
About Bacillus
- Gram-positive Bacilli form bacteria are Actinomyces, Clostridium, Bacillus or gram-negative bacteria, e.g. Escherichia, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Streptobacillus, etc.
- They have the capability of serving at high temperatures i.e. ...
- They are mostly non-parasitic and free-living in nature.
- They are known to be one of the most abundantly found bacteria.
Full Answer
Is Bacillus harmful to humans?
Some types of Bacillus bacteria are harmful to humans, plants, or other organisms. For example, B. cereus sometimes causes spoilage in canned foods and food poisoning of short duration. B. subtilis is a common contaminant of laboratory cultures (it plagued Louis Pasteur in many of his experiments) and is often found on human skin.
What does the term Bacillus refer to?
bacillus, (genus Bacillus ), any of a genus of rod-shaped, gram-positive, aerobic or (under some conditions) anaerobic bacteria widely found in soil and water. The term bacillus has been applied in a general sense to all cylindrical or rodlike bacteria.
What is the difference between Bacillus and bacilli?
What are the Similarities Between Lactobacillus and Bacillus Clausii?
- Lactobacillus and Bacillus Clausii are probiotics.
- Both classify under the class
- They are both gram-positive, rod-shaped, and motile bacteria.
- These bacteria can form mutualistic relationships with the human host.
- Both bacteria are considered as helpful or good bacteria to humans.
- They produce proteases and survive in harsh acidic environments.
What are facts about bacteria?
- There are around 40 million bacteria in a gram of soil.
- Bacteria can survive in very harsh conditions including deep areas of the Earth's crust and in radioactive waste.
- There are around as many bacteria cells in a human body as there are human cells.
- Bacteria are used to help the environment by treating sewage and breaking down oil from oil spills.
See more

What are bacilli bacteria?
Bacillus species are aerobic, sporulating, rod-shaped bacteria that are ubiquitous in nature. Bacillus anthracis, the agent of anthrax, is the only obligate Bacillus pathogen in vertebrates. Bacillus larvae, B lentimorbus, B popilliae, B sphaericus, and B thuringiensis are pathogens of specific groups of insects.
What class of bacteria is Bacillus?
BacilliBacillus / ClassBacillus (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum Bacillota, with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of certain bacteria; and the plural Bacilli is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs.
What is a common example of Bacillus bacteria?
Bacillus: Single unattached cell, that looks like a rod. Examples are Bacillus cereus, Salmonella enterica, etc. Diplobacilli: In these bacteria, two rods are attached and found in pairs after cell division. Examples are Moraxella Bovis, Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis, etc.
Where do you find Bacillus bacteria?
The vast majority of these bacteria are nonpathogenic, environmental organisms found in soil, air, dust, and debris. These organisms typically dominate indoor air in occupied buildings, are abundant in dust and on surfaces, and are common components of the microflora of cleanrooms.
Is E coli a Bacillus?
E coli is a gram-negative bacillus that grows well on commonly used media. It is lactose-fermenting and beta-hemolytic on blood agar.
Is Bacillus a Gram-positive bacteria?
Gram-positive bacilli (rods) subdivide according to their ability to produce spores. Bacillus and Clostridia are spore-forming rods while Listeria and Corynebacterium are not. Spore-forming rods that produce spores can survive in environments for many years.
What is Bacillus give two examples?
Definition of bacillus 1 : any of a genus (Bacillus) of rod-shaped gram-positive usually aerobic bacteria producing endospores and including many saprophytes and some parasites (such as B. anthracis of anthrax) broadly : a straight rod-shaped bacterium. 2 : bacterium especially : a disease-producing bacterium.
What are the 4 types of bacteria?
Bacteria can be classified based on their shape into bacillus, coccus, vibrio and spirillum.
What are the 3 main types of bacteria?
There are three basic shapes.Spherical: Bacteria shaped like a ball are called cocci, and a single bacterium is a coccus. Examples include the streptococcus group, responsible for “strep throat.”Rod-shaped: These are known as bacilli (singular bacillus). ... Spiral: These are known as spirilla (singular spirillus).
