What is body system(s) do(es) the heart belong to?
The heart belongs to the circulatory system which is otherwise called as Transport System.
Which body system does the heart belong to?
some heart diseases are Rheumatic heart disease, Hypertensive heart disease, Ischemic heart disease, Cerebrovascular disease and Inflammatory heart disease. The heart belongs to the circulatory system. This system transports blood within the body. Can we live without the heart?
What does the heart do in the human body?
Your heart is the main organ of your cardiovascular system, a network of blood vessels that pumps blood throughout your body. It also works with other body systems to control your heart rate and blood pressure.
What system does the heart belong in?
The heart is the key organ in the circulatory system. As a hollow, muscular pump, its main function is to propel blood throughout the body. This is thoroughly answered here. Moreover, what system does liver belong to? The liver is the largest solid organ and the largest gland in the human body. It carries out over 500 essential tasks.
Where is the heart located in the human body?
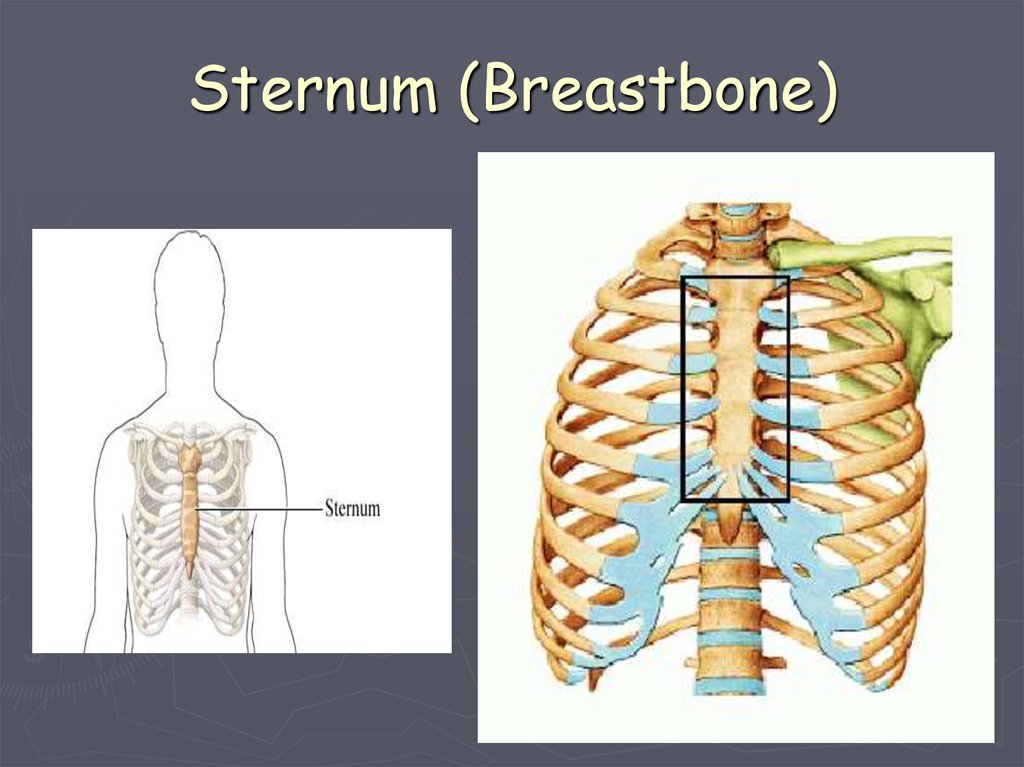
In humans, the heart is situated between the two lungs and slightly to the left of center, behind the breastbone. It rests on the diaphragm, the mu...
What is the heart wall made up of?
The heart consists of several layers of a tough muscular wall, the myocardium. A thin layer of tissue, the pericardium, covers the outside, and ano...
What causes the heart to beat?
The pumping of the heart, or the heartbeat, is caused by alternating contractions and relaxations of the myocardium. These contractions are stimula...
What are heart sounds?
The rhythmic noises accompanying the heartbeat are called heart sounds. The two distinct sounds are heard, a low, slightly prolonged “lub” (first s...
What is the heart responsible for?
The heart is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. To do this, the heart fills with blood and then contracts to push the blood through the circulatory system. Electrical impulses tell the heart how often to contract or “beat.”
Where is the heart in the heart diagram?
Press on the buttons to interact, including adding and removing layers, and moving around the diagram. The heart is in the chest, slightly left of center. It sits behind the breastbone and between the lungs. The heart has four distinct chambers.
What is the term for a heartbeat that is too fast, too slow, or irregular?
Heart arrhythmia is the medical term for a heartbeat that is too fast, too slow, or irregular. Arrhythmias occur when the electrical impulses that control the heartbeat malfunction. This can give rise to a fluttering sensation in the chest, which doctors refer to as palpitations.
