
A zonal statistics operation is one that calculates statistics on cell values of a raster (a value raster) within the zones defined by another dataset. There are two tools that calculate statistics by zones, Zonal Statistics and Zonal Statistics as Table.
What is a zonal statistics Operation?
A zonal statistics operation is one that calculates statistics on cell values of a raster (a value raster) within the zones defined by another dataset. There are two tools that calculate statistics by zones, Zonal Statistics and Zonal Statistics as Table. The Zonal Statistics tool calculates only one statistic at a time and creates a raster output.
What is the output of zonal statistics raster?
The output zonal statistics raster. This example determines for each zone the range of cell values in the Value input raster. This example determines for each zone the range of cell values in the Value input raster. # Name: ZonalStatistics_Ex_02.py # Description: Calculates statistics on values of a raster # within the zones of another dataset.
Why are my statistics only for one zone?
If a zone feature contains overlapping zones, the statistic is computed for only one zone because a cell in the output raster can represent only one value. The Zonal Statistics as Table tool calculates one or multiple statistics using predefined subsets or all statistics and creates a table output.
How do you find the Zonal Value of a cell?
For such cells, the zone value is determined by the point with the lowest ObjectID field (for example, OID or FID). If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) has overlapping polygons, the zonal analysis will not be performed for each individual polygon.
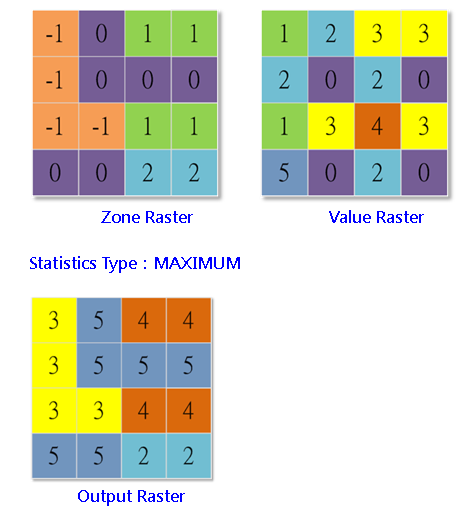
How do you use zonal statistics?
Zonal Statistics uses groupings to calculate statistics for specified zones. For example, it can calculate the mean, median, sum, minimum, maximum, or range in each zone. The zonal extent could include anything from country boundaries, watershed catchment areas, or property parcels as a vector or raster dataset.
Why is zonal statistics not working?
If the raster cell size is larger than a given boundary, there may be no cells with centroids within the boundary, and hence no statistics or inaccurate statistics are produced for that zone.
What are zonal operations?
Zonal operations: value of each output cell determined by all the input cells of the same zone. An example zonal operation is to return the mean (average) of values from the first dataset that fall within a specified zone of the second.
What are zones in GIS?
Any two or more cells with the same value belong to the same zone. A zone can consist of cells that are adjacent, disconnected, or both. Zones whose cells are adjacent usually represent a single feature of an area, such as a building, road, or water body.
How do you do zonal statistics in Arcgis pro?
0:091:53Example of Zonal Statistics as Table in ArcGIS Pro - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOkay so our input raster. Features own data will be what we're wanting to use as our zones. So inMoreOkay so our input raster. Features own data will be what we're wanting to use as our zones. So in that case we're going to use our counties data and then we want a unique identifier. For each zone.
Where are zonal stats in Qgis?
0:315:39Zonal statistics in QGIS - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn the lower left of the qgis window you can find the search box where you can search for tools if iMoreIn the lower left of the qgis window you can find the search box where you can search for tools if i type zono a lot of tools will pop up. We're going to use the zono statistics.
What is neighborhood analysis GIS?
Neighbourhood operations are a method of analysing data in a GIS environment. They are especially important when a situation requires the analysis of relationships between locations, rather than interpret the characteristics at individual locations.
What is GIS spatial analysis?
The true power of GIS lies in the ability to perform analysis. Spatial analysis is a process in which you model problems geographically, derive results by computer processing, and then explore and examine those results.
What is the purpose of spatial interpolation?
Spatial interpolation is the process of using points with known values to estimate values at other points. In GIS applications, spatial interpolation is typically applied to a raster with estimates made for all cells. Spatial interpolation is therefore a means of creating surface data from sample points.
What are focal statistics?
The Focal Statistics tool performs a neighborhood operation that computes an output raster where the value for each output cell is a function of the values of all the input cells that are in a specified neighborhood around that location.
What is zone of influence?
The zone of influence is the area above and beside an asset where loads may have an impact on that asset. Generally this will be 1.5 metres either side of the main.
What is map algebra in GIS?
Map Algebra is a simple and powerful algebra with which you can execute all Spatial Analyst tools, operators, and functions to perform geographic analysis. Map Algebra is available through the Spatial Analyst module; an extension of the ArcPy Python site package.
What is zone in Python?
A zone is defined as all areas in the input that have the same value. The areas do not have to be contiguous. Both raster and feature can be used for the zone input. If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) is a raster, it must be an integer raster. If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) ...
When are zone and value inputs rasters of the same cell size and the cells are aligned?
When the zone and value inputs are both rasters of the same cell size and the cells are aligned, they will be used directly in the tool and will not be resampled internally during tool execution.
What is the default zone field in Python?
When specifying the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python), the default zone field will be the first available integer or text field. If no other valid fields exist, the ObjectID field (for example, OID or FID) will be the default.
What happens when there is a tie in a zone?