How do you get a Bacillus infection?
Serious infections caused by Bacillus species include ocular infections, endocarditis, bacteremia and septicemia, pneumonia, meningitis, musculoskeletal infections (40), and infections associated with injuries from motor vehicle accidents associated with road trauma (44) and gunshot injuries (23).
Is Bacillus harmful or helpful?
Some types of Bacillus bacteria are harmful to humans, plants, or other organisms. For example, B. cereus sometimes causes spoilage in canned foods and food poisoning of short duration.
What is Bacillus probiotic?
Bacillus coagulans is a type of bacteria. It is used similarly to lactobacillus and other probiotics as "beneficial" bacteria. People take Bacillus coagulans for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diarrhea, gas, airway infections, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
What is the family of Bacillus?
Family: Bacillaceae. Genus: Bacillus. Cohn. Species. See text. Bacillus (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum Firmicutes, with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of certain bacteria; and the plural Bacilli is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus ...
When was the bacterium Bacillus named?
The genus Bacillus was named in 1835 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, to contain rod-shaped (bacillus) bacteria. He had seven years earlier named the genus Bacterium. Bacillus was later amended by Ferdinand Cohn to further describe them as spore-forming, Gram-positive, aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacteria.
What is the role of Bacillus subtilis in the production of enzymes?
Many species of Bacillus can produce copious amounts of enzymes, which are used in various industries, such as in the production of alpha amylase used in starch hydrolysis and the protease subtilisin used in detergents. B. subtilis is a valuable model for bacterial research.
How many endospores are there in Bacillus anthracis?
Only one endospore is formed per cell. The spores are resistant to heat, cold, radiation, desiccation, and disinfectants. Bacillus anthracis needs oxygen to sporulate; this constraint has important consequences for epidemiology and control.
What are the conditions that Bacillus species are found in?
in soil. They can occur in extreme environments such as high pH ( B. alcalophilus ), high temperature ( B. thermophilus ), and high salt concentrations ( B. halodurans ). B. thuringiensis produces a toxin that can kill insects and thus has been used as insecticide. B. siamensis has antimicrobial compounds that inhibit plant pathogens, such as the fungi Rhizoctonia solani and Botrytis cinerea, and they promote plant growth by volatile emissions. Some species of Bacillus are naturally competent for DNA uptake by transformation.
How to isolate Bacillus species?
An easy way to isolate Bacillus species is by placing nonsterile soil in a test tube with water, shaking, placing in melted mannitol salt agar, and incubating at room temperature for at least a day. Cultured colonies are usually large, spreading, and irregularly shaped.
How long can Bacillus survive in a controlled environment?
This resistance allows them to survive for many years and especially in a controlled environment. Bacillus species are well known in the food industries as troublesome spoilage organisms.
Bacillus Bacteria Classification
The prokaryotes that people come into contact with on a daily basis are classified as domain Bacteria. Their cell walls include peptidoglycan. Amino acids and sugars combine to form peptidoglycan. It is also responsible for forming the cell wall. Prokaryotes are mostly single-celled organisms.
Bacillus Bacteria: Importance and Uses
Bacillus spp. are found in a variety of habitats, including soil, and are resistant to a variety of stresses. Because of their capacity to live in harsh environments such as high pH (B. alcalophilus), high temperature (B. thermophilus), and high salt concentrations, Bacillus bacteria are found all over the world.
Bacillus Bacteria: Disease
Bacillus subtilis infections, including endocarditis, pneumonia, and septicemia. This is more common in patients with immunological disorders.
Things to Remember
One of the largest species of Bacillus is B megaterium, which is approx 1.5 μm (micrometres; 1 μm = 10−6 m) across 4 μm long. Bacilli typically live in groups.
What bacteria can survive in extreme conditions?
These Bacillus bacteria have the capability to survive in extreme conditions like high pH (B. alcalophilus), high temperature (B. thermophilus), and high salt concentrations, because of this nature they are ubiquitous in nature. One of species of Bacillus bacteria i.e. Bacillus thuringiensis has the ability to produce toxins ...