What is the thin tissue that covers the chambers and valves of the heart?
Endocardium: A thin tissue that covers the chambers and valves of the heart.
Which valve opens and closes to regulate blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery?
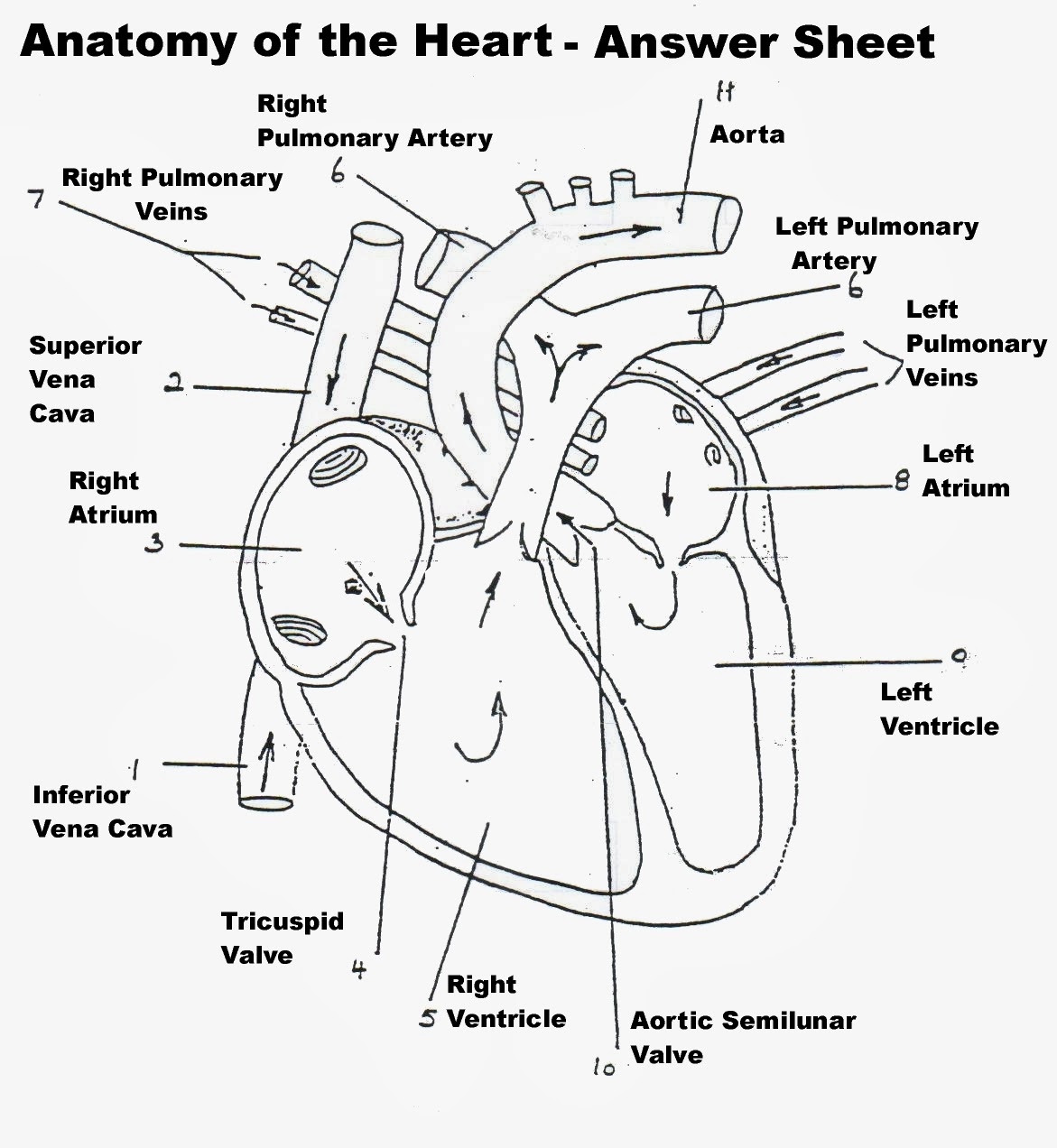
The pulmonic valve opens and closes to regulate blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery (lungs). The aortic valve opens and closes to regulate oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the aorta (the largest artery in the body).
What is the umbrella term for a range of conditions that affect the heart?
Heart disease is the umbrella term for a range of conditions that affect the heart. Some people may have “silent” heart disease . This means that a person will not develop symptoms until they experience a cardiac event, such as a heart attack, arrhythmia, or heart failure.
Which side of the heart receives oxygenated blood?
Here, the blood receives oxygen and removes carbon dioxide for the lungs to breathe out. The left side of the heart then receives the oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it through arteries to the rest of the body.