For majority and minority calculations, when there is a tie, the output for the zone is based on the lowest of the tied values. See How the zonal statistics tools work for more information.
What is minority in raster?
Minority —The value that occurs least often of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell will be calculated.
What is used to make resolutions match before zonal operation?
If the resolutions are different, an internal resampling is applied to make them match before the zonal operation is performed.
What happens when the zone input is a feature dataset with relatively small features?
If the zone input is a feature dataset with relatively small features, keep in mind that the resolution of the information needs to be appropriate relative to the resolution of the value raster. If the areas of single features are similar to or smaller than the area of single cells in the value raster, in the feature-to-raster conversion some of these zones may not be represented.
What is zone in raster?
A zone is defined as all areas in the input that have the same value. The areas do not have to be contiguous. Both raster and feature datasets can be used for the zone input. When the zone and value inputs are both rasters of the same resolution, they will be used directly.
Why use rasters in zone?
It is recommended to only use rasters as the zone input, as it offers you greater control over the vector-to-raster conversion. This will help ensure you consistently get the expected results.
What happens when reserved field is selected in a zone field?
If a reserved field (for example, OBJECTID, FID, or OID) is selected for the Zone field, then this may cause some ambiguity in the result. The result includes the particular reserved field name necessary for the particular output format type, as well as the Zone field specified. If the specified field has the same name as the reserved field for the particular output format, in the output, the name for the zone field will be altered in such a way that all field names in the result are unique.
When there is a tie, what is the output for the zone?
For majority and minority calculations, when there is a tie, the output for the zone is based on the lowest of the tied values.
Can you have more than one point in a zone?
If the zone input is a point feature dataset, it is possible to have more than one point contained within any particular cell of the value input raster. For such cells, the zone value is determined by the point with the highest feature ID.
What is zonal statistics?
A zonal statistics operation is one that calculates statistics on cell values of a raster (a value raster) within the zones defined by another dataset. There are two tools that calculate statistics by zones, Zonal Statistics and Zonal Statistics as Table.
What is zonal operation?
A zonal operation is fundamentally a raster analysis performed on two rasters, in which one is the zone and other is the value. If the zones are defined by features, an internal feature to raster conversion will occur. The internal conversion for a polygon zone uses the cell center method in the Polygon to Raster tool to rasterize the input using the cell size and the snap raster of the value raster. This can lead to an unexpected result of missing zones in the output when none of the cell centers of the rasterization grid fall within the feature zone. This can occur with zones that are smaller than the area of a cell of the internal zone raster as well as with larger zones.
How to determine the number of slices in a multidimensional raster?
The number of slices in the output multidimensional raster is determined by multiplying the number of slices in the zone raster by the number of slices in the value raster.
How to find maximum salinity of ocean?
Finding the maximum salinity at various depths of the ocean for various temperature ranges at a corresponding depth will require performing zonal statistics with a multidimensional zone representing temperature zones and a multidimensional value raster representing salinity. The zonal operation will be performed for each zone slice with the corresponding slice from the value raster. The output multidimensional raster will have the same number of slices as the value raster.
What is multidimensional raster data?
Multidimensional raster data represents data at multiple times and multiple depths or heights. This type of data is commonly used in atmospheric, oceanographic, and earth sciences and is observed by monitoring platforms, captured by satellites, or generated from numerical simulation models where data is processed, aggregated, or interpolated using various statistical techniques. To learn more about multidimensional rasters, see An overview of multidimensional raster data.
Why is the statistic computed for only one zone?
If a zone feature contains overlapping zones, the statistic is computed for only one zone because a cell in the output raster can represent only one value.
What is zone in raster?
In raster data, a zone is all the cells that have the same value, whether they are contiguous or not. Each zone must have a unique identity and if it is a raster, it must have an integer data type.
What is a zonal statistic?
The Zonal Statistics as Table tool calculates all, a subset or a single statistic that is valid for the specific input but returns the result as a table instead of an output raster.
What is the median of the values in each zone assigned to?
The median of the values in each zone is assigned to all output cells in that zone.
When there is a tie for the majority value in a zone, the output for all cell locations in the zone?
When there is a tie for the majority value in a zone, the output for all cell locations in the zone is assigned the lowest of the tied values.
What is standard deviation assigned to?
The standard deviation of the values in each zone is assigned to all cells in that zone.
Summary
Calculates statistics on values of a raster within the zones of another dataset.
Usage
A zone is defined as all areas in the input that have the same value. The areas do not have to be contiguous. Both raster and feature can be used for the zone input.
What is the default setting for statistics?
Unchecked—Statistics will be calculated from the current slice of the input multidimensional dataset. This is the default.
What happens when a feature zone data is overlapping?
If the Input raster or feature zone data ( in_zone_data in Python) has overlapping features, the zonal analysis will be performed for each individual feature.
What is standard deviation in raster?
Standard deviation —The standard deviation of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell will be calculated.
What is minority in raster?
Minority —The value that occurs least often of all cells in the value raster that belong to the same zone as the output cell will be calculated.
What happens when there is a tie in a zone?
For majority and minority calculations, when there is a tie, the output for the zone is based on the lowest of the tied values. See How the zonal statistics tools work for more information.
When are zone and value inputs rasters of the same cell size and the cells are aligned?
When the zone and value inputs are both rasters of the same cell size and the cells are aligned, they will be used directly in the tool and will not be resampled internally during tool execution.
What is the number of rows in the output table?
The number of rows in the output table is the number of zones.