What are the diseases caused by Bacillus subtilis?
Disease Caused by Bacillus. Some of the common disease caused by Bacillus bacteria are: Infections caused by Bacillus subtilis are endocarditis, pneumonia, and septicemia. This problem mainly occurs in patients who have an immune disorder. Bacillus anthracis, as it causes skin, lungs, and bowel infection and these diseases are deadly to ...
What is the cause of food poisoning?
Bacillus anthracis, as it causes skin, lungs, and bowel infection and these diseases are deadly to the human body. Bacillus cereus causes food spoilage which can cause food poisoning.
What is a rod shaped bacteria?
About Bacillus Bacteria. Any gene which are rod shaped, gram positive in nature, aerobic or anaerobic bacteria and majorly found in soil and water are termed to be Bacillus bacteria. In general science the term bacillus means cylindrical or rod like bacteria.
What is Bacillus subtilis?
Bacillus subtilis acts as an important model organism along with that it is also a notable food spoiler which lead to ropiness in bread and related food. Bacillus subtilis also does production and secretion of antibiotics . Bacillus coagulans also act as a food spoilage of highly acidic, tomato-based products.
What are some examples of unattached cells?
Bacillus: Single unattached cell, that looks like a rod. Examples are Bacillus cereus, Salmonella enterica, etc. Diplobacilli: In these bacteria two rods are attached to each other and found in pairs after cell division. Examples are Moraxella bovis, Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis, etc.
How big is a hat bacillus?
One of the largest species of Bacillus is B. megaterium, which is approx 1.5 μm (micrometres; 1 μm = 10−6 m) across by 4 μm long. These bacteria majorly occur in chains. Ferdinand Cohn in 1877 provided a full description about two different forms of hat bacillus.
What is the cause of anthrax?
Anthrax is caused by Bacillus anthracis. Humans acquire the disease directly from contact with infected herbivores or indirectly via their products. The clinical forms include ( 1 ) cutaneous anthrax (eschar with edema), from handling infected material (this accounts for more than 95 percent of cases); (2) intestinal anthrax, ...
What is the protein that causes diarrhea?
This protein is believed to be responsible for the necrotic and toxemic nature of severe B cereusinfections and for the diarrheal form of food poisoning. Bacillus cereusalso produces two hemolysins; one of these, cereolysin (58 kDa), is a potent necrotic and lethal toxin.
What is the plasmid px02?
Plasmids pX01 and pX02 encode, respectively, the anthrax toxin and capsule. Curing the bacteria of pX01 produces an encapsulated, nontoxigenic strain that is nonprotective. Curing of pX02 produces (more...) The only other Bacillusspecies for which virulence factors have been identified is B cereus.
What is the best treatment for anthrax?
Anthrax is readily treated with antibiotics (e.g., penicillin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, gentamicin, or erythromycin).
What is the function of the PA in a toxin?
The toxin is composed of three proteins. Protective antigen (PA) binds to an appropriate site on the host cell membrane. A cell surface protease cleaves off a 20-kDa piece from the protective antigen and thereby (more...)
What is the family of Bacillaceae?
The family Bacillaceae, consisting of rod-shaped bacteria that form endospores, has two principal subdivisions: the anaerobic spore-forming bacteria of the genus Clostridium, and the aerobic or facultatively anaerobic spore-forming bacteria of the genus Bacillusfrequently known as ASB (aerobic spore-bearers).
How long does it take for nausea to start after eating contaminated rice?
In emetic disease, on the other hand, nausea and vomiting begin 1 to 5 hours after the contaminated food is eaten. Boiled rice that is held for prolonged periods at ambient temperature and then quick-fried before serving is the usual offender, although dairy products or other foods are occasionally responsible.
Where is E. coli found?
Escherichia coli is of faecal origin and almost exclusively found in the digestive tract of warm-blooded animals, particularly humans. As a consequence, detection of E. coli in potable water is used as an indicator of human or animal excreta contamination, and is referred to as the coliform index (Leclerc et al., 2001 ).
Which bacteria are resistant to HPP?
