uncommon that patients undergo more than one treatment option. There is currently no treatment that can restore the “taut” tissue quality in the vocal folds; therefore,treatment more often focuses on improving vocal fold muscle bulk and/or optimizing voicing techniques in light of the patient’s anatomical deficit through voice therapy. At present, response to treatment for vocal fold atrophy remains variable.
Why do vocal folds deteriorate?
The primary cause of vocal fold atrophy is aging . The larynx (voice box) and vocal fold muscles age just like the muscles in the rest of the body. Just as we all age differently, the degree and severity of age-related changes to the vocal folds vary from person to person. In other cases, people may develop vocal fold atrophy as a consequence of a nerve injury. Some people are simply born with thinner vocal fold muscles than others.
What is vocal fold atrophy?
Vocal fold atrophy is a voice disorder that usually occurs gradually over time as people age. The vocal fold muscles become thin and less taught, preventing the vocal folds from closing normally when voicing.
What is the treatment for aging voice?
Surgical Treatment for Aging Voice. In more severe cases of vocal fold atrophy which do not respond to voice therapy, surgical intervention is offered. Surgical options consist of procedures that attempt to assist in closing the gap between the vocal folds during voicing.
What does it mean when your voice is weak?
In general, vocal fold atrophy may result in a “weak” or quiet voice that is effortful or fatiguing to use. Some patients experience pitch changes, hoarseness, or roughness in vocal quality. In more significant cases, patients report a sensation of “running out of air” when speaking. Other symptoms may include throat clearing or difficulty swallowing.
What is the term for a curved voice?
Vocal fold atrophy, also often called "aging voice" or "presbyphonia," is a voice condition characterized by thinning of the vocal fold muscles and tissues. This loss of muscle bulk often results in a curved appearance that prevents the vocal folds from closing normally when speaking or singing. Other surrounding laryngeal muscles may squeeze more ...
What is the voice and swallowing center?
Our voice care team at the Voice and Swallowing Center has the advanced training and skills necessary to diagnose this voice condition. During the initial visit, you will be assessed by one of our laryngologists and likely, an additional session with one of our voice pathologists. We use cutting-edge diagnostic tests to determine the cause of your voice disorder and to develop your plan of care. Following a thorough discussion of your symptoms and medical history, be expected to undergo the following assessments:
Can voice therapy be combined with surgery?
In other cases, voice therapy may need to be combined with surgical treatment (i.e. before surgery, after surgery, or both).
What is the term for a white plaque on the vocal fold?
Vocal fold leukoplakia is a white plaque-like lesion that forms on the surface of the vocal fold. Dysplasia is a pre-cancerous condition that occurs due to abnormal cell changes in the vocal fold.
What is vocal fold leukoplakia?
Referring Physicians. Vocal fold leukoplakia is a white patch-like lesion that forms on the surface of one or both vocal folds. The lesion has a white appearance due to an increased growth of cells. Abnormal cell growth is called dysplasia, which can be indicative of an early cancerous process.
Can vocal fold leukoplakia be treated?
In many cases of vocal fold leukoplakia, close observation only is an appropriate treatment option.
Can LPR cause vocal fold leukoplakia?
If laryngopharyngeal reflux (LP R) is a suspected contributor to the vocal fold leukoplakia or dysplasia, LPR is often managed with dietary and lifestyle modifications and/or prescription medications. In some cases, voice therapy with special attention to efficient and healthy voice use may help to reduce some symptoms including vocal effort/fatigue.