What are the parts of the circulatory system?
Together, the heart, blood, and blood vessels — arteries, capillaries, and veins — make up the circulatory system. In this article, we explore the structure of the heart, how it pumps blood around the body, and the electrical system that controls it.
What are the two parts of a heartbeat?
Each heartbeat has two parts: Diastole: The ventricles relax and fill with blood as the atria contract, emptying all blood into the ventricles. Systole: The ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart as the atria relax, filling with blood again.
What separates the left and right atria and the left and right ventricle?
A wall of tissue called the septum separates the left and right atria and the left and right ventricle. Valves separate the atria from the ventricles. The heart’s walls consist of three layers of tissue: Myocardium: This is the muscular tissue of the heart.
How does the heart produce carbon dioxide?
The heart enables the body to eliminate the unwanted carbon dioxide. Oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves it through the capillaries of the alveoli.
How many times does the heart beat a day?
The heart beats around 100,000 times a day, pumping approximately 8 pints of blood throughout the body 24/7. This delivers oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to tissues and organs and carries away waste. The heart sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where the blood loads up with oxygen and unloads carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism.
How many BPM is normal?
When you feel your pulse, you feel the rush of blood as the heart pumps it through the body. A healthy pulse is usually 60–100 bpm, and what is normal can vary from person to person. A very active person may have a pulse as low as 40 bpm.
What is the electrical signal that pumps blood?
Electrical impulses coordinate this activity. The electrical signal begins at the sino-atrial node, sometimes called the sinus, or SA, node.
Where is the heart located in the human body?
In humans it is situated between the two lungs and slightly to the left of centre, behind the breastbone; it rests on the diaphragm, the muscular partition between the chest and the abdominal cavity.
What is the heart? What function does it serve?
heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood. It may be a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or a somewhat more elaborate structure with one or more receiving chambers (atria) and a main pumping chamber (ventricle), as in mollusks. In fishes the heart is a folded tube, with three or four enlarged areas that correspond to the chambers in the mammalian heart. In animals with lungs —amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals—the heart shows various stages of evolution from a single to a double pump that circulates blood (1) to the lungs and (2) to the body as a whole.
What are the two sounds that occur at the beginning of ventricular contraction?
The two distinct sounds are heard, a low, slightly prolonged “lub” (first sound) occurring at the beginning of ventricular contraction or systole and a sharper, higher-pitched “dup” (second sound), caused by the closure of aortic and pulmonary valves at the end of systole. In humans and other mammals and in birds, ...
What are the two sounds that accompany the heartbeat?
The rhythmic noises accompanying the heartbeat are called heart sounds . The two distinct sounds are heard, a low, slightly prolonged “lub” (first sound) occurring at the beginning of ventricular contraction or systole and a sharper, higher-pitched “dup” (second sound), caused by the closure of aortic and pulmonary valves at the end of systole.
What is the heart in a fish?
In fishes the heart is a folded tube, with three or four enlarged areas ...
What does it mean when your heart murmurs?
Murmurs may indicate that blood is leaking through an imperfectly closed valve and may signal the presence of a serious heart problem.
Where is the greatest pressure in the body?
Blood pressure is greatest in the left ventricle and in the aorta and its arterial branches. Pressure is reduced in the capillaries (vessels of minute diameter) and is reduced further in the veins returning blood to the right atrium.
What is the heart surrounded by?
The heart is situated within the chest cavity and surrounded by a fluid-filled sac called the pericardium. This amazing muscle produces electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract, pumping blood throughout the body. The heart and the circulatory system together form the cardiovascular system.
What is the organ that supplies blood and oxygen to all parts of the body?
Updated April 05, 2020. The heart is the organ that helps supply blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. It is divided by a partition (or septum) into two halves. The halves are, in turn, divided into four chambers. The heart is situated within the chest cavity and surrounded by a fluid-filled sac called the pericardium.
Which arteries carry oxygenated blood to the head and neck?
Carotid arteries: Supply oxygenated blood to the head and neck regions of the body. Common iliac arteries: Carry oxygenated blood from the abdominal aorta to the legs and feet. Coronary arteries: Carry oxygenated and nutrient-filled blood to the heart muscle. Pulmonary artery: Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
What is the role of the heart in conduction?
Cardiac conduction is the rate at which the heart conducts electrical impulses. Heart nodes and nerve fibers play an important role in causing the heart to contract. Atrioventricular Bundle: A bundle of fibers that carry cardiac impulses. Atrioventricular Node: A section of nodal tissue that delays and relays cardiac impulses.
What are the two phases of the cardiac cycle?
The Cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats. Below are the two phases of the cardiac cycle: Diastole phase: The heart ventricles are relaxed and the heart fills with blood. Systole phase: The ventricles contract and pump blood to the arteries.