Several studies showed the high resistance of pathogenic spores under HPP treatment ( Table 5.7 ). Among different bacteria, Bacillus and Clostridium ( C. botulinum, Clostridium perfringens, and B. cereus) have the most resistant foodborne spores. Rajan, Pandrangi, Balasubramaniam, and Yousef (2006) reported that Bacillus amyloliquefaciens formed extremely high-pressure resistant spores and suggested as the target organism in the development of standards for high-pressure treatments. Spores of this species withstood 16 min at 800 MPa and 70°C without reduction in carrot pulp ( Margosch, Ehrmann, Gänzle, & Vogel, 2004 ).
What is the shape of E. coli?
Escherichia coli are typically Gram-negative, rod shaped (2.0–6.0 μm in length and 1.1–1.5 μm wide bacilli) bacteria with rounded ends. The actual shape of these bacteria does, however, vary from spherical (cocci) cells through to elongated or filamentous rods. Escherichia coli are non-spore forming, and are usually motile through the action of peritrichous flagella. Escherichia coli are facultatively anaerobic and produce gas from fermentation of carbohydrates, as seen by acid and gas production from lactose at 37°C and 44°C. Most E. coli yield a positive ortho-nitrophenyl-β-D-galactoside (ONPG) reaction, indicating β-galactosidase activity. The methyl red reaction is also positive for E. coli indicating mixed acid fermentation of glucose, but the Voges–Proskauer reaction (acetoin production) is negative. Escherichia coli produce indole, but are unable to hydrolyze urea or grow in Møller's KCN broth (demonstrating an inability to grow in the presence of cyanide). Furthermore, production of hydrogen sulphide is not normally evident when E. coli are cultured on triple sugar iron (TSI) agar or Kligler's iron agar (KIA). Escherichia coli also do not induce gelatin liquefaction through gelatinase activity. The majority of strains decarboxylate lysine, use sodium acetate, but do not grow on Simmons' citrate agar, where citrate is the sole carbon source.
What are some examples of antibiotics?
They produce a number of antibiotics as well as siderophores. Several have received patents and are marketed commercially for control of root rot in cotton (Campbell, 1989 ). One example is the use of isolates of a species of Pseudomonas as an antagonist of take-all disease of wheat ( Weller, 1985 ).
What are the three types of colony types of P. aeruginosa?
Three colony types of P. aeruginosa are observed: small, rough colony isolated from nature; large, smooth , colony with flat edges and an elevated appearance from clinical samples; and mucoid colony frequently obtained from respiratory and urinary tract secretions.
Which organism is a high pressure resistant spore?
Rajan, Pandrangi, Balasubramaniam, and Yousef (2006) reported that Bacillus amyloliquefaciens formed extremely high-pressure resistant spores and suggested as the target organism in the development of standards for high-pressure treatments.
Which two organisms colonize the upper respiratory tract?
Both S. pneumoniae and C. kutscheri colonize the upper respiratory tract (nasopharynx and tympanic bulla with S. pneumoniae and oropharynx, cervical, and submandibular lymph nodes with C. kutcheri) and can remain subclinical in the absence of concurrent disease.
What is the genus Bacillus?
The genus Bacillus is a diverse group of spore-forming bacteria. Bacillus species have implications in both medical and biodefence aspects of microbiology. This chapter attempts to summarize key molecular aspects of these bacteria (with an emphasis on B. anthracis ).
What is pumilacidin?
Lichenysin A and pumilacidin belong to a family of lipopeptides produced by certain Bacillus species. These lipopeptides are small, structurally diverse cyclic lactones, and are characterized by their high resistance to extreme heat, pH, and enzymatic challenges.
Is Bacillus cereus a foodborne illness?
Although Bacillus spp. other than B. cereus have been incriminated as foodborne illness agents, the link between toxin production in such strains and foodborne illness has not been fully established, although various toxins have been found. A sperm-toxic compound produced by B. licheniformis strains isolated from baby milk powder involved in the fatality of an infant has been isolated, characterized, and later identified as lichenysin A. In the incident in the Chinese restaurant described above, B. pumilus producing the boar sperm-toxic compound pumilacidin was isolated in nearly pure culture from the implicated food. Recently, a novel toxin produced by strains of B. subtilis and B. mojavensis isolated from cases of foodborne illness was partly characterized. This toxin, amyloisin, is non-ribosomally synthesized, heat-stable, and exhibits similar toxic properties as cereulide.
Is Bacillus a probiotic?
Bacillus species are ubiquitous in nature but found in higher concentrations in soil, water, and food products that have a plant origin. Strains of Bacillus are very good potential candidates to be used as probiotics. Metabolically, Bacillus species are very active and previous research has identified a number of useful enzymes and numerous antibiotics they produce. In addition to these secreted products, Bacillus remains stable in probiotic products much longer than conventional probiotics due to their ability to form endospores [1]. Most survive the rigors of food processing, including those designed to deplete microorganisms such as pasteurization. They have a history of use in fermented foods largely in Africa and Asia, but are becoming more prominent in global probiotics relatively recently. While there are pathogenic species of Bacillus, including B. cereus and B. anthracis, the more benign members have a good record of safety and their appearance in randomized controlled studies in humans is increasing. This chapter demonstrates the evolution of the use of Bacillus from environmental and food microorganism to that of a clinically used probiotic type and its potential future uses.
Is Bacillus anthracis an aerobic organism?
Bacillus spp. are aerobic or facultatively anaerobic , gram-positive or gram-variable, encapsulated, spore-forming rods that usually are motile. Bacillus spp. produce several toxins (including enterotoxin, emetic toxin, phospholipases, proteases, and hemolysins 5) responsible for much of the morbidity and mortality associated with B. anthracis. 4 The species are differentiated by a variety of laboratory observations involving colony morphology, growth on selective media, agglutination reactions, and penicillin susceptibility. B. anthracis grows well on blood agar as large, opaque, irregular, “curled-hair” colonies. 6
Is there a promoter system for B. subtilis?
Although these systems are not generally available, there is now a range of promoter systems have been developed for the controlled, high-level expression of proteins from B. subtilis. Some of these have been adapted from E. coli system, others from Bacillus species and other Gram-positive bacteria.
Is Bacillus cereus a hemolysin?
Although speculated early to be an important contributor to the fulminance of B. cereus infection, one hemolysin termed hemolysin BL or HBL, was shown to make a relatively minor contribution to the course and severity of disease. B. cereus cytolytic factors are regulated by a quorum-sensing system termed plcR. Isogenic plcR -deficient mutants of B. thuringiensis (a derivative of B. cereus used as a surrogate in these tests) are significantly attenuated in severity in a rabbit model of endophthalmitis, but the infection nevertheless remains explosive, showing that these toxins collectively made a surprisingly minor contribution to the pathogenesis of infection. As Bacillus spp. are aerophilic and motile, it was hypothesized that chemotaxis along an oxygen gradient led to the margination of B. cereus to the blood–retina barrier, leading to its compromise and ensuing inflammation. This hypothesis was tested directly in a rabbit model, where motile and nonmotile B. cereus strains were compared. It was observed that deficiencies in swarming prevented Bacillus from migrating to the anterior segment, leading to less severe anterior segment disease.
Bacilli Definition
The word bacilli is used to describe both an entire class of bacteria, as well as a type of rod-shaped bacterium with the plural of the word being bacillus. When used as the name of a class of bacteria, this includes the two orders: Bacillales and Lactobacillales.
Types of Bacillus
There are many different types of Bacillus bacteria that function in different ways. Bacillus are found in the environment in the soil, ocean, and even in human bodies. These bacteria play important roles in the environment as well as the human body, in which they aid in digestion and immune health.
What is a bacillus?
Definition. Bacillus subtilis, hay bacillus, or grass bacillus was one of the first Gram-positive bacteria to be studied. It is an aerobic, rod-shaped spore-forming microorganism that can spread in extreme cold, heat, and even disinfected environments. It transfers to the gastrointestinal tracts of animals and humans via the soil.
What is the morphology of Bacillus subtilis?