What is the blood vessel?
Blood vessels are intricate networks of hollow tubes that transport blood throughout the entire body. The following are some of the blood vessels associated with the heart:
How many layers are there in the heart wall?
The heart wall consists of three layers:
What is the human heart?
Introduction to the Human Heart. The human heart is one of the most important organs responsible for sustaining life. It is a muscular organ with four chambers. The size of the heart is the size of about a clenched fist. The human heart functions throughout a person’s lifespan and is one of the most robust and hardest working muscles in ...
Where is the heart located?
The human heart is situated to the left of the chest and is enclosed within a fluid-filled cavity described as the pericardial cavity. The walls and lining of the pericardial cavity are made up of a membrane known as the pericardium. The pericardium is a fibre membrane found as an external covering around the heart.
What is the right ventricle of the heart?
The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs for re-oxygenation through the pulmonary arteries.
What is the outermost layer of the heart?
The heart wall is made up of 3 layers, namely: Epicardium – Epicardium is the outermost layer of the heart. It is composed of a thin-layered membrane that serves to lubricate and protect the outer section. Myocardium – This is a layer of muscle tissue and it constitutes the middle layer wall of the heart.
Which chambers receive blood?
The ventricles are the chambers that pump blood and atrium are the chambers that receive blood. Among which both right atrium and ventricle make up the “right heart,” and the left atrium and ventricle make up the “left heart.”. The structure of the heart also houses the biggest artery in the body – the aorta.
Which part of the circulatory system is responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the?
Types of Circulation. Pulmonary circulation is a portion of circulation responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the lungs and then brings oxygenated blood back to the heart.
How much does a heart weigh?
The average male heart weighs around 280 to 340 grams (10 to 12 ounces). In females, it weighs around 230 to 280 grams (8 to 10 ounces). An adult heart beats about 60 to 100 times per minute, and newborn babies heart beats at a faster pace than an adult which is about 90 to 190 beats per minute.
Which system provides a framework on which the human body is arranged?
Musculoskeletal system. The skeleton provides a framework on which the human body is arranged. It is articulated to allow free movement in conjunction with the skeletal muscles. They control movement, posture and assist the body with heat generation.
What is the purpose of a body system?
Body systems. A body system is a collection of parts able to work together to serve a common purpose – growth, reproduction and survival.
What system is the digestive system?
It is part of the cardiovascular system and it carries products of digestion ( digestive system) to body cells, excretory wastes ( excretory system) to the kidneys and hormones ( endocrine system) to target organs such as those forming part of the reproductive system. Explore topics. Explore concepts. Citizen science.
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is made up of a network of specialised cells, tissues and organs that coordinate and regulate the responses of the body to internal and external stimuli. Equipped with his five senses, man explores the universe around him and calls the adventure science. Edwin Powell Hubble (1889–1953)
What is the central nervous system made of?
The central nervous system (CNS) is made of the brain and spinal cord. It receives information and responds to it.
What is the purpose of breathing?
The process of breathing allows these gases to be exchanged between the blood and lungs. The human body has a system of organs that work together for the purpose of reproduction. The biological purpose of this process is the continuation of life.
Which system coordinates the metabolic activity of body cells by interacting with the nervous system?
Endocrine system. Composed of a number of small organs distributed throughout the body, the endocrine system coordinates the metabolic activity of body cells by interacting with the nervous system.
What is the cardiovascular system?
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Its primary function is to transport nutrients and oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body and to carry deoxygenated blood back to the lungs.
Which system moves blood between the heart and lungs?
The second is the pulmonary circulatory system. This circulatory system moves blood between the heart and lungs. It is where oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves the blood.
What is the second phase of the pulmonary system?
The second phase is systole, in which the ventricles contract and eject blood. It begins when the mitral or tricuspid valve closes and ends when the aortic or pulmonary valve closes. The pressure inside the ventricles becomes greater than the pressure inside adjacent blood vessels, thereby forcing the blood from the ventricles to the vessels.
What is the first phase of a heart contraction?
The first phase is diastole, in which the ventricles fill with blood. It begins when the aortic or pulmonary valve closes and ends when the mitral or tricuspid valve closes. During diastole, blood vessels return blood to the heart in preparation for the next contraction of the ventricles.
How many blood circulatory systems are there in the human body?
There are two blood circulatory systems in the body. The first is the systemic circulatory system. This is the main blood circulatory system that transports blood to the organs, tissues, and cells throughout the body.
What are the common conditions that affect the cardiovascular system?
Common conditions that can affect the cardiovascular system include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, and stroke.
What happens when the heart muscle does not receive enough blood?
A heart attack happens when a part of the heart muscle does not receive enough blood. This can occur due to a blockage, a tear in an artery around the heart, or if the heart requires more oxygen than is available.