Bacillus subtilis morphology describes rod-shaped, Gram-positive bacteria that show up on both positive and negative Gram stain techniques. A bacterial rod is a symmetrical cylinder with rounded ends. A significant difference in pressure across the cytoplasmic membrane pushes the cell wall into a specific shape.
What is the purpose of Bacillus subtilis biofilms?
Once in the gut, these spores become active and colonize. As Bacillus subtilis biofilms in worm intestines seem to lengthen the worm’s lifespan, many human users hope for the same effect. Another use of B. subtilis is in wastewater treatment.
Why is B. subtilis dormant?
This is because when under stress, these bacteria (including B. subtilis ) transform into spores and become dormant . A colony of Bacillus subtilis survived on the outside of a NASA satellite for six years. The colony morphology of B. subtilis refers to how it appears in large quantities.
Which bacteria have a thicker peptidoglycan layer?
The image below shows how Gram-positive bacteria have a much thicker peptidoglycan layer (in purple). Gram positive and negative differences. B. subtilis contains only one double-stranded DNA molecule contained within a circular chromosome. A circular chromosome is typical of bacteria, mitochondria, and plant chloroplasts.
Which bacteria reduces plastic by 1.75%?
Without the support of synthetic chemicals, B. subtilis is not the fastest strain – it reduces dry-weight plastic by around 1.75% over a term of 30 days. However, when paired with another bacteria called Pseudomonas aeruginosa both types of bacteria perform more efficiently.
What is the rod shape of bacteria?
The rod shape also helps bacteria glide or move through watery environments and provides regular building block shapes that make biofilm formation easier. Bacteria groups can be categorized according to specific arrangements. An arrangement is a microbiological term that refers to species-specific bacteria communities.
What is the name of the chromogenic agar used to detect Bacillus cereus?
January 2012: The Bacillus Chapter has been updated with the inclusion of a new optional chromogenic agar, Bacara agar, for the detection and enumeration of Bacillus cereus in foods. Bacillus cereus is an aerobic spore-forming bacterium that is commonly found in soil, on vegetables, and in many raw and processed foods.
What foods are contaminated with B. cereus?
Foods incriminated in past outbreaks include cooked meat and vegetables, boiled or fried rice, vanilla sauce, custards, soups, and raw vegetable sprouts. Two types of illness have been attributed to the consumption of foods contaminated with B. cereus.
What is the name of the species that grows in a pink orange colony?
The identification would include all species from the B. cereus group: B. cereus, B. thuringiensis, B. anthracis,B. mycoides, and B. weihenstephanensis.
Is Bacara a selective agar?
Bacara is a chromogenic selective and differential agar that promotes the growth and identification of B. cereus, but inhibits the growth of background flora. The chromogenic agar has been suggested for the enumeration of B. cereus group as a substitute for MYP 1,2 .
Can B. cereus be tested for emetic toxin?
However, results with atypical strains of B. cereus are quite variable, and further testing may be necessary to identify the isolates. Test for cereulide (emetic toxin). Intoxication is caused by the pre-formed cereulide produced by B. cereus spores after germinating in food that has not been stored properly.
Overview
Bacillus (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum Bacillota, with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of certain bacteria; and the plural Bacilli is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. Bacillus species can be either obligate aerobes: oxygen dependent; or facultative anaerobes: having the abilit…
Structure
The cell wall of Bacillus is a structure on the outside of the cell that forms the second barrier between the bacterium and the environment, and at the same time maintains the rod shape and withstands the pressure generated by the cell's turgor. The cell wall is made of teichoic and teichuronic acids. B. subtilis is the first bacterium for which the role of an actin-like cytoskeleton in cell shape d…
Origin of name
The genus Bacillus was named in 1835 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, to contain rod-shaped (bacillus) bacteria. He had seven years earlier named the genus Bacterium. Bacillus was later amended by Ferdinand Cohn to further describe them as spore-forming, Gram-positive, aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacteria. Like other genera associated with the early history of microbiology, such as Pseudomonas and Vibrio, the 266 species of Bacillus are ubiquitous. The g…
Isolation and identification
An easy way to isolate Bacillus species is by placing nonsterile soil in a test tube with water, shaking, placing in melted mannitol salt agar, and incubating at room temperature for at least a day. Cultured colonies are usually large, spreading, and irregularly shaped.
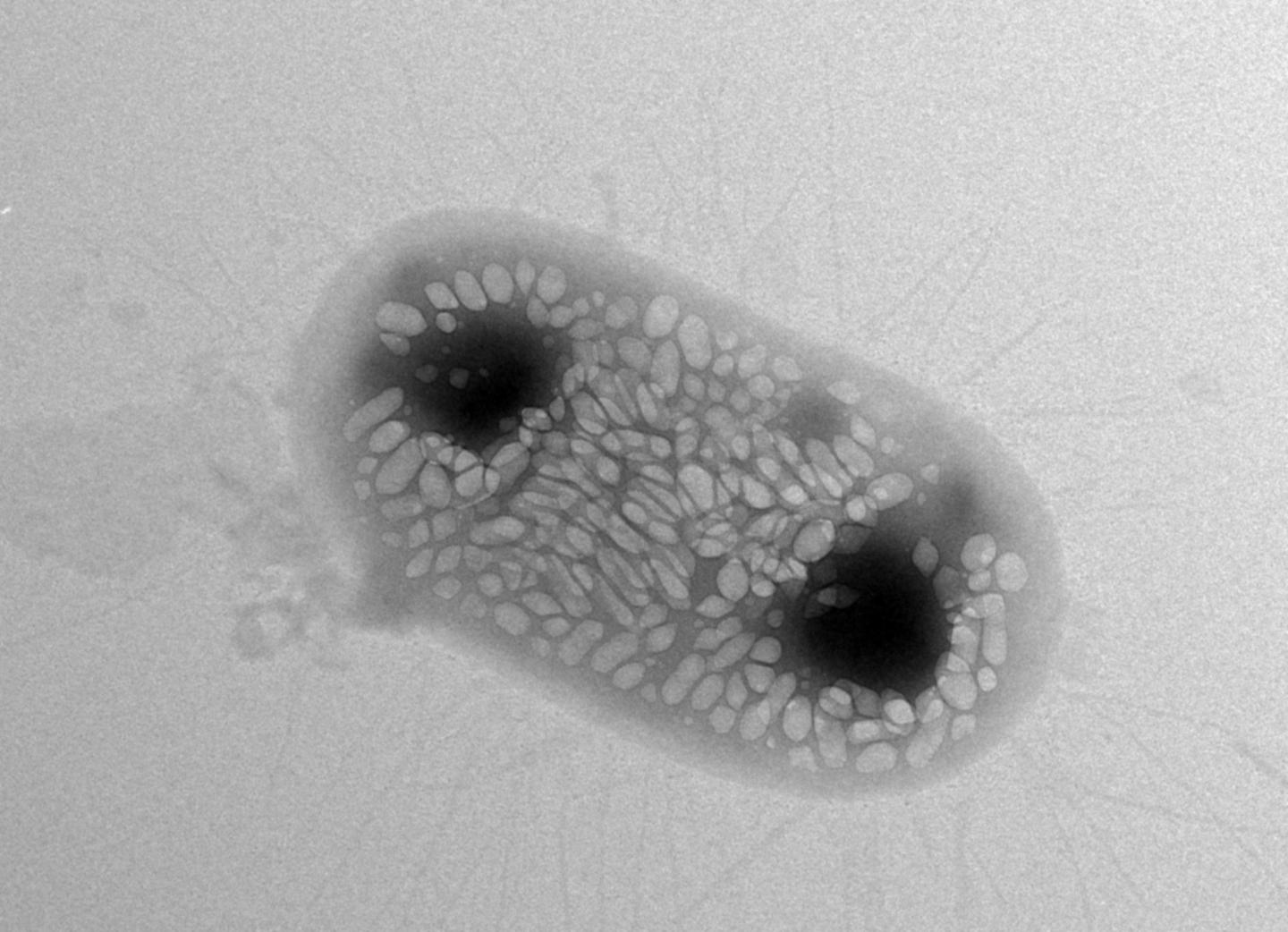
Under the microscope, the Bacillus cells appear as rods, and a substantial portion of the cells usually contain oval endospores at one end, making them bulge.
Characteristics of Bacillus spp.
S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and identified multiple strains of Bacillus species (strains WS1A, YBS29, KSP163A, OA122, ISP161A, OI6, WS11, KSP151E, S8) from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island Area of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Based on their study, colony, morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of Bacillus spp. are shown in the Table below.
Note: + = Positive, – =Negative, O= Oxidative, F= Fermentative
Phylogeny
Three proposals have been presented as representing the phylogeny of the genus Bacillus. The first proposal, presented in 2003, is a Bacillus-specific study, with the most diversity covered using 16S and the ITS regions. It divides the genus into 10 groups. This includes the nested genera Paenibacillus, Brevibacillus, Geobacillus, Marinibacillus and Virgibacillus.
The second proposal, presented in 2008, constructed a 16S (and 23S if available) tree of all valid…
Species
• B. acidiceler
• B. acidicola
• B. acidiproducens
• B. acidocaldarius
• B. acidoterrestris
Ecological and clinical significance
Bacillus species are ubiquitous in nature, e.g. in soil. They can occur in extreme environments such as high pH (B. alcalophilus), high temperature (B. thermophilus), and high salt concentrations (B. halodurans). They also are very commonly found as endophytes in plants where they can play a critical role in their immune system, nutrient absorbtion and nitrogen fixing capabilities. B. thuringiensis produces a toxin that can kill insects and thus has been used as inse…
Bacillus Are Further Classified Into Different Types Based on Rod-Shape Cells
- Bacillus:Single unattached cell, that looks like a rod. Examples are Bacillus cereus, Salmonella enterica, etc. Diplobacilli:In these bacteria, two rods are attached and found in pairs after cell division. Examples are Moraxella Bovis, Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis, etc. Streptobacilli:In them, bacilli are arranged in a single chain due to cell division in a single plane. Examples are Streptob…
Nature of Cell Wall
- The structure which is found outside the cell, which forms a second barrier between the bacterium and the environment is called cell structure.
- The cell wall also maintains the rod shape and withstands the pressure generated by the cell's turgor.
- Its cell structure is made up of an inner membrane and thick peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan k…
- The structure which is found outside the cell, which forms a second barrier between the bacterium and the environment is called cell structure.
- The cell wall also maintains the rod shape and withstands the pressure generated by the cell's turgor.
- Its cell structure is made up of an inner membrane and thick peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan keeps the cell in shape.
- The polysaccharide part of the cell wall accounts for half of the cell wall.
Importance and Uses
- Bacillus spp. are widespread in a wide range of environments, including soil, and are resistant to harsh environmental conditions. These Bacillus bacteria have the capability to survive in extreme...
- The majority of Bacillus species, as well as their products, are deemed safe for use in the environment.
- Bacillus spp. are widespread in a wide range of environments, including soil, and are resistant to harsh environmental conditions. These Bacillus bacteria have the capability to survive in extreme...
- The majority of Bacillus species, as well as their products, are deemed safe for use in the environment.
- Because of their potential to release many bioactive compounds, these bacteria are recommended for commercialization.
- They keep their viability and are simple to store.
Disease
- Some of the common diseases caused by Bacillus bacteria are: 1. Infections caused by Bacillus subtilis are endocarditis, pneumonia, and septicemia. This problem mainly occurs in patients who have an immune disorder. 2. Bacillus anthracis, as it causes skin, lungs, and bowel infections and these diseases are deadly to the human body. 3. Bacillus cereus causes food spoilage which ca…
About Bacillus
- Gram-positive Bacilli form bacteria are Actinomyces, Clostridium, Bacillus or gram-negative bacteria, e.g. Escherichia, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Streptobacillus, etc.
- They have the capability of serving at high temperatures i.e. at 4200 C.
- They are mostly non-parasitic and free-living in nature.
- They are known to be one of the most abundantly found bacteria.